American Samoa is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the south-central Pacific, and home to captivating Polynesian culture as well as American influence. The islands that make up American Samoa are part of the larger Samoan archipelago, which is beloved by visitors for its volcanic islands, verdant rainforests, and rich aquatic life.
American Samoa's unique political status and the core of 'fa'a Samoa' (Samoan way of life) provide American Samoans with a rich life. From American Samoa's institutional positioning to its collective customs, American Samoa is a wondrous place with both a great history and a unique sense of its own strength. Let's take a better look at American Samoa's uniqueness.
Check out: List of 9 Most Incredible Animals in South America You Need to Discover
What is the meaning of the American Samoa flag?
The flag of American Samoa is a distinctive flag adopted on April 17, 1960, that is designed with an overall dark blue rectangle featuring a red-edged white triangle pointing toward the hoist, which features the traditional image of a bald eagle. The bald eagle, which symbolizes the United States, is holding a traditional Samoan war club (uatogi) and fly-whisk (fue), representing the power of government and the wisdom of traditional leaders, respectively.
The white additionally bleeds into a bandeau flag of a dark blue field, which is then bifurcated into two triangular sets by the white triangle. The color scheme of red, white, and blue mimics the colors of the U.S. flag about the territory.

Source: wikipedia.com
What is the Capital of American Samoa?
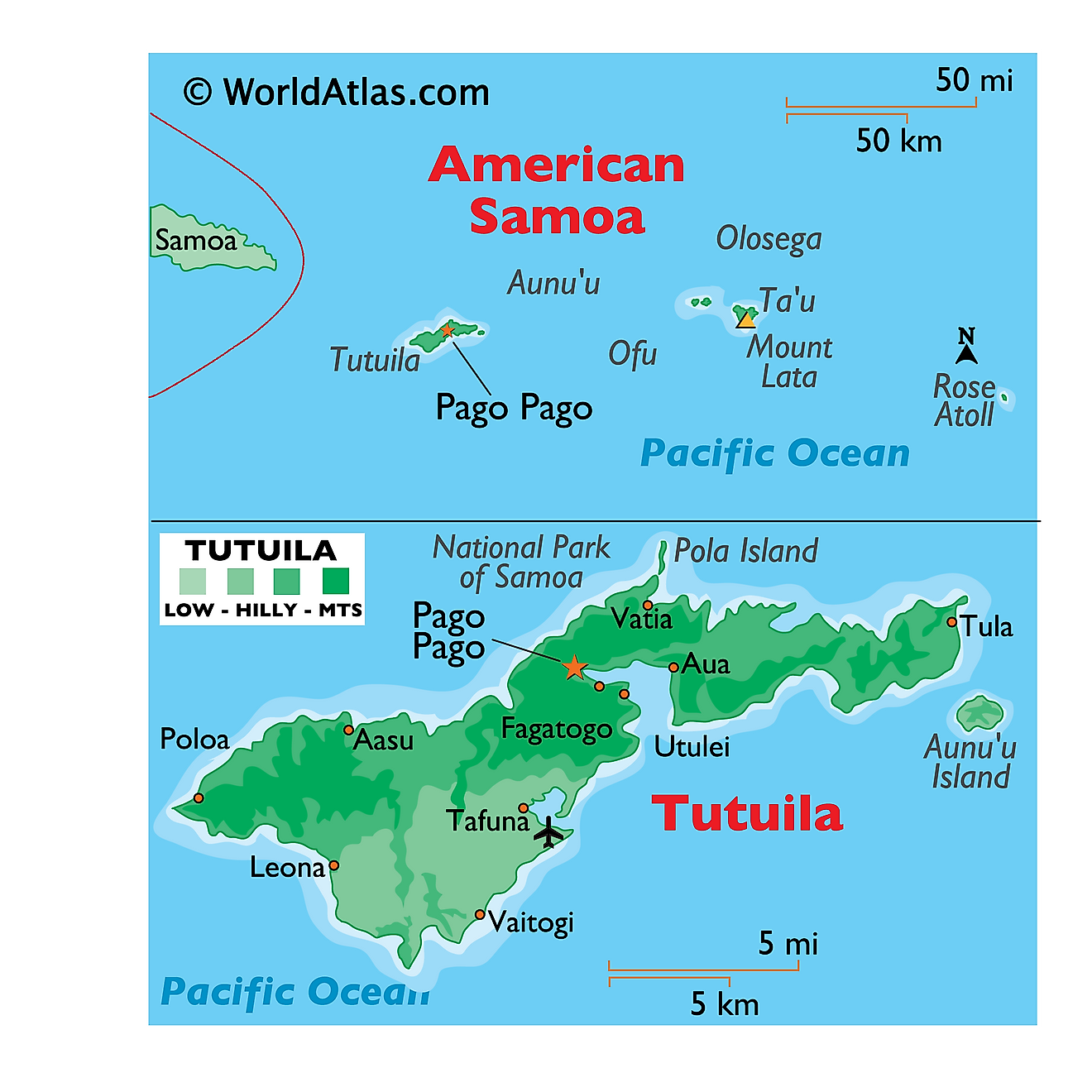
The capital of American Samoa is Pago Pago, a bustling urban area located on the main island of Tutuila. It is famous for its beautiful, deep natural harbor, which is an important port in the South Pacific. While the name Pago Pago is used for the entire capital region, the key government buildings are actually located in two nearby villages: Fagatogo holds the legislature and judiciary, and Utulei is where the Governor's office is found. Essentially, Pago Pago is the main city and administrative center for the territory.
What is the geography of the American Samoa?
American Samoa is a U.S. territory consisting of six Samoan islands in the Pacific, which includes inhabited islands such as Tutuila and uninhabited islands like Rose Atoll and Swains Island. Most of the islands are volcanic in origin with steep, rugged, and high interiors, as is the case of Tutuila where the eastern part of the island contains the deep harbor of Pago Pago and Matafao Peak at 653 meters (2,141 feet).
American Samoa's climate is tropical and it gets an average of 200 inches (5,000 mm) of rain annually, whereas its temperatures remain fairly constant at around 21 - 32 °C (70 - 90 °F) year-round. The islands are almost entirely covered in rainforests while the lowland coastal areas have been developed into plantations of taro, coconut and other food crops.
Source: worldatlas.com
What is the History of American Samoa?
Approximately 1000 BCE, the Polynesians settled the Samoan islands and became an essential departure point for eastern Polynesian voyagers by 500 CE. Jacob Roggeveen had the distinction of contacting the islands of Samoa in 1722.
At the end of the 19th century, with heightened global conflict, Samoa was partitioned in 1899 when Germany claimed the western islands and the United States took the eastern islands, known as American Samoa. The U.S. established a naval station in Pago Pago Harbor in 1878 was formally ceded by local chiefs in 1904 but was not accepted by Congress until 1929.
During U.S. Navy Rule (1900 - 1951) American Samoa was a base used for the Navy. After 1951 American Samoa came under the control of the U.S. Department of the Interior. Samoans pushed for a more significant role in how they governed themselves, culminating in the popular election of Samoans' first governor, Peter Coleman, in 1977, and their first nonvoting delegate to the U.S. House of Representatives in 1981. The islands were affected by a tsunami generated by an underwater earthquake in 2009.
Check out: How Well Do You Know the U.S. Judiciary System? Check Quiz Questions with Answers and Facts
What is the Education system in Samoa?
Education is compulsory from the age of 6 till 18. Most primary and secondary school education is provided through public schools operated by the American Samoa Department of Education (ASDOE) although private and religious schools exist as well. Educational television is available for learning opportunities. Higher education is available through the American Samoa Community College, which offers a variety of programs. Those wishing to complete university degrees typically transfer to Hawaii or to the mainland U.S.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation