Technology is moving at a pace faster than most of us can keep up with, and one of the biggest drivers of that change is Machine Learning (ML). From personalized recommendations on Netflix to fraud detection in banks, machine learning is quietly powering systems we rely on every day. But what exactly is it, how does it work, and where is it being used today? Let’s understand this all in simple language
Check out: Difference Between Veo3 and Veo3 Fast: Which one Should You Use?
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a branch of computer science that teaches computers to 'learn' patterns from data instead of being programmed step by step. Think of it like this: instead of telling a computer every single rule for recognizing a cat in a photo, you feed it thousands of cat and non-cat images. Over time, the computer figures out the hidden patterns, like the shape of ears, the fur texture, or the outline of whiskers, and learns to spot a cat on its own.
In simple terms, machine learning is about training computers with data so they can make predictions or decisions without human interference. It’s different from traditional programming because the computer is not limited to pre-written instructions; it adapts as it processes more data.
Types of Machine Learning
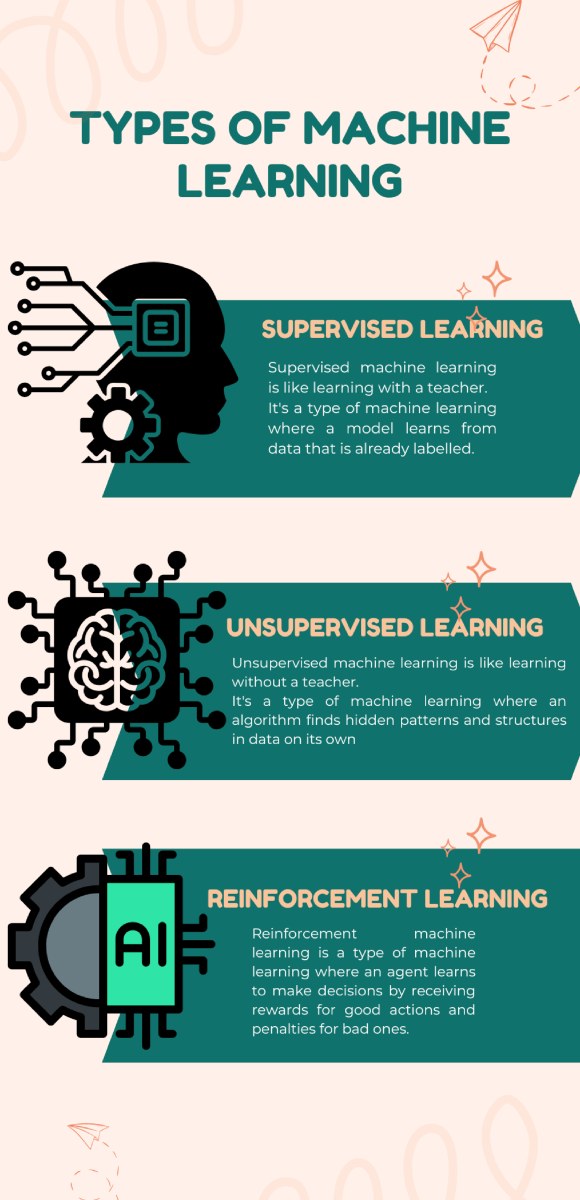
While the concept sounds straightforward, not all machine learning works the same way. Broadly, there are three main types:
1. Supervised Learning
This is the most common form. Here, the computer is trained on labeled data, which means the answers are already known. For example, if you want a program to predict house prices, you train it on a dataset that includes house features (size, location, age) along with their actual prices.
2. Unsupervised Learning
In this method, the data fed to the machine isn’t labeled. The system has to find hidden structures or patterns on its own. A good example is customer segmentation in marketing. Companies feed customer purchase histories into a machine learning model, and the system clusters buyers into groups with similar behaviours.
3. Reinforcement Learning
This type is about trial and error. The computer learns by interacting with an environment and receiving rewards or penalties for its actions. It’s like teaching a dog tricks with treats.
Real-Life Use Case Examples of Machine Learning
Machine learning is no longer just a buzzword; it is already embedded in daily life across the world, here are some practical examples:
-
Healthcare: Hospitals are using ML to predict patient risks, detect diseases in medical scans, and even recommend personalized treatment plans. For example, machine learning models can analyze X-rays faster than a human radiologist in some cases.
-
Banking & Finance: U.S. banks rely heavily on machine learning for fraud detection. Every time you swipe your credit card, an ML system checks the transaction against your spending history. If something looks suspicious, like a purchase in another state while your phone is in your pocket, the system can flag or block it instantly.
-
Retail & E-commerce: Amazon’s recommendation engine is powered by machine learning. It studies what you’ve bought, searched, or even hovered over, and then suggests products you’re likely to buy next. This personalization is one of the reasons online shopping has become so addictive.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation