The U.S. Federal Reserve System is the nation’s central bank, which is run by the Board of Governors and 12 regional banks. It was created on December 23, 1913, following a series of financial panics. The Fed Chair leads it and sets monetary policy, including interest rate changes.
| US Fed Rate Cut News Live: The Federal Reserve announced a 25-basis-point rate cut, and with this, the suspense is over. The benchmark range has been lowered to 4.00%–4.25%. This is the Fed’s first move of 2025, a decision Chair Jerome Powell framed as a response to mounting labour market weakness, even as inflation continues to challenge policymakers. |
Speech by Chair Powell on the economic outlook @Provchamber: https://t.co/yvKjS6frQH
— Federal Reserve (@federalreserve) September 23, 2025
Watch live: https://t.co/z7JxK6cDst
Learn more about Chair Powell: https://t.co/3kYVCuuLhW
What is the Role of the Federal Reserve?
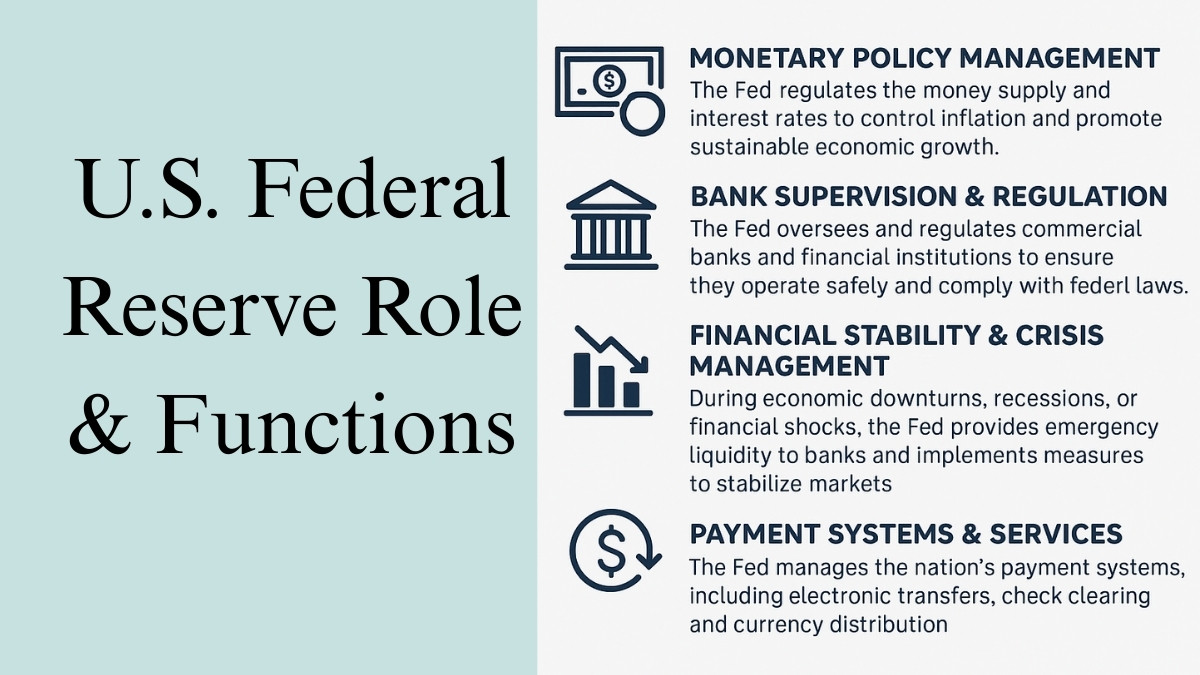
(Image shows the various functions and roles of the U.S. Federal Reserve including the Monetary Policy Management, Bank Supervision, Financial Stability & Payments System and Service
The U.S. Fed is independent from politics, but it oversees the banking system, even amid discussions from figures like Trump. Today, the Fed plays a crucial role in shaping the U.S. economy, influencing everything from interest rates to inflation control, employment, and financial market stability.
Its establishment under the Federal Reserve Act aimed to provide the nation with a safer, more flexible, and stable monetary and financial system. Its major roles and functions are listed below:
1. Monetary Policy Management
The Fed regulates the money supply and interest rates to control inflation and promote sustainable economic growth. Through the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), it sets the federal funds rate, which influences borrowing costs for consumers and businesses.
2. Bank Supervision and Regulation
The Fed oversees and regulates commercial banks and financial institutions to ensure they operate safely and comply with federal laws. This role prevents systemic risks and maintains public confidence in the US banking system.
3. Financial Stability & Crisis Management
During economic downturns, recessions, or financial shocks, the Fed provides emergency liquidity to banks and implements measures to stabilise markets, such as during the 2008 financial crisis or the COVID-19 pandemic.
4. Payment Systems & Services
The Fed manages the nation’s payment systems, including electronic transfers, check clearing, and currency distribution, ensuring that the financial system operates efficiently.
U.S. Fed Timeline of Key Events
The history of the U.S. Fed includes major key events that transformed the powers and functioning of the Fed entirely:
| Year | Events |
| 1913 | The Federal Reserve Act was signed into law, creating the Fed |
| 1933 | The Banking Act enhanced the Fed’s regulatory powers during the Great Depression |
| 1951 | The Treasury-Fed Accord gives the Fed independence in monetary policy |
| 1977 | Full employment and inflation targets were introduced |
| 2008 | The Fed implements emergency measures during a financial crisis |
| 2020 | Pandemic response: liquidity injections and near-zero interest rates |
Source: Federal Reserve Board, Wikipedia
Key Facts About the US Fed: Trivia
The key facts about the Federal Reserve System in the U.S. include:
-
The Fed consists of 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks and the Board of Governors in Washington, D.C.
-
The Chair of the U.S. Fed is currently Jerome Powell, who oversees all the policy decisions and communicates them via press conferences.
-
The Fed’s decisions impact stock markets, including the DJIA, S&P 500, and NASDAQ, as well as mortgage rates, consumer loans, and business investments.
-
The Federal Reserve uses tools such as open market operations, discount rates, and reserve requirements to implement policy.
Also Read: October Visa Bulletin 2025, Check Major Changes for Green Card Applicants!
Trump Awards Highest Civilian Award to Charlie Kirk
What Does the US State Department Do?
Conclusion
Therefore, the U.S. Federal Reserve System remains one of the pillars of US monetary policy. From balancing economic growth, inflation, and financial stability to the decisions being closely monitored globally. It not only influences the stock markets but shapes the consumer finance and international economic conditions as well. Whether it’s cutting rates, raising interest, or providing emergency liquidity, the Fed’s actions reverberate through every corner of the economy.
To see more of such stories, you can go ahead and add this site to your preferred sources by clicking here.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation