AR technology is transforming the way we interact with the world around us. In simple terms, augmented reality refers to the integration of computer-generated images into the real world in a way that enhances the user's experience.
AR technology uses a combination of hardware and software to overlay digital images onto the real world, creating a hybrid environment that blurs the lines between the digital and physical worlds.
What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that combines the real world with virtual objects in real time. It is computer-generated imagery that can be overlaid on top of the real world, providing an enhanced experience. The images can be seen through a device like a smartphone, tablet, or smart glasses. AR technology enhances the real world with additional information, graphics, or sound, creating a more in-depth and engaging experience.
How does it work?
AR technology uses sensors such as cameras, GPS, gyroscopes, and accelerometers, to capture the real-world environment and position the virtual objects in the user's field of view. The AR software processes real-world data and overlays it with computer-generated images to create an augmented idea of what the user is seeing. The result is a seamless integration of digital and real-world photos, providing the user with a more immersive experience.
What are the types of AR?
AR technology has two primary types:
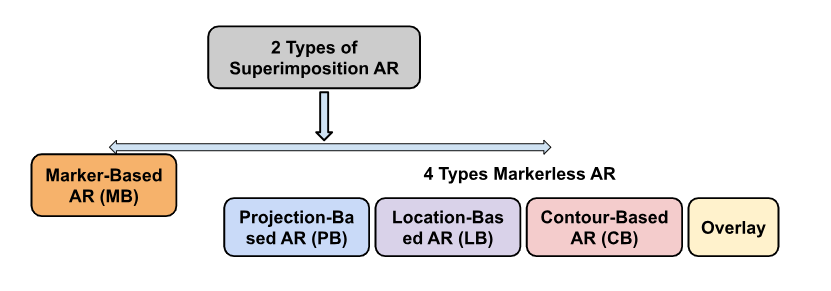
1. Marker-based AR: It uses markers such as QR codes, images, or objects to trigger the display of digital images. The camera on a gadget recognizes the machine-readable barcode and responds by providing visual effects.
- Marker-based AR has significant limitations as it can only be used with mobile devices such as smartphones or tablets. Furthermore, users must download the app or software in order to view the information, so it lacks the instant gratification that we've grown accustomed to in today's digital world.
2. Markerless AR: To produce visual effects, markerless augmented reality does not require image recognition. Instead, the technology detects positional information using a device's camera, location software, and accelerometer, including the orientation of distinct objects and the space between them.
- Markerless AR uses simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) to analyze the surrounding three-dimensional environment. The AR material is then rendered on top of the physical viewpoint and is visible from any position or angle.
It is further divided into four parts:
1. Projection-Based Augmented Reality
2. Location-Based Augmented Reality
3. Overlay AR
4. Contour-Based AR
Both marker-based and markerless AR have their strengths and weaknesses. Marker-based AR provides precise and reliable tracking since markers serve as explicit reference points. On the other hand, markerless AR offers more flexibility as it can be used in various environments without the need for predefined markers, but it may be less accurate and may require more computational power for robust tracking.
Applications of Augmented Reality
AR technology has several applications in different industries.
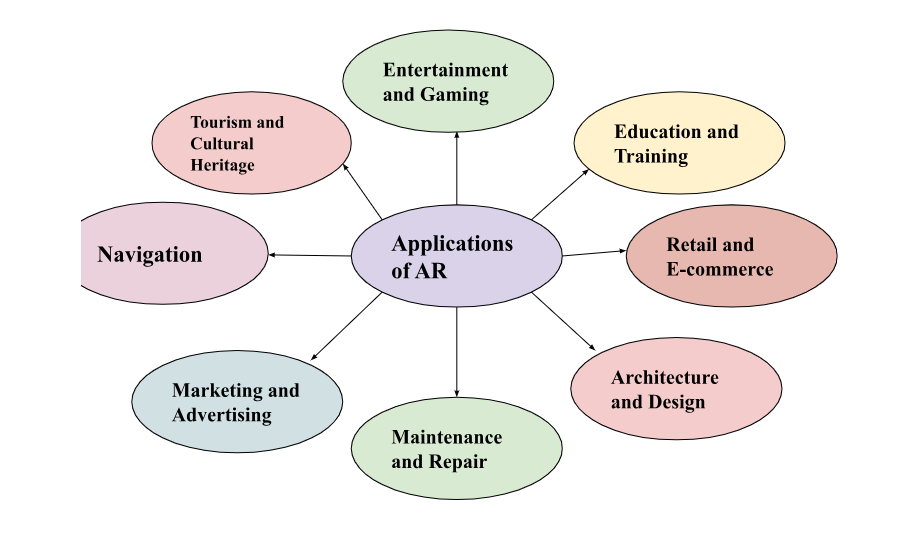
Potential applications of AR continue to expand as the technology advances. From entertainment to education, healthcare to retail, AR is revolutionizing various industries by providing enhanced and interactive experiences that blend the digital and physical worlds. Let’s check out examples of AR applications in different industries.
| S. No. | Industry | Examples |
| 1 | Entertainment and Gaming | AR has transformed the gaming industry, providing immersive experiences and blending virtual objects with the real world. Games like Pokémon Go and Harry Potter: Wizards Unite allow players to interact with virtual characters and objects in their physical surroundings. |
| 2 | Education and Training | AR is used to enhance learning experiences by overlaying digital content onto real-world objects. Students can interact with 3D models, explore historical sites, or perform virtual experiments, making education more engaging and interactive. |
| 3 | Retail and e-commerce | AR enables customers to virtually try on products like clothing, accessories, or makeup before making a purchase |
| 4 | Healthcare | AR is used in medical training, allowing students to simulate surgeries or visualize internal organs and structures |
| 5 | Architecture and Design | AR allows users to visualize and explore architectural designs, interior layouts, and furniture placements, providing a realistic sense of the final product before construction begins. |
| 6 | Maintenance and Repair | Real-time guidance and overlays digital information onto physical machinery, helping troubleshoot, identifying faulty components, or providing step-by-step instructions. |
| 7 | Tourism and Cultural Heritage | Interactive guides, virtual tours, and historical information about landmarks and cultural sites. |
| 8 | Marketing and advertising: | Brands can create interactive and immersive experiences by overlaying digital content on physical advertisements or products, enhancing brand awareness and customer engagement. |
| 9 | Navigation and Wayfinding | Indoors (such as airports or shopping malls) or outdoors. |
In conclusion, augmented reality is a technology that has transformed the world of technology. It has the potential to revolutionize several industries, providing users with a more immersive and engaging experience. AR technology is still in its early stages, but its potential is enormous, and we can expect to see more applications of AR in the future.
Also read:
Current Affairs Quiz: June 13 2023- New Director General of BSF
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation