Highlights
|
Heatwave intensifies in Europe. All major Italian cities are on ‘red’ heat alert. Wildfires scorching forests across the continent. What is causing such an extreme heat wave?
Europe is currently experiencing the most extreme heatwave ever, with temperatures soaring well above average. In some parts of the continent, the temperature has reached 40 degrees Celsius (104 degrees Fahrenheit), and there are concerns that the heatwave could have serious consequences for human health, the environment, and infrastructure. The European Space Agency (ESA) has forecasted a high of 48 degrees Celsius (118 degrees Fahrenheit) to hit Italy’s islands of Sicily and Sardinia.
Health authorities have issued alarms to people in Europe, North America, and Asia to avoid the harsh Sun and stay hydrated. For the first time, the UK’s Meteorological Office has issued a ‘red’ heat warning, its highest heat alert level, for Manchester, London, and other regions in the UK. France has also issued a ‘red’ alert where the temperate is also forecasted to reach 104 degrees Fahrenheit.
Vicious wildfires have been reported across Europe due to record-breaking temperatures. In addition to this, the roads and power lines have melted, and railway lines have warped.
 Image: AFP
Image: AFP
Recent Trends in Temperature Change Across the Globe
Jennifer Francis, a senior scientist at Woodwell Climate Research Center in a statement to CNN said these temperatures currently are “almost certainly” the warmest temperatures the planet has seen “probably going back at least 100,000 years”.
Based on the data from NOAA Centers for Environmental Information, the heat map below shows that most of the planet is warming. See below the trends in the global average surface temperature of the planet between 1993 to 2022.
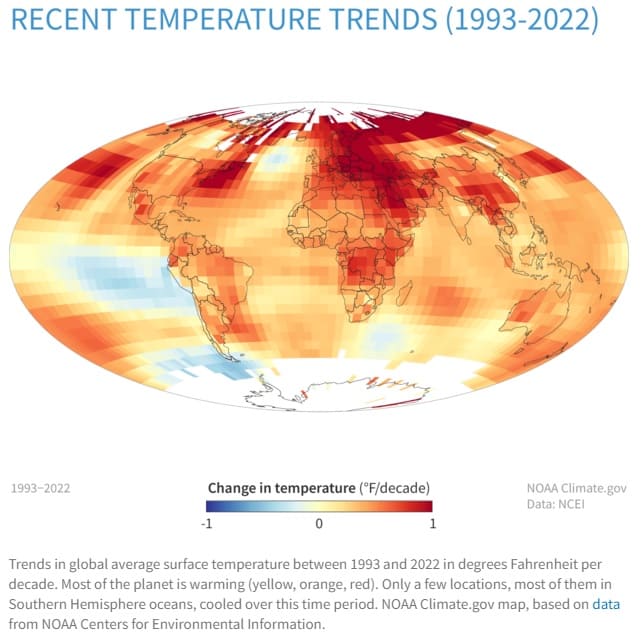
Extreme heat waves are one of the biggest weather-related causes of death worldwide. Let us understand what a heat wave is and its causes along with the impacts of temperature change and ways to mitigate the challenge of temperature rise.
What is a Heat Wave?
A heatwave is a period of abnormally hot weather that lasts for several days. Heatwaves can occur in any season, but they are most common during the summer months. Heatwaves can be caused by several factors, including high-pressure systems, warm ocean currents, and changes in the jet stream.
What is causing an extreme heat wave across Europe?
The latest heat wave event over Europe is reportedly being caused by a phenomenon known as a ‘cut-off low’ where a low-pressure system gets cut off from the rest of the jet stream thereby causing severe long-lasting heat waves to build up in a certain region.
Dr Malcolm Mistry, Assistant Professor in Climate and Geo-spatial Modelling, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, said, “Currently, the Jet stream from North America to Europe is stuck in a position that is roughly south of the English Channel in a U-shape flow, with both the trough and the crest of this wave lying south of the UK.
“To the north of the jet stream, we have cooler Arctic air and areas of low pressure, which in turn bring rain spells to the UK.
“To the south of the jet stream, we have an opposite weather pattern with a high-pressure system stalled drawing hot air from north Africa and maintaining the hot dry conditions.
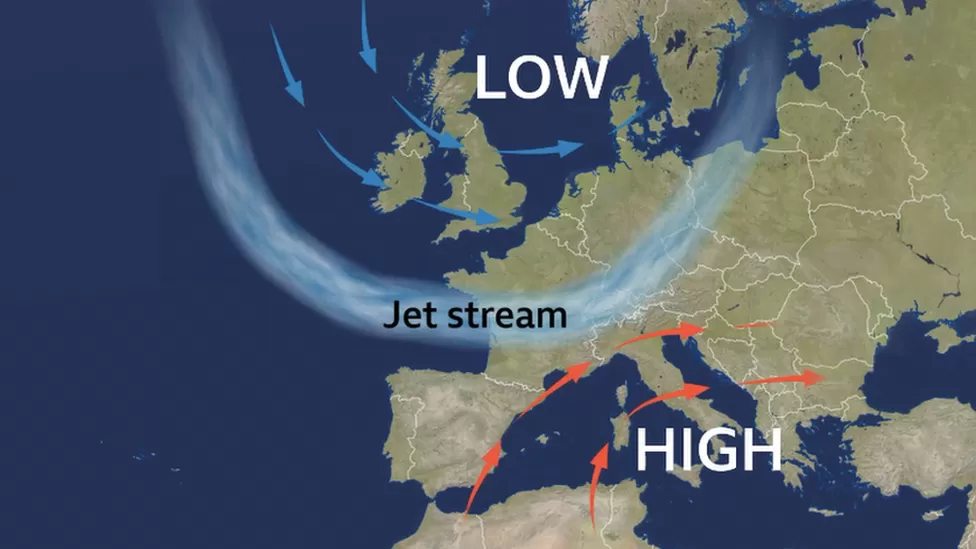 Image: BBC
Image: BBC
Major Causes of Heat Waves or Temperature Change
The main factors that are driving temperature change in the US and Europe, such as greenhouse gas emissions and changes in land use.
“Greenhouse gas emissions, from burning fossil fuels like coal, gas and oil, are making heatwaves hotter, longer-lasting and more frequent,” Friederike Otto, a climate scientist at Imperial College London and co-lead of the extreme weather research consortium World Weather Attribution, said in a statement.
Here are some of the causes of heat waves:
High-pressure systems: Heat waves are often caused by high-pressure systems. These systems are areas of high atmospheric pressure that cause the air to sink. As the air sinks, it warms up.
Warm ocean currents: Heat waves can also be caused by warm ocean currents. These currents can bring warm water to the surface, which can then evaporate and cause the air to warm up.
Changes in the jet stream: The jet stream is a band of strong winds that flows high in the atmosphere. Changes in the jet stream can cause warm air to be trapped in certain areas, which can lead to heat waves.
Climate change: Climate change is also a factor that can contribute to heat waves. As the Earth's atmosphere warms, it can hold more moisture. This moisture can then evaporate and cause the air to warm up.
It is important to note that heat waves can be caused by a combination of factors. For example, a heat wave that is caused by a high-pressure system can be made worse by warm ocean currents or changes in the jet stream.
Impacts of Temperature Change
The impacts of temperature change on Europe are already being felt, and they are expected to become more severe in the future.
The Earth's climate has been changing for millions of years, but the rate of change in recent decades is unprecedented. This is due to human activities that are releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, trapping heat and causing the planet to warm.
Some of the most serious impacts include:
Heat waves: Heat waves are becoming more frequent and intense, and they are posing a serious threat to human health.
Rise in ozone pollution levels: Heatwaves increase ozone pollution levels because they cause more volatile organic compounds (VOCs) to be released into the atmosphere. These VOCs react with sunlight to form ozone, which is a harmful pollutant.
Droughts: Droughts are becoming more common, and they are drying up rivers, lakes, and aquifers. This is having a devastating impact on agriculture and ecosystems.
Floods: Floods are becoming more severe, and they are causing widespread damage to property and infrastructure.
Wildfires: Wildfires are becoming more frequent and destructive, as dry conditions and heat waves create the perfect conditions for fires to start and spread.
Sea level rise: Sea levels are rising, and this is threatening coastal communities around the world.
Loss of biodiversity: Temperature change is causing the extinction of plant and animal species.
Changes in agricultural yields: As temperatures rise, crop yields are expected to decline in some areas. This could lead to food shortages and price increases.
Spread of diseases: Warmer temperatures are allowing mosquitoes and other disease-carrying insects to spread to new areas. This is increasing the risk of diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and yellow fever.
Damage to infrastructure: Warmer temperatures are causing roads, bridges, and other infrastructure to deteriorate more quickly. This could lead to costly repairs and disruptions.
Economic losses: The impacts of temperature change are expected to have a significant economic impact. This could lead to job losses, business closures, and increased insurance costs.
Way Forward: Mitigation
Earth’s temperature has risen by an average of 0.14° Fahrenheit (0.08° Celsius) per decade since 1880, or about 2° F in total, stated NOAA Climate Centers.
Heat waves are becoming more frequent and intense, and they are a serious threat to human health and the environment. The impacts of heat waves are already being felt around the world, and they are expected to become more severe in the future.
The Europe Heatwave 2023 is a stark reminder of the dangers of climate change. The heat wave is having a serious impact on human health, the environment, and infrastructure. It is important to take action to mitigate and adapt to the impacts of temperature change to protect Europe from the worst effects of climate change.
There are several things that can be done to mitigate and adapt to the impacts of heat waves. Some of these measures include:
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions: This is the most important step that can be taken to mitigate climate change, which is the main cause of heat waves.
Building more resilient infrastructure: This includes measures such as making buildings more energy-efficient and providing shade in public spaces.
Educating the public about the risks of heat waves: This will help people to stay safe during heat waves and to take steps to reduce their risk of heat-related illness.
Providing cooling centers: This is a place where people can go to cool down during a heat wave. Cooling centers can be set up in public buildings, such as libraries and community centers.
Monitoring air quality: Air quality can deteriorate during heat waves, so it is important to monitor air quality and take steps to protect yourself if air quality is poor.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation