Maxwell’s Equation Definition, Laws And Applications: Maxwell’s equations are a set of fundamental principles that form the foundation of classic electromagnetism.
They describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated by electric charges, currents and changes in the fields.
1. Gauss's Law for Electricity
Maxwell’s equation is based on the first law of electrostatic, which states that ‘when a closed surface integral of electric flux is always equal to charge enclosed over that surface.
Importance of Gauss's Law for Electricity
This law establishes a direct connection between the total electric charge enclosed by the closed surface and the electric flux that passes through that surface.
2. Gauss’s Law For Magnetism Or Corresponding Formula For Magnetic Fields
Gauss's law for magnetism states that the magnetic flux B across any closed surface is zero.
Importance Of Gauss’s Law Of Magnetism
This law reflects the symmetry and continuity of magnetic fields. It provides a deep conceptual understanding of the magnetic fields.
3. Faraday’s Law Of Magnetic Induction
Faraday’s law of magnetic induction, often known as Faraday’s law describes how changing magnetic fields can induce an electromotive force in a closed-loop conductor.
Importance Of Faraday’s Law
This law provided a crucial link by demonstrating how electric currents generate magnetic fields. Ampere’s law allows us to calculate the magnetic field generated by various current configurations.
4. Ampere’s Law
Maxwell’s fourth equation, also known as Ampere’s Law describes the relationship between magnetic fields, electric current and changes in electric fields.
The law states that a magnetic field can be produced not only by an electric current but also by a changing electric field.
Importance Of Maxwell’s Fourth Law or Ampere’s Law
This law helped Maxwell to explain the propagation of electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves. Maxwell’s fourth law shows how the changing electric field creates a magnetic field, which in turn creates a changing electric field, and so on, leading to a propagating wave.
Students can easily learn the equation with the help of these notes.
Also, check
Refraction Of Light: Definition, Laws, Applications And FAQs
Newton’s Laws Of Motion: Definition, Formula, Applications And Examples
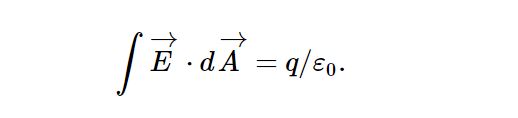
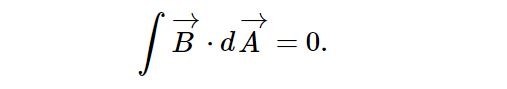
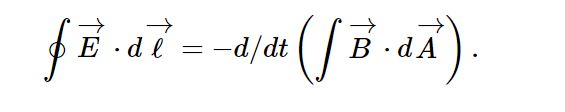
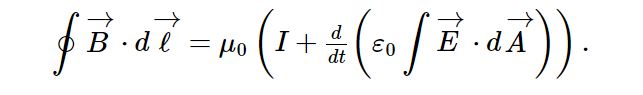
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation