Series and Parallel Circuit Series and parallel circuits are two fundamental configurations in electrical circuits, each with distinct characteristics that affect how electricity flows through them. By understanding series and parallel circuits, you can visualize how electricity flows through electronic devices and design circuits for various applications!
What is a Series Circuit?
A series circuit is characterised by having the same current flow through all its components. In this configuration, there is only one path for the current. For example, household decorative string lights are often arranged in a series circuit where multiple small bulbs are connected sequentially. If one bulb burns out, all bulbs in the series will not light up.
What is a Parallel Circuit?
A parallel circuit allows electric current to flow through multiple paths simultaneously. Components within a parallel circuit maintain a consistent voltage across all connections.
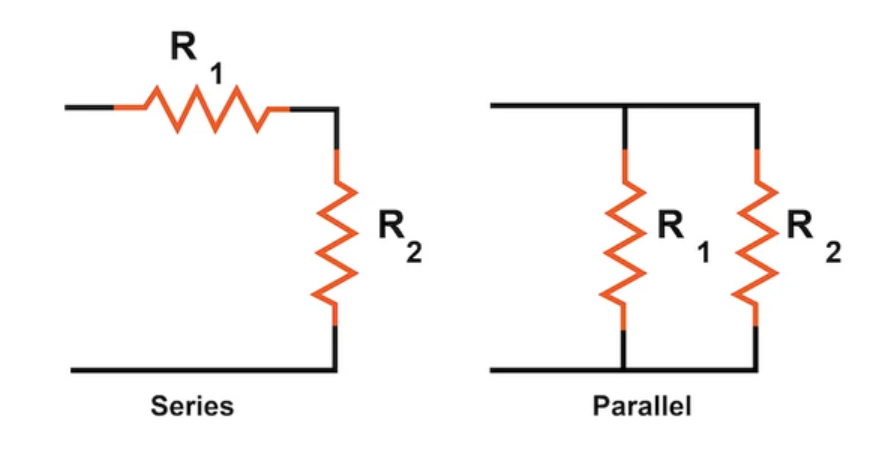
Source: Quora
Difference Between Series and Parallel Circuits
The primary distinction between series and parallel circuits lies in how current flows through the components. In a series circuit, the identical current passes through every component connected in the circuit. Conversely, in parallel circuits, components are arranged side by side, causing the circuit to divide the current flow. As a result, the current originating from the source is divided among the various components, each receiving its own portion of the total current.
| Feature | Series Circuit | Parallel Circuit |
| Current Flow | Same current through all components | Current varies in each branch |
| Impact of a Broken Component | Entire circuit malfunctions | Only affected branch stops working |
| Voltage Distribution | Voltage divided across components | Same voltage across each branch |
Video Lessons Link For Students
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation