The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2021 was jointly awarded to David Julius and Ardem Patapoutian for their discoveries of receptors for temperature and touch.
Speaking on the occasion, the Nobel jury said, “The groundbreaking discoveries…by this year’s Nobel Prize laureates have allowed us to understand how heat, cold and mechanical force can initiate the nerve impulses that allow us to perceive and adapt to the world around us.”
BREAKING NEWS:
— The Nobel Prize (@NobelPrize) October 4, 2021
The 2021 #NobelPrize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded jointly to David Julius and Ardem Patapoutian “for their discoveries of receptors for temperature and touch.” pic.twitter.com/gB2eL37IV7
Discoveries by David Julius and Ardem Patapoutian
David Julius utilized capsaicin, a pungent compound from chilli peppers that induces a burning sensation to identify a sensor in the nerve endings of the skin that responds to heat.
David Julius – awarded this year’s #NobelPrize in Physiology or Medicine – utilised capsaicin, a pungent compound from chilli peppers that induces a burning sensation, to identify a sensor in the nerve endings of the skin that responds to heat. pic.twitter.com/GInY2q6RlD
— The Nobel Prize (@NobelPrize) October 4, 2021
Ardem Patapoutian used pressure-sensitive cells to discover a novel class of sensors that respond to mechanical stimuli in the skin and internal organs.
2021 #NobelPrize laureate in physiology or medicine Ardem Patapoutian used pressure-sensitive cells to discover a novel class of sensors that respond to mechanical stimuli in the skin and internal organs. pic.twitter.com/6T7661lRPq
— The Nobel Prize (@NobelPrize) October 4, 2021
Both the Nobel laureates have identified the missing links to help us understand the complex interplay between our senses and the environment. Their discoveries are being used to develop treatments for a wide range of diseases such as chronic pain.
The seminal discoveries by this year’s #NobelPrize laureates in physiology or medicine have explained how heat, cold and touch can initiate signals in our nervous system. The identified ion channels are important for many physiological processes and disease conditions. pic.twitter.com/TxMTwSDHas
— The Nobel Prize (@NobelPrize) October 4, 2021
Discovery of TRPV1 and TRPM8
In the late 1990s, David Julius at the University of California, USA, saw the possibility for major advances by analyzing how capsaicin causes the burning sensation when humans come into contact with chilli peppers. To solve this, Julius along with his co-workers created a library of millions of DNA fragments equivalent to genes that can react to pain, heat, and touch.
The team hypothesized that the aforementioned library would include a DNA fragment that encodes the protein capable of reacting to capsicum. They further expressed individual genes from this collection in cultured cells that normally do not react to capsaicin. The researchers were able to identify a single gene that made cells capsaicin-sensitive.
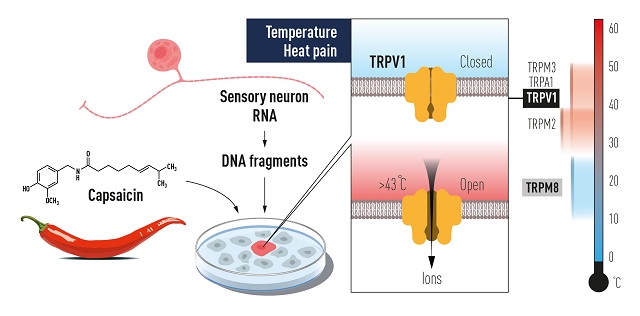
Further experiments pointed out that the identified gene encoded a novel ion channel protein and the newly discovered capsaicin receptor was named TRPV1. Julius then investigated the ability of the protein to respond to heat and discovered a heat-sensing receptor that is activated at temperatures perceived as painful.
The breakthrough discovery led to the identification of TRPM8, a receptor that is activated by cold. Both David Julius and Ardem Patapoutian independently used menthol to identify TRPM8.
Many laboratories perform research on genetically modified mice. They investigate the roles of different channels in thermal sensation.
"I thought it was some kind of prank!"
— The Nobel Prize (@NobelPrize) October 4, 2021
Listen to our interview with 2021 medicine laureate David Julius, who was making coffee with his wife when he discovered he had been awarded the #NobelPrize. pic.twitter.com/m8ohOL526Y
Discovery of Piezo Channels
With the unfolding of mechanisms for temperature sensation, the conversion of mechanical stimuli into our senses of touch and pressure remained unclear. This time, Ardem Patapoutian who was working at Scripps Research in La Jolla, USA, expressed the need to identify the evasive receptors that are activated by mechanical stimuli.
Ardem Patapoutian and the team first identified a cell line that gave off a measurable electrical signal when individual cells were poked with a micropipette. The researchers then assumed that the activated receptor is an ion channel. They then identified 72 candidate genes encoding possible receptors that were one by one inactivated to find the gene responsible for mechanosensitivity in the studied cells.
The team was successful in identifying the gene whose silencing rendered the cells insensitive to poking with the micropipette. The newly discovered mechanosensitive ion channel was named Piezo1, after the Greek word for pressure (í; píesi). Further research disclosed that Piezo1 and Piezo2 are ion channels that are directly activated by the exertion of pressure on cell membranes.
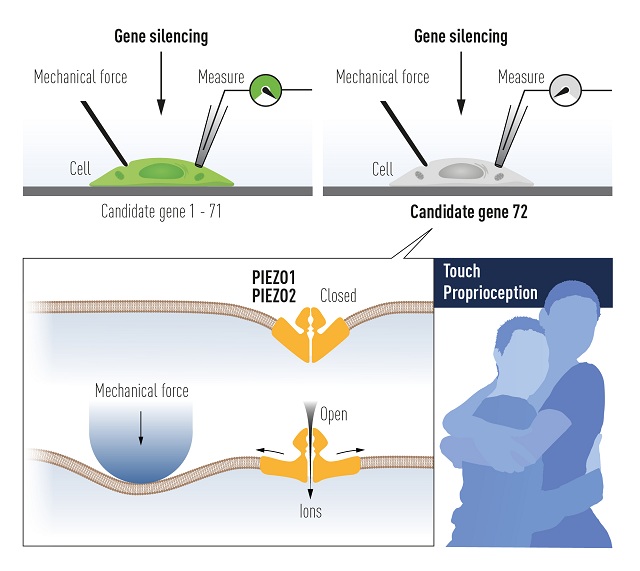
The breakthrough discovery led to the demonstration of the Piezo2 ion channel and its importance for the sense of touch. Later findings have also revealed that Piezo1 and Piezo2 channels regulate additional important physiological processes such as blood pressure, respiration and urinary bladder control.
"This was kind of the big elephant in the room."
— The Nobel Prize (@NobelPrize) October 4, 2021
For 2021 medicine laureate Ardem Patapoutian, figuring out how our sense of touch works was an unsolved mystery.
Listen to our interview with our new #NobelPrize laureate now! pic.twitter.com/HionvwPMnG
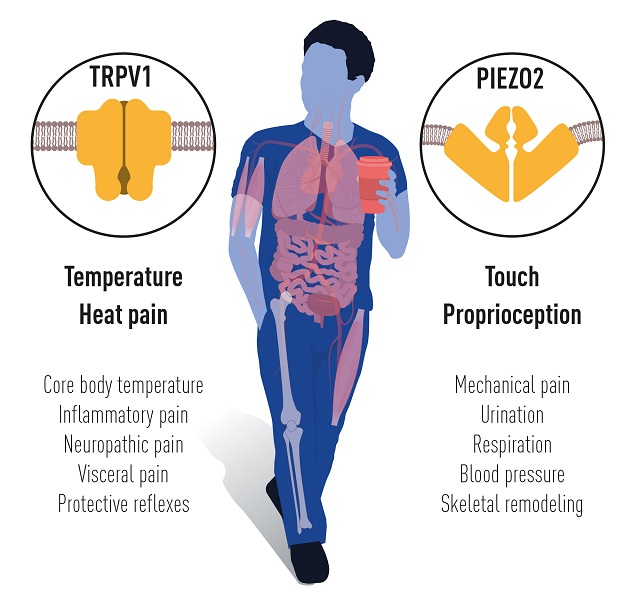
The above mentioned groundbreaking discoveries of TRPV1, TRPM8 and Piezo channels by 2021 Nobel Laureates of Physiology or Medicine have helped us in understanding how heat, cold and mechanical force initiate nerve impulses and allow us to perceive and adapt to the world around us. They also put up different additional physiological processes that depend on sensing temperature or mechanical stimuli.
The groundbreaking discoveries of the TRPV1, TRPM8 and Piezo channels by this year’s #NobelPrize laureates have allowed us to understand how heat, cold and mechanical force can initiate the nerve impulses that allow us to perceive and adapt to the world around us. pic.twitter.com/YWnOwayJri
— The Nobel Prize (@NobelPrize) October 4, 2021
Discoveries prior to David Julius and Ardem Patapoutian
In the 17th century, René Descartes visualised threads that connect different parts of the skin with the brain. As evident from the below figure, a foot touching an open flame would send a mechanical signal to the brain. Later discoveries have shown the existence of specialized sensory neurons that register changes in our environment.

In 1944, Joseph Erlanger and Herbert Gasser received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery of different types of sensory nerve fibres that react to distinct stimuli, such as responses to painful and non-painful touch. These nerve cells are highly specialized for detecting and transducing different stimuli that allow a nuanced perception of our surroundings.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2021: About the winners
| David Julius | Ardem Patapoutian |
| Born in 1955 in New York, USA, David Julius received a Ph.D. in 1984 from the University of California and was a postdoctoral fellow at Columbia University. He has been a Professor at the University of California, San Francisco since 1989. |
Born in 1967 in Beirut, Lebanon, Ardem Patapoutian received a Ph.D. in 1996 from the California Institute of Technology and was a postdoctoral fellow at the University of California, San Francisco. Since 2000, he has been a scientist at Scripps Research, La Jolla, California where he is now Professor. He has been a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator since 2014. |
About Nobel Prize
According to Sir Alfred Nobel’s will of 1895, Nobel Prize is awarded to people who during the preceding year have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind. The award is presented in six different fields, namely Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, and Peace.
It comes with a gold medal and 10 million Swedish Kronor (over $1.14 million) and was first awarded in 1901. The prize money comes from a bequest left by the creator of the Prize, Alfred Nobel.
How are the winners selected?
First, eligible candidates are selected by the nominators (these nominators have received invitations from the Nobel Committee to submit names for consideration). The jury then decides who to award the Nobel Prize.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine is awarded for discoveries that have changed the scientific paradigm and are of great benefit for humankind. Lifetime achievements or scientific leadership cannot be considered for the prize. The winner(s) is selected by the Karolinska Institutet (now The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet).
Read more on Nobel Prize: Nobel Prize: History, Creation, Categories, Selection Process, and Winners
Nobel Prize 2021 schedule
It is to be noted that the Nobel Prizes will be announced from 4 October to 11 October 2021. Check the complete schedule below:
| 4 October 2021 | Physiology or Medicine |
| 5 October 2021 | Physics |
| 6 October 2021 | Chemistry |
| 7 October 2021 | Literature |
| 8 October 2021 | Peace |
| 11 October 2021 | Economics |
Related Articles:
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2021 jointly awarded to David Julius and Ardem Patapoutian
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation