Chandrayaan-3 was designed for the precise purpose of effecting a gentle touchdown upon the lunar terrain. This successful touchdown occurred on the 23rd of August, precisely at 6:04 PM.
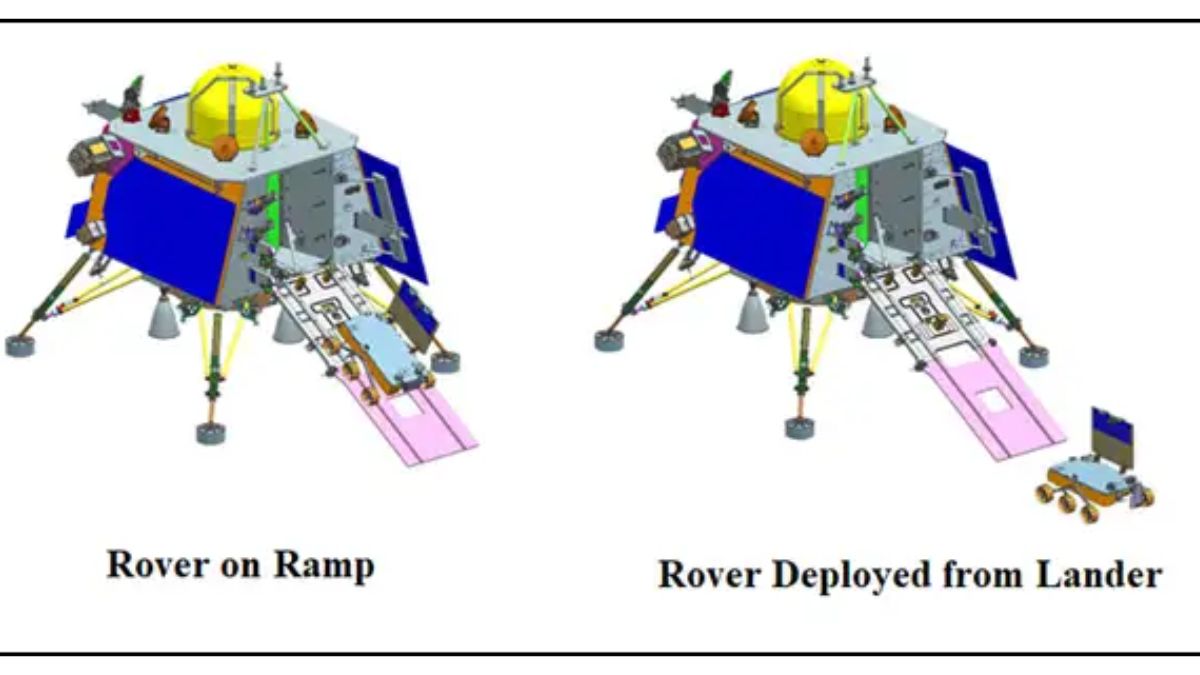
They are accompanied by a rover that is presently engaged in the systematic exploration of the lunar expanse. The pivotal mechanism enabling the trajectory of both the lander and rover toward the moon was rooted in the auspices of a dedicated propulsion module (PM). Notably, this very propulsion module accommodated an additional scientific payload, thoughtfully integrated to bestow supplementary value.
Read| List of all scientists behind the historic Chandrayaan-3 mission success
Instruments used in Chandrayaan-3 ISRO Moon Mission
Embedded within the Chandrayaan 3 mission is a multitude of pivotal scientific instruments, curated to propel the fulfilment of its mission objectives: an in-depth analysis of the lunar landscape, its elemental constitution, and atmospheric dynamics. This arsenal of instruments encompasses:
| Instrument | Type | Developer | Loaded On |
| ILSA | Seismometer | LEOS | Lander Module |
| RAMBHA-LP | Langmuir Probe | SPL/VSSC | Lander Module |
| CHASTE | Thermal Probe | SPL/VSSC | Lander Module |
| LRA | Retroreflector | NASA | Lander Module |
| APXS | X-ray Spectrometer | PRL | Rover Module |
| LIBS | Laser-based Spectrometer | LEOS | Rover Module |
| SHAPE | Spectro-polarimeter | URSC | Propulsion Module |
Also Check - ISRO Chairman List | Who is S. Somanath?
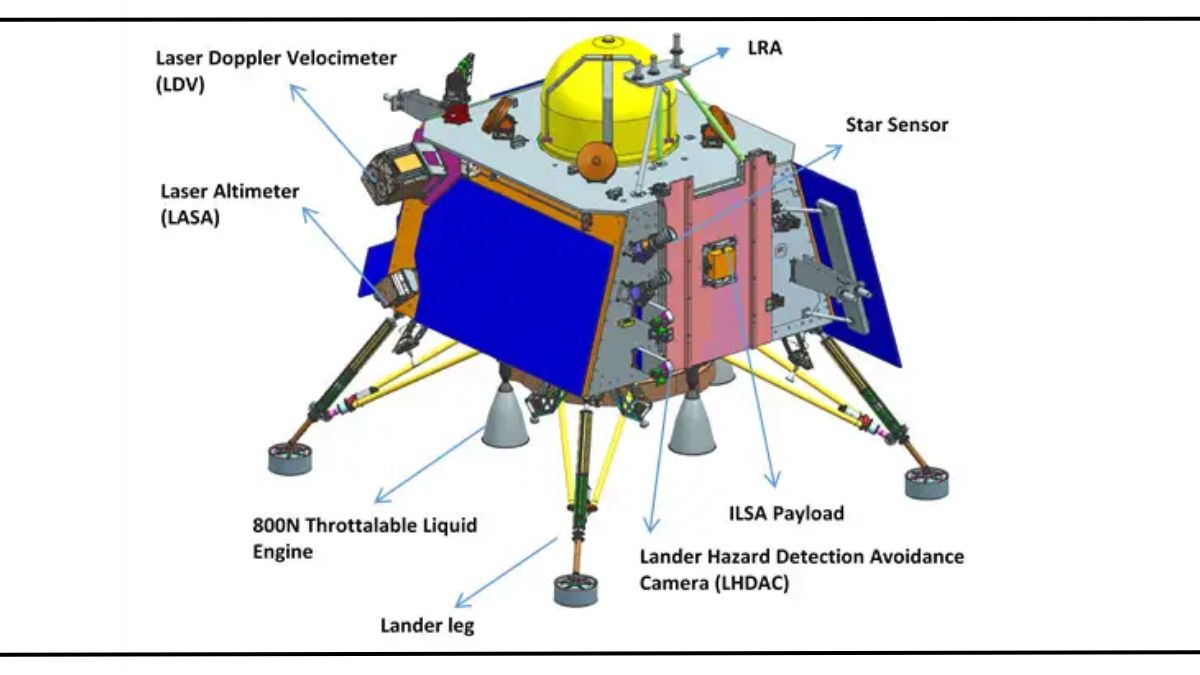
- ILSA (Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity): The ILSA instrument emerges as a vanguard for studying seismic occurrences within the lunar expanse. Through its adept sensing capabilities, it discerns and quantifies moonquakes, thereby facilitating a profound understanding of the moon's internal architecture. Furthermore, ILSA aids in charting the distribution of seismic events, uncovering invaluable insights into lunar dynamics.
- RAMBHA (Radar for Moon Bound Experiments): The RAMBHA apparatus stands as an instrumental resource for comprehensively exploring the lunar atmosphere and surface. Its operational prowess involves emitting precisely calibrated radar pulses followed by astute measurement of reflected signals. This dynamic instrument empowers the creation of intricate lunar surface maps while affording unparalleled insights into the complexities of the lunar atmosphere.
- ChaSTE (Chandrayaan-3 Surface Thermophysical Experiment): A crucial instrument integral to the mission's scientific arsenal, ChaSTE serves the purpose of meticulously gauging the thermal properties inherent to the lunar regolith. This undertaking involves meticulous measurements of both heat flow from the lunar surface and the regolith's temperature, collectively enabling an insightful grasp of lunar soil characteristics.
- LRA (Laser Retroreflector Array): Serving as an elegant yet passive experiment, the LRA mechanism undertakes the crucial task of measuring the spatial interval between Earth and the moon. This ingeniously simple apparatus reflects laser pulses transmitted from Earth back to their origin. This innovative approach underpins the meticulous tracking of lunar motion and offers a unique vantage point for investigating the intricate dynamics of the Earth-moon system.
- APXS (Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer): This cutting-edge apparatus will play a pivotal role in ascertaining the elemental composition of the lunar surface. Employing a technique wherein alpha particles are judiciously directed at the lunar terrain, subsequent measurement of the ensuing X-ray emissions will enable precise identification of elemental constituents. This encompassing capacity extends to discerning elements like oxygen, silicon, iron, and magnesium.
- LIBS (Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy): A technologically advanced system, the LIBS apparatus contributes significantly to the mission's objectives by deciphering the elemental composition of lunar rocks and soil. Employing a laser-induced approach, this instrument engages the lunar surface, facilitating the measurement of emitted spectra. Distinctive elements such as calcium, titanium, and iron are discernible through this innovative method.
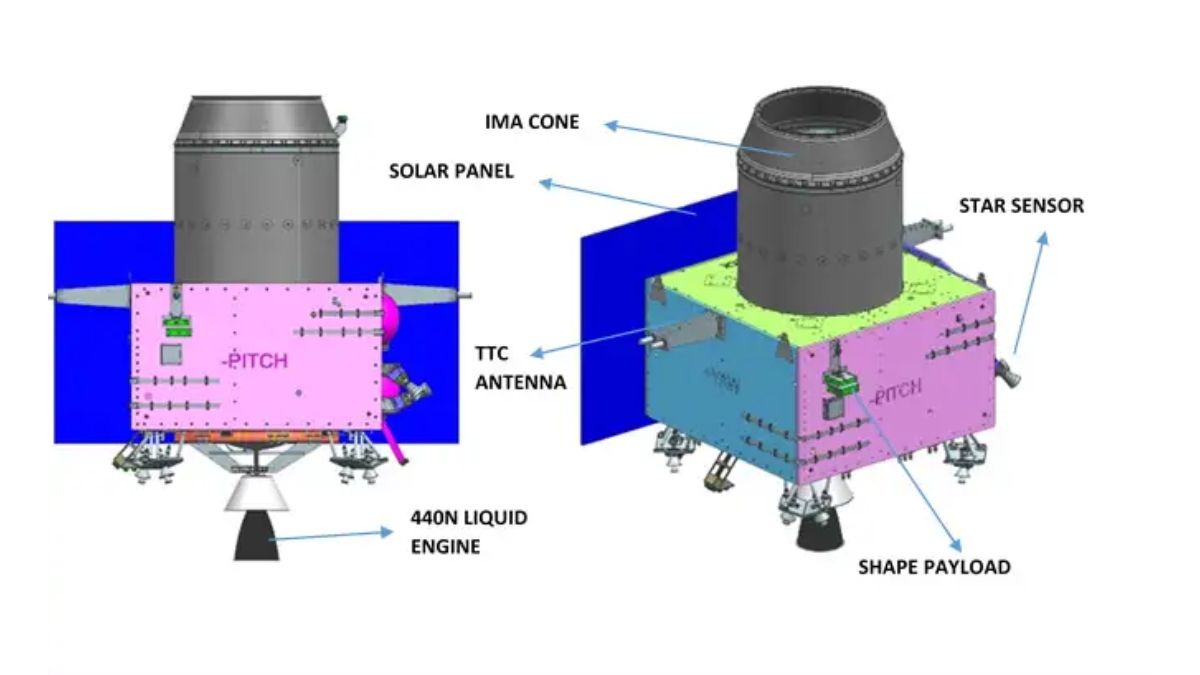
- SHAPE (Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth): The payload will be used to study the spectral and Polari metric measurements of Earth from the lunar orbit. in the near-infrared (NIR) wavelength range (1–1.7 μm [3.9×10−5–6.7×10−5 in]).
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation