With the passing days, the earth changes its position from one point to another, welcoming different seasons and weather patterns. But do you know how these seasons are determined?
The reason is simple: the Earth doesn't rotate in a straight line but rather on a tilted axis.
This causes the changing of seasons as different parts of the Earth receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the year. Additionally, it also causes equinox and solstice events, marking significant points in the Earth's orbit around the sun.
But do you know what an equinox is? When does it occur? How is it different from a solstice? There are so many questions that need to be answered to truly understand the impact of Earth's tilted axis on our planet's seasons and weather patterns.
Recommended for you: What Is the Summer Solstice and Why Is It Called the Longest Day of the Year 2023?
What is an Equinox?
Imagine searching for the meaning of an equinox online and getting results like this: "An equinox is an astronomical phenomenon characterised by the occurrence of a biannual event during which the plane of Earth's equator passes through the geometric centre of the Sun's disc.
This celestial alignment results in an ephemeral state of equilibrium, where the diurnal and nocturnal periods exhibit an approximate isotropy, thereby engendering a quasi-bifurcation of photoperiodicity across the planet."
It is difficult to understand, isn't it? Until and unless you hold a degree in the field of astronomy or have a strong background in scientific terminology, deciphering such complex definitions can be quite challenging.
However, to make it easy for you to understand, here is the simplest explanation: Equinox is when the sun is directly above the equator, resulting in equal day and night lengths. This phenomenon occurs twice a year, in March and September.
Equal day and night = Equinox
The Science Behind the Formation of an Equinox
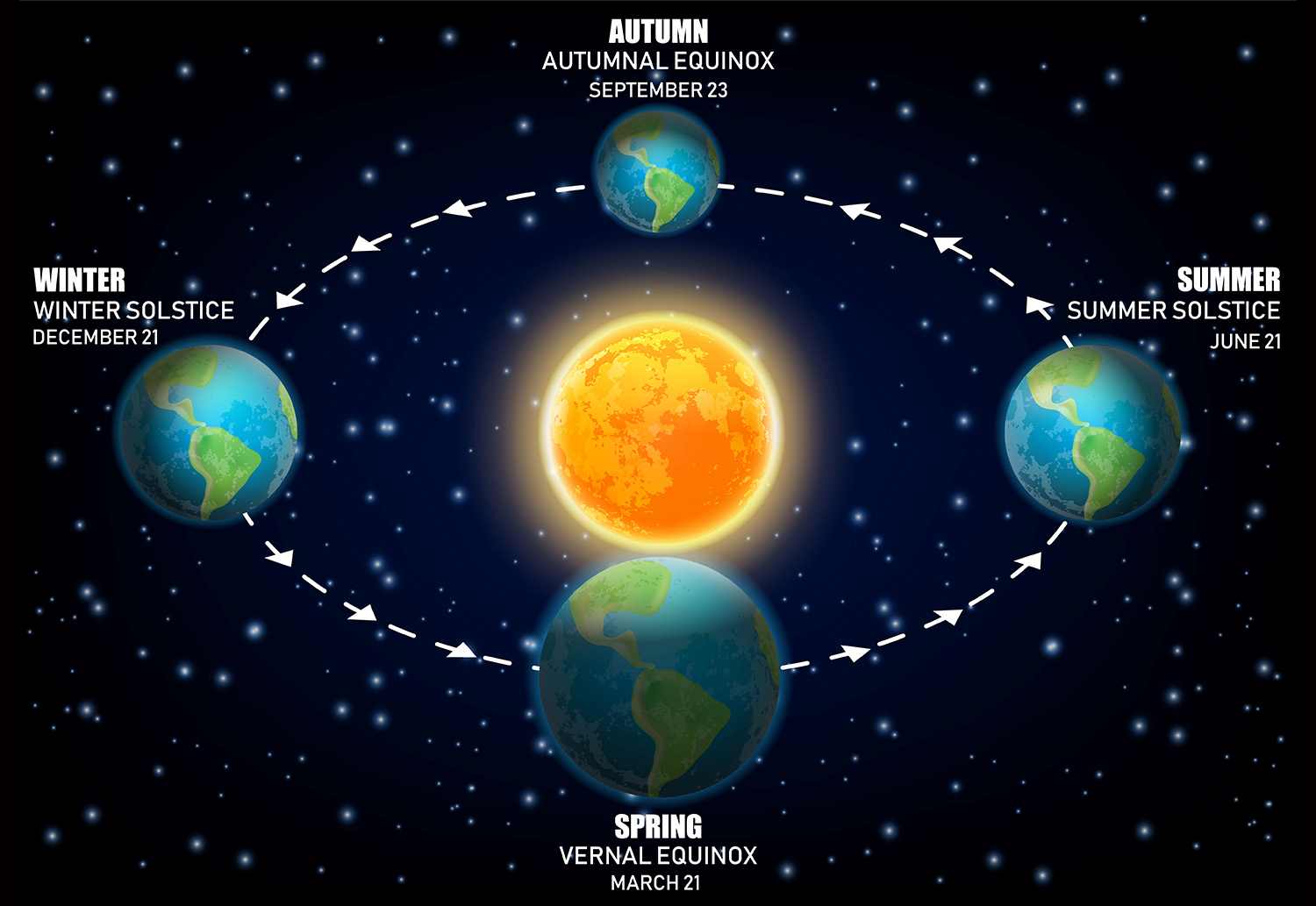
We all know that the Earth revolves around the sun, but did you know that this movement is what causes the changing of seasons? The earth doesn't rotate in a straight line; rather, it rotates on a tilted axis.
Due to this tilt, the northern hemisphere and the southern hemisphere get different amounts of light at different times of the year, resulting in the seasons we experience.
Sometimes the Northern Hemisphere gets more direct sunlight, causing summer, while the Southern Hemisphere gets less direct sunlight, causing winter. This phenomenon is known as axial tilt.
But at one point in time, the sunlight falls directly on the equator, which causes equal day and night, known as the equinox. This balance of light and darkness occurs twice a year, marking the beginning of spring and autumn.
You Might Like: What Is The Vernal Equinox? When Will Spring Start This Year? All You Need To Know
What is the difference between a solstice and an equinox?
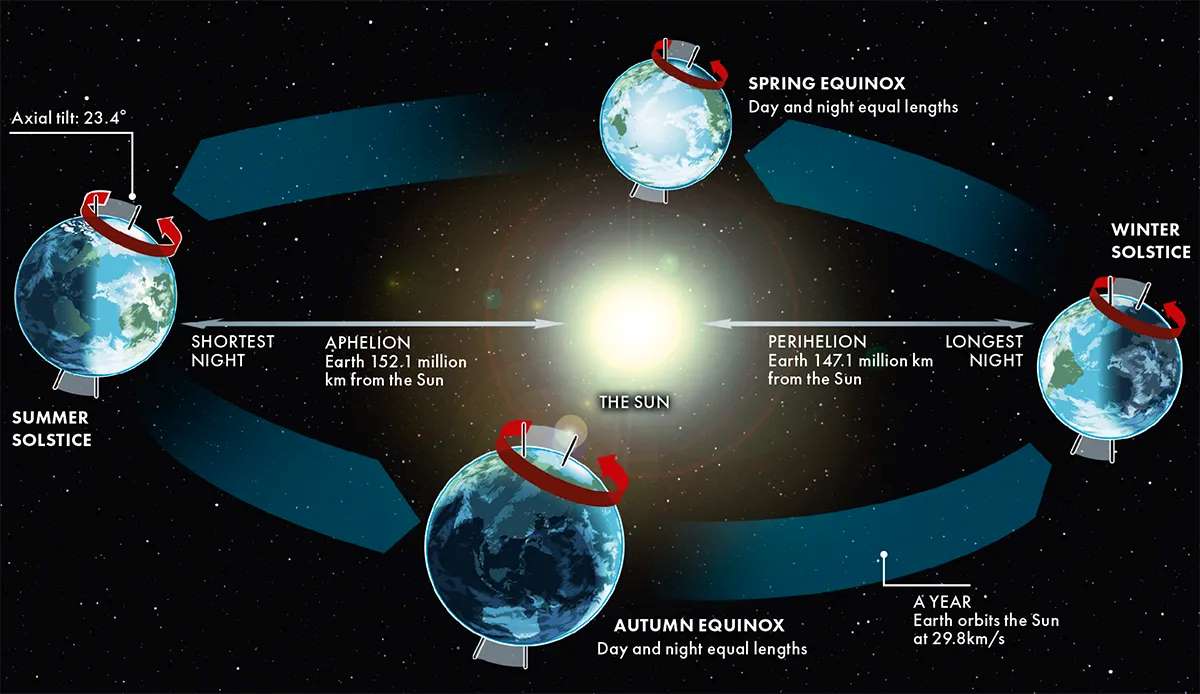
Solstice and Equinox happen due to the tilt of the Earth's axis in its orbit around the sun. However, the meaning and event are slightly different from each other.
Before diving directly into what a solstice is, you should first be aware of three important latitudes: the Tropic of Cancer, the Tropic of Capricorn, and the Equator.
The Tropic of Cancer is at 23.5 degrees north. The equator is the circle where the sun can be directly overhead at noon. The Tropic of Capricorn can be found at latitude 23.5 degrees south.
Due to the tilt of the Earth's axis, the sun's rays hit different latitudes at varying angles throughout the year, causing the changing seasons. When the sun's rays directly hit the tropic of Cancer, it causes the summer solstice in the Northern Hemisphere, marking the year's longest day.
Likewise, the southern hemisphere doesn't get the most of the sun's rays, which causes the winter solstice, marking the shortest day of the year.
Conversely, during the winter solstice, the sun's rays directly hit the Tropic of Capricorn, resulting in the shortest day of the year in the Northern Hemisphere. In the southern hemisphere, this marks the summer solstice, the year's longest day.
When does Equinox occur?
Equinoxes occur twice a year, around March 21st (the vernal or spring equinox) and around September 23rd (the autumnal equinox). During these times, day and night are nearly equal in length due to the Earth's equator aligning with the centre of the Sun.
Also Read: Types of Equinoxes: Importance, Dates, Seasonal Shifts, and Cultural Impact
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation