Just as the world started to recover from COVID-19, a new virus called human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is emerging. HMPV is a respiratory virus that can cause symptoms similar to other respiratory illnesses, such as the common cold, RSV, and pneumonia. Read below to learn more
What is Human Metapneumovirus?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) states “Discovered in 2001, HMPV is in the Pneumoviridae family along with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Broader use of molecular diagnostic testing has increased identification and awareness of HMPV as an important cause of upper and lower respiratory infection.”
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory virus that causes mild to severe illness in people of all ages. Although it is common with young children, the virus also affects older adults and people that have weak immune systems.
The CDC has mentioned that there has been a surge in the cases of HMPV and the reason is unknown. The percentage of positive cases for HMPV surged to a high of 19.6% for Antigen tests and 10.9% for PCR tests.
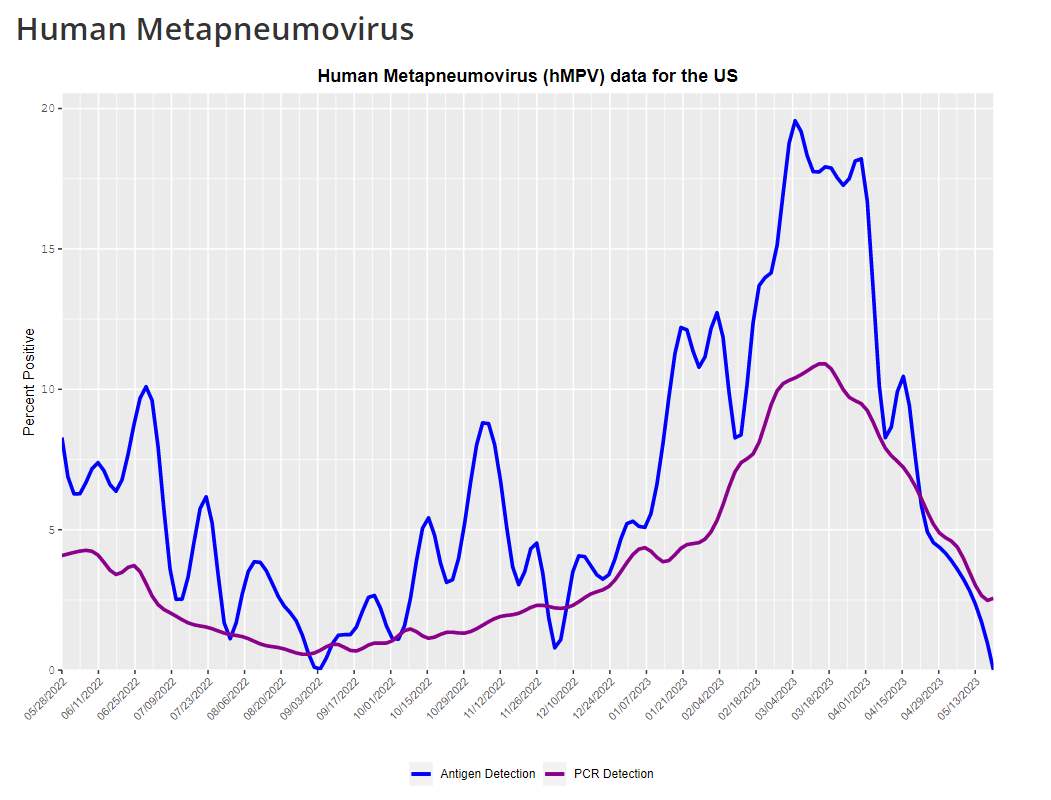 Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
CDC also mentioned that in the US, the outbreak of HMPV usually occurs during late fall, spring, and winter and it declines during the summer just like any normal flu or cold infection.
What are the Causes of Human Metapneumovirus?
HMPV can be spread through respiratory droplets that are produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Here are the causes of the spread of Human Metapneumovirus:
- Respiratory droplets: HMPV is spread through respiratory droplets that are produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes. These droplets can reach the mouth of people nearby.
- Contact with contaminated surfaces: HMPV can also be spread by touching a surface or object that has the virus on it and then touching your eyes, nose, or mouth.
The incubation period for HMPV is 3-7 days. This means that it will take 3-7 days to show symptoms if a person has been exposed to the virus.
There are certain cases where the HMPV infection can lead to major issues such as pneumonia or bronchitis. The CDC states “Clinical symptoms of HMPV infection may progress to bronchitis or pneumonia and are similar to other viruses that cause upper and lower respiratory infections.”
What are the Symptoms of Human Metapneumovirus?
The symptoms of this infection can vary from person to person depending on their age, and overall health. However, here are the common symptoms of HMPV:
Upper respiratory issues: HMPV usually shows symptoms just like a common cold that include a runny or stuffy nose, sore throat, and cough.
Cough: The cough can be persistent and may worsen over time.
Fever: Many individuals infected with HMPV develop a fever, although not everyone experiences this symptom.
Shortness of breath: The virus can cause breathing difficulty, especially in infants, young children, and older adults.
Fatigue: Feeling tired or experiencing a lack of energy is common during any respiratory infection, including HMPV.
Muscle aches: Some individuals infected with HMPV may experience muscle aches or body pains.
It is essential to know that these symptoms can resemble those of other respiratory viruses such as Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV).
The National Library of Medicine mentioned that “Adult patients with an HMPV infection might be asymptomatic or might have symptoms ranging from mild upper RTI symptoms to severe pneumonia.
“Most patients present with cough, nasal congestion and dyspnoea. Purulent cough, wheezing, sore throat, fever, pneumonia, bronchi(oli)tis, conjunctivitis and otitis media are other reported symptoms. Described a HMPV infection in an immunocompetent adult presenting as a mononucleosis-like illness.
“Adults with HMPV infection were less likely to report fever in contrast to adults with RSV or influenza infection. In addition, adults with an HMPV infection presented more often with wheezing compared to adults with RSV or influenza. Falsey et al. showed that this is mainly in the elderly population (>65 years).
“Elder patients also showed more dyspnoea compared to younger adults. Young adults with HMPV infection had greater complaints of hoarseness. In the frail elderly patients, the patients with pulmonary or cardiovascular disease and immunocompromised patients, infections can be severe.”
To conclude, Human Metapneumovirus is a common respiratory virus that can cause a range of symptoms that might go away on its own. To ensure safety from this virus, CDC recommends following basic hygiene tips such as washing hands frequently and maintaining appropriate distance from people who are sick.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation