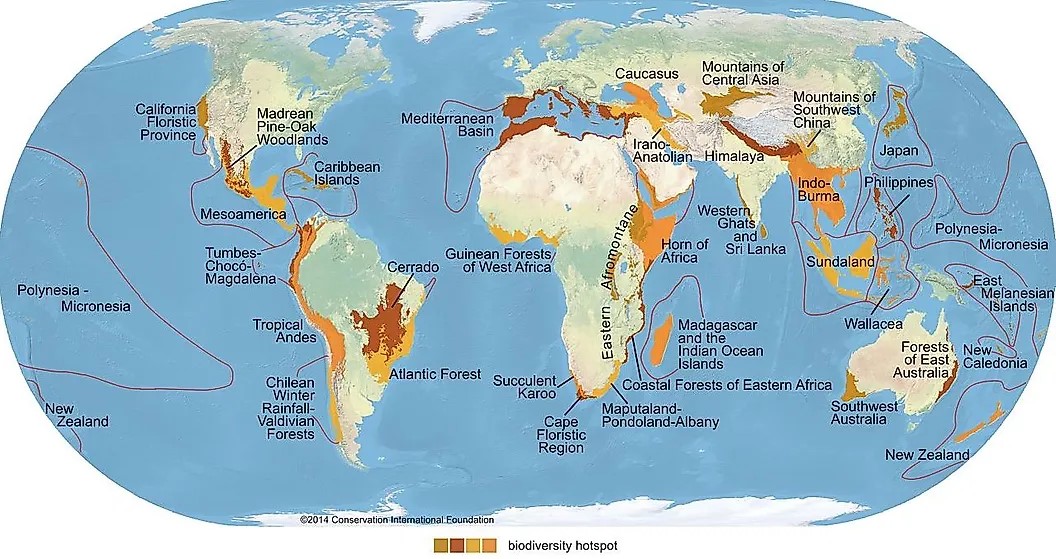
Biodiversity Hotspot are the biogeographic regions that have the most richest biodiversity also with the most threatened species of plants and animals life on the Earth. These regions play a very important and significant role in ecosystem are home to many endemic species that also provide crucial ecosystem services for the benefit of human.
According to CEPF, there are currently 36 recognized biodiversity hotspots, which occupied over 15.7%, which is about 23.7 million sq.km of the total Earth’s land area but due to anthropogenic activities, there is extreme habitat loss in these regions and as a results, currently, only 2.4% (about 3.4 million sq.km) is left of the total Earth’s land area.
Source: worldatlas
In this article, we will explore the list of Biodiversity Hotspot in the world
List of Biodiversity Hotspot in the world
| Rank | Name | Location |
| 1 | California Floristic Province | California, USA |
| 2 | Caribbean Islands | East of Central America |
| 3 | Madrean Pine-Oak Woodlands | Southern USA |
| 4 | Mesoamerica | Central Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, Nicaragua, and Northern Costa Rica |
| 5 | Atlantic Forest | Parts of Brazil, Argentina, and Paraguay |
| 6 | Cerrado | Central Brazil |
| 7 | Chilean Winter Rainfall-Valdivian Forests | Central northern Chile to Argentina’s western regions |
| 8 | Tumbes-Chocó-Magdalena | Pacific coast of South America and Galapagos Islands |
| 9 | Tropical Andes | Part of the Andes Mountains in South America |
| 10 | Caucasus | Border between Europe and Asia, separating Caspian and Black seas |
| 11 | Irano-Anatolian | Parts of Iran, Azerbaijan, Turkey, Armenia, Iraq, Turkmenistan |
| 12 | Mediterranean Basin | Surrounding the Mediterranean Sea |
| 13 | Mountains of Central Asia | Central Asia region including parts of Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, China, and Afghanistan |
| 14 | Cape Floristic Region | South Africa’s southern tip |
| 15 | Coastal Forests of Eastern Africa | Eastern coast of Africa |
| 16 | Eastern Afromontane | Mountainous parts of Eastern Africa |
| 17 | Guinean Forests of West Africa | Coastal West Africa |
| 18 | Horn of Africa | Northeastern Africa |
| 19 | Madagascar | Island of Madagascar in the southeast African coast |
| 20 | Indian Ocean Islands | Comoros, Seychelles, Mauritius |
| 21 | Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany | Southeastern coast of South Africa |
| 22 | Succulent Karoo | Coastal region of South Africa |
| 23 | Eastern Himalayas | Parts of India, China, Bhutan, Tibet, and Myanmar |
| 24 | Indo-Burma | Parts of India, Bangladesh, China, Myanmar, Cambodia, Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, and Malaysia |
| 25 | Western Ghats and Sri Lanka | Western part of the Indian Peninsula and country of Sri Lanka |
| 26 | East Melanesian Islands | Islands of Melanesia to the Northeast of Australia |
| 27 | New Caledonia | New Caledonia islands in Southwest Pacific Ocean |
| 28 | New Zealand | New Zealand islands in Southwest Pacific Ocean |
| 29 | Philippines | Philippines Southeast Asia |
| 30 | Polynesia-Micronesia | Islands in Southern Pacific Ocean |
| 31 | Southwest Australia | Southwest tip of Australia |
| 32 | Forests of East Australia | Eastern Australian coast |
| 33 | Sundaland | Parts of Southeast Asia including Borneo, Java, and Sumatra islands, the Malay Peninsula, and some small islands |
| 34 | Wallacea | Eastern Indonesia |
| 35 | Japan | Northern Pacific Ocean |
| 36 | Mountains of Southwest China | Tibet, parts of China and Myanmar |
Data Source: cepf
These regions support more than 152,000 (about 50%) of the global vascular plant species and 42% of all vertebrate species (amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals) as endemics. It has been estimated that about 3608 amphibians, 3723 reptiles, 3551 birds, and 1845 mammals are found as endemics in these hotspot regions.

The spectacular Jog Falls in the Western Ghats of Karnataka state of India.
Source: Shutterst
As per the Red List of Threatened Species that have been prepared by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN), more than 79% of the threatened amphibians, 63% of the threatened birds, and 60% of the threatened mammals can be found exclusively within these hotspots.
The current population data also shows that about 2.08 billion people reside in the hotspot regions and are dependent on these forest areas for their survival.
Conclusion
Biodiversity hotspots are vital regions supporting rich and unique species, many of which are endangered. Despite covering only 2.4% of Earth’s land, they sustain nearly half of all plant species and numerous vertebrates. Urgent conservation efforts are essential to preserve these ecosystems, ensuring ecological balance and human survival for future generations.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation