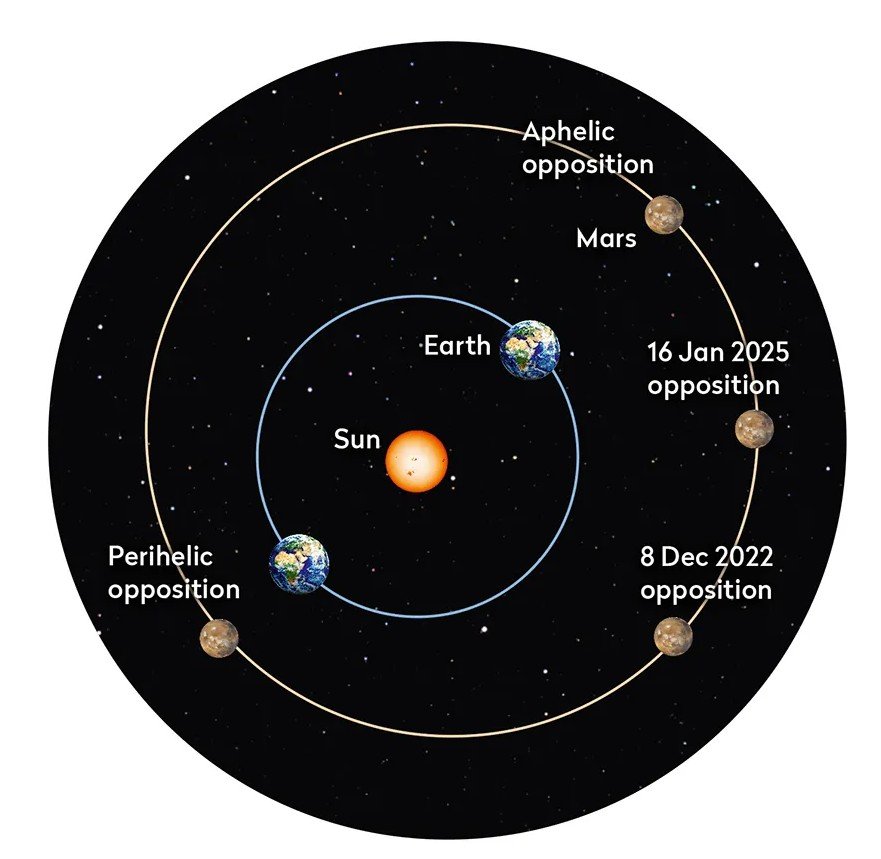
Did you know that Mars at opposition is a special time when Earth and Mars are closest? This happens when Earth passes directly between Mars and the Sun.
At this point, Mars appears larger and brighter in the night sky, making it an excellent time for stargazing. Mars at Opposition 2025 will occur on January 16th.
In this article, we'll take a look at the best times to view this spectacular event, discover essential viewing tips, and explore some fascinating facts about the Red Planet.
Check Out| Which planet in the solar system is known as the "Red Planet"? Find Out Now!
What is Mars At Opposition?
Source: BBC Sky at Night Magazine
When Mars is at opposition, it means that Earth is positioned directly between Mars and the Sun. This alignment occurs approximately every 26 months.
During this event, Mars is fully illuminated by sunlight, making it appear particularly bright and large in the night sky. This year the opposition will occur on January 16, 2025.
During this time, Mars will shine brightly in the constellation Gemini. Observers can see Mars rising in the east around sunset and setting in the west at sunrise. This phenomenon allows for exceptional viewing opportunities, especially through telescopes.
When is Mars at Opposition?
Mars will reach opposition on January 16, 2025. During this event, Mars will be directly opposite the Sun from Earth's perspective, making it particularly bright and visible throughout the night.
The peak visibility will occur around midnight local time, when Mars will be at its highest point in the sky.
Additionally, the closest approach of Mars to Earth happened a few days earlier, on January 12, 2025, when it was approximately 59.7 million miles away. Following this opposition, the next one is scheduled for February 19, 2027.
What Makes Mars Appear Larger During Opposition?
Mars appears larger during opposition, primarily due to its proximity to Earth and the alignment of the planets in the solar system. Here are the key factors that contribute to this phenomenon:
1. Proximity to Earth
Closest Approach: During opposition, Mars is positioned directly opposite the Sun from Earth's perspective, making it one of the closest points in its orbit.
This year, Mars reached its closest approach on January 12, just before the opposition on January 15, 2025. At this time, it is approximately 0.43 astronomical units (AU) away from Earth, which significantly enhances its visibility.
2. Full Illumination
Complete Illumination: At opposition, Mars is fully illuminated by the Sun. This means that the entire face of Mars is lit up, allowing for better observation of its surface features. The full illumination contributes to its brightness and makes it easier to see details through telescopes.
3. Angular Size
Increased Angular Diameter: The angular size of Mars at opposition can vary, but during this event, it measures about 14.6 arcseconds in diameter.
While this may seem small compared to other celestial objects, it is significantly larger than when Mars is farther away. For context, during a perihelic opposition (the closest type), Mars can appear as large as 24 arcseconds.
4. Visibility and Brightness
Brightness: Mars shines at a magnitude of -1.4 during this opposition, making it one of the brightest objects in the night sky, comparable to Sirius, the brightest star. This brightness is due to both its proximity and full illumination.
For You| Three Full Supermoons Are Coming Up in 2025! Here's When to See Them
How Often Does Mars Reach Opposition With Earth?
Mars reaches opposition approximately every 26 to 27 months. This event occurs when Earth is positioned directly between Mars and the Sun, allowing Mars to appear particularly bright and large in the night sky.
The next opposition will take place on January 15-16, 2025. Following this, the subsequent opposition is expected on February 19, 2027. While the general interval is around 26 months, some oppositions can be more closely spaced due to the elliptical nature of Mars's orbit.
For instance, "perihelic oppositions," which occur when Mars is near its closest point to the Sun, happen roughly every 15 to 17 years. These events provide even more spectacular views of the planet. The last notable perihelic opposition was in 2018, with the next one anticipated in 2033.
Best Locations and Times to View Mars at Opposition
Mars is currently in a prime position for observation as it approaches opposition, which occurs on January 16, 2025. Here are the best locations and times to view Mars during this event:
1. Key Dates for Viewing Mars
- Opposition Date: January 16, 2025, at 01:17 GMT (January 15, 20:17 EST).
- Best Viewing Window: From January 12 to January 16, when Mars will be at its brightest and closest to Earth.
- Lunar Occultation: On January 13, a full moon will briefly obscure Mars, providing a unique viewing opportunity.
2. Best Times to Observe Mars
- Evening: Mars will rise in the east at sunset and remain visible throughout the night.
- Peak Viewing: Around midnight, when Mars is highest in the sky.
- Visibility: Mars will shine brightly with a magnitude of -1.4, making it comparable to Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky.
3. Where to Spot Mars
- Location in the Sky: Look for Mars in the constellation Gemini, where it will appear as a bright red point of light.
4. Rising and Setting:
- Rises in the east at dusk
- Sets in the west around sunrise.
Discover| List of Astronomical Events 2025: Don’t Miss These 10 Amazing Upcoming Astronomical Events in India
9 Lesser-known Facts About Mars
Mars, often referred to as the "Red Planet," holds many intriguing secrets beyond its well-known characteristics. Here are seven lesser-known facts about this fascinating celestial body:
1) Olympus Mons: The Tallest Volcano
Mars is home to Olympus Mons, the largest volcano in the solar system, standing at approximately 21 kilometres (13 miles) high. This shield volcano is about 600 kilometres (373 miles) in diameter, making it nearly three times taller than Mount Everest.
2) Unique Blue Sunsets
Unlike Earth, where sunsets are typically red and orange, Mars experiences blue sunsets. This phenomenon occurs due to the planet's thin atmosphere and the scattering of sunlight by dust particles, which creates a distinct blue hue during sunset.
3) Potential for Rings in the Future
Mars has two small moons, Phobos and Deimos. Phobos is gradually spiralling inward towards Mars and is expected to crash into the planet within 40 million years, potentially forming a ring system around Mars.
4) Massive Global Dust Storms
Mars frequently experiences dust storms that can envelop the entire planet. These storms can last for days or even months, significantly affecting visibility and atmospheric conditions on the surface.
5) Valles Marineris: A Grand Canyon on Mars
The Valles Marineris canyon system on Mars is one of the largest canyons in the solar system, stretching over 4,000 kilometres (2,500 miles) and reaching depths of up to 8 kilometres (5 miles). This immense canyon dwarfs the Grand Canyon on Earth.
6) Mars' Atmosphere: Thin and Harsh
The Martian atmosphere is composed of about 96% carbon dioxide, with very little oxygen available for human survival. This thin atmosphere contributes to extreme temperature fluctuations and makes Mars a challenging environment for potential human colonisation.
7) Martian Days Are Slightly Longer Than Earth Days
A day on Mars, known as a "sol," is approximately 24.6 hours long, making it just a bit longer than an Earth day. This similarity could aid in future timekeeping for potential Mars missions.
8) The Surface Area of Mars Is Comparable to Earth's Landmass
Surprisingly, the total surface area of Mars is roughly equivalent to the land area of Earth, providing ample space for exploration and potential habitation.
9) Mars Experiences Extreme Temperature Fluctuations
Temperatures on Mars can vary dramatically, with highs reaching around 20°C at the equator during the day but plummeting to -140°C at the poles at night. This extreme range poses challenges for any future human presence.
What's Next| From New Moon to Full Moon: Understanding the 8 Moon Phases
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation