The Ministry of Commerce and Industry released the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) data for March on April 15, 2025. India’s wholesale inflation decreased to 2.05% in March, down from 2.38% in February 2025. The sharp decline was primarily driven by an increase in prices of the manufacture of food products, other manufacturing items, food articles, electricity, and textiles, said the Commerce Ministry in a press release.
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation also released the Consumer Price Index (CPI) data for March on April 15, 2025. As per the data, India’s retail inflation rate based on All India Consumer Price Index (CPI) for March 2025 over March 2024 is 3.34% (Provisional). It is the lowest year-on-year inflation after August 2019. Food inflation, measured through All India Consumer Food Price Index (CFPI), during March 2025 is mainly attributed to a decline in inflation of vegetables, eggs, pulses & products, meat & fish, cereals & products and milk & products.
Why is it important to understand WPI and CPI? Wholesale Price Index (WPI) and Consumer Price Index (CPI) are some of the important indices that give a fairly good idea as to what is happening in the economy. In this article, we will understand what is Wholesale Price Index (WPI), Consumer Price Index (CPI) and their key differences.
What is Wholesale Price Index (WPI)?
Wholesale Price Index (WPI) is an important tool to monitor the changes in prices at the wholesale level, i.e., goods sold in bulk and traded between businesses. WPI is widely recognized among business people, economists, statisticians, and accountants to understand price trends, formulate policies, and track wholesale inflation and input costs.
WPI is used as an important tool to measure inflation in India till April 2014, especially at the wholesale level. However, the RBI shifted to Consumer Price Index (CPI) as its key inflation measure.
Who releases WPI data?
The Office of the Economic Adviser in the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) under Ministry of Commerce and Industry releases the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) data on a monthly basis, usually on the 14th of each month. In case of a holiday on 14th, the data is released the next working day.
The Office published for the first time, the index number of wholesale prices, with base week ended August 19, 1939, from the week commencing January 10, 1942. Since 1947 the index is being published regularly. In 2017, the base year of All-India WPI was revised from 2004-05 to 2011-12.
How does WPI work?
The Wholesale Price Index (WPI) tracks the price movement of goods at the wholesale level, before they reach the retail market. It covers bulk transactions of goods between businesses and is compiled based on price quotations from wholesale markets across India.
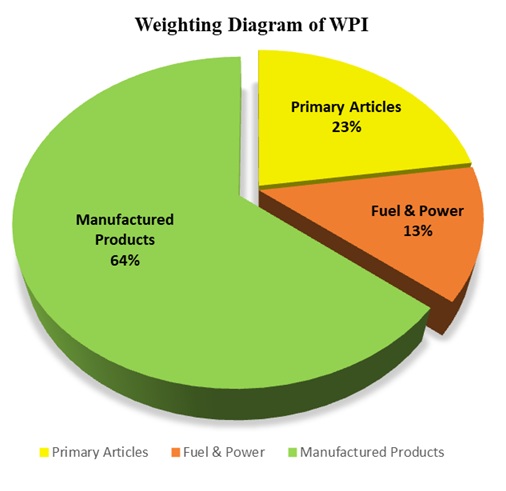
WPI is composed of three major groups:
- Primary articles (e.g., food, minerals) – about 22.6% weight
- Fuel and power – about 13.2% weight
- Manufactured products – about 64.2% weight
WPI excludes services and is less reflective of prices faced by consumers. It primarily influences business-level pricing, industrial contracts, and macroeconomic policy planning.
What is Consumer Price Index (CPI)?
Consumer Price Index (CPI) is designed to measure the changes over time in general level of retail prices of selected goods and services that households purchase for consumption. The CPI measures price changes by comparing, through time, the cost of a fixed basket of commodities.
CPI is widely used as a macroeconomic indicator of inflation. It is used as a tool by governments and central banks for inflation targeting and for monitoring price stability, and as deflators in the national accounts.
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) uses CPI data to control inflation. In April 2014, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had adopted the CPI as its key measure of inflation.
Who releases CPI data?
Four types of CPI are as follows: CPI for Industrial Workers (IW), CPI for Agricultural Labourer (AL), CPI for Rural Labourer (RL), and CPI (Rural/Urban/Combined).
Of these, the first three are compiled by the Labour Bureau in the Ministry of Labour and Employment, while CPI (Rural/Urban/Combined) is compiled by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
The Central Statistics Office (CSO) of the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation releases every month CPI for the entire rural population, viz. CPI (Rural), and CPI for the entire urban population, viz. CPI (Urban), which reflects the changes in the price levels of various goods and services consumed by the rural and urban population and also CPI (Combined).
The Office revised the base year of CPI from 2010 to 2012 with effect from the release of indices for January 2015.
How CPI Works?
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) measures the average change in prices paid by households for a basket of goods and services over time. It is more directly related to everyday consumer experiences and includes both goods and services, unlike WPI.
CPI is based on spending patterns of consumers in urban and rural India and consists of categories like:
- Food & beverages
- Clothing & footwear
- Housing
- Fuel & light
- Miscellaneous (healthcare, education, transport, etc.)
It is used as the primary inflation gauge by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) for setting interest rates and monetary policy.
Comparison Table: WPI vs. CPI
While both WPI and CPI aim to measure inflation, they differ significantly in terms of their level of measurement, coverage, and usage. Here’s how the two indices compare:
| Aspect | Wholesale Price Index (WPI) | Consumer Price Index (CPI) |
|---|---|---|
| Level of Measurement | Measures price changes at the wholesale level | Measures price changes at the retail level |
| Scope | Broad coverage including raw materials and bulk trade items | Narrower focus on goods and services commonly consumed by households |
| Items Covered | 697 items; Includes raw materials, intermediate goods, and manufactured products | 448 items (rural basket) and 460 (urban basket); Includes food, housing, clothing, healthcare, education, etc. |
| Purpose | Tracks inflationary trends among producers and businesses | Tracks the cost of living and purchasing power of consumers |
| Includes Services | No | Yes |
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between WPI and CPI is crucial for anyone interested in economics, public policy, or even personal finance. While both indices aim to measure inflation, they do so at different levels of the economy — wholesale vs. retail — and have different purposes and implications.
WPI provides insights into producer-level inflation and helps industries gauge price trends in the supply chain. CPI, on the other hand, reflects the cost of living and is used by the RBI to frame interest rate policies aimed at maintaining economic stability.
Keeping track of both helps us understand the broader picture of inflation and its impact on businesses, households, and government policy.
Also read: Difference Between Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation