Mixtures: Have you ever noticed the word ‘pure’ written on the packs of milk? For a layman, it means that it is not adulterated. However, in scientific terms, milk is actually a mixture of various substances. It is a mixture of fat, proteins etc. Look around and you will notice that most of the matter exists as mixtures of components.
What is a Mixture?
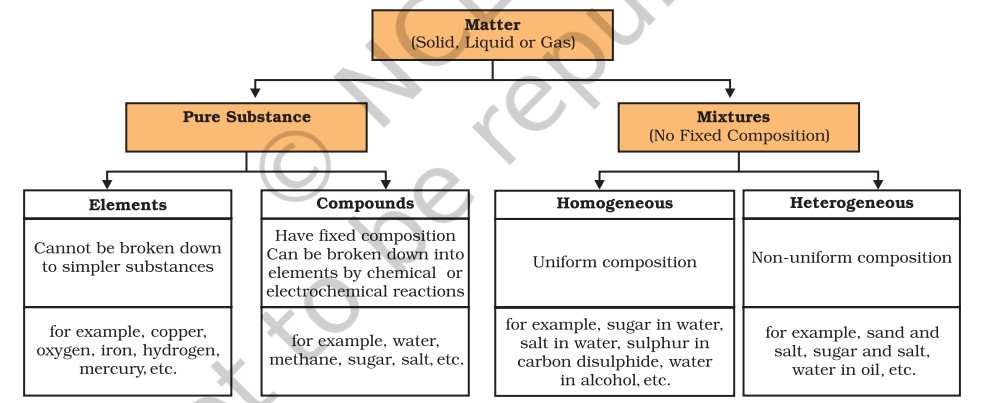
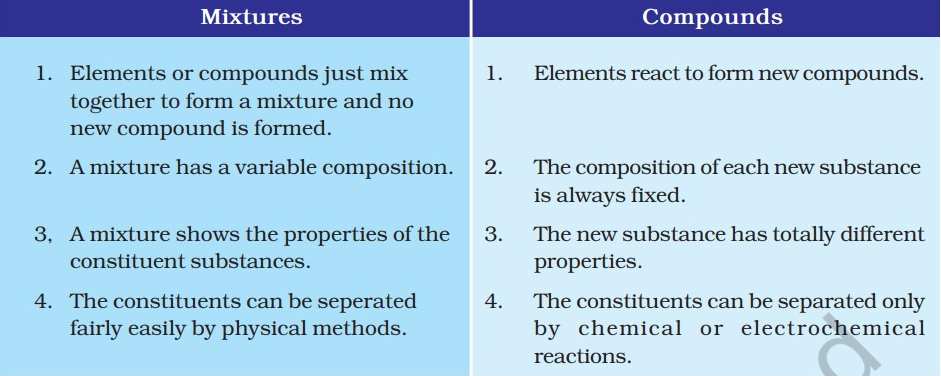
Put simply, the combination of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded is a mixture. Mixtures are constituted by more than one kind of pure form of matter. A mixture contains atoms or molecules which don't react chemically but are physically mixed together.
Also Check: CBSE Class 11 Science Video Courses
Types of Mixtures
Mixtures can be categorised into two broad types-homogeneous mixtures and heterogeneous mixtures.
Homogeneous mixture- A mixture which has a uniform composition throughout is a homogeneous mixture. It consists of a single phase. Examples of such mixtures are salt dissolved in water and sugar dissolved in water.
Heterogeneous mixture- A mixture which contains physically distinct parts and has non-uniform compositions is a heterogeneous mixture. It has two phases. Examples of such mixtures are mixtures of sodium chloride and iron filings, salt and sulphur.
Also Check: Heat Capacity: Specific Heat Capacity of Water, Molar Specific Heat Capacity And More
Characteristics of Mixtures
| Mixtures have variable compositions. Mixtures can be separated easily. They can be homogeneous or heterogeneous in nature. Components affect the properties of a mixture. A mixture’s aspects of boiling and melting point depend on its components. |
What are Elements?
Elements are basic forms of matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical reactions. They are categorised into metals, non-metals and metalloids. Metals have a lustre and conduct heat and electricity. They are malleable and sonorous. Examples of metals are gold, silver, copper, iron etc. Non-metals display a variety of colours and are poor conductors of heat and electricity. Examples of non-metals are hydrogen, oxygen, iodine etc. Metalloids have intermediate properties between those of metals and nonmetals. Some examples are boron and silicon.
What are Compounds?
A compound is a substance composed of two or more elements, chemically combined with one another in a fixed proportion.
Note: All images have been taken from NCERT Class 9 Science textbook.
Also, check
Pure and Mixed Substances: Definition, Characteristics and Example
Electronegativity: Meaning, Periodic Trends in Electronegativities of Elements And More
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation