Electronegativity: In the world of chemistry, electronegativity is often considered to be an important topic. As you might be already aware, periodic trends are observed in various aspects such as atomic sizes, electronegativity and valence. Simply defined, electronegativity is the measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons. Atoms with low electronegativity lose electrons, while atoms with high electronegativity gain electrons.
What is Electronegativity?
A qualitative measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract shared electrons to itself is called electronegativity. As per NCERT, it is not a measurable quantity and the electronegativity of any given element is not constant; it varies depending on the element to which it is bound.
Also Check: CBSE Class 12 Physics Video Tutorials
How is Electronegativity Measured?
There are several scales on which electronegativity is measured. However, the Pauling scale designed by American scientist Linus Pauling is the most commonly used scale.
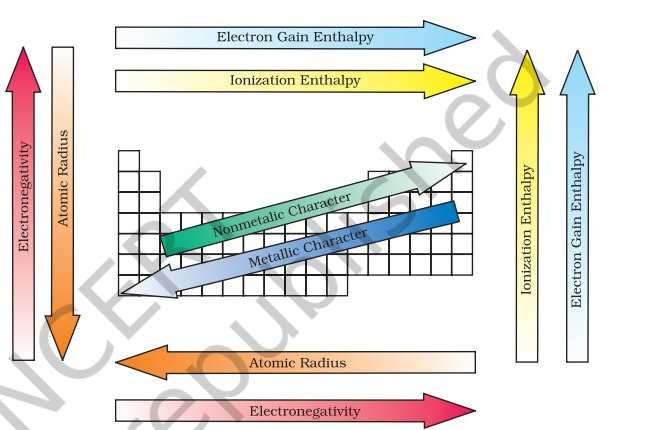
Periodic Trends in the Electronegativities of Elements
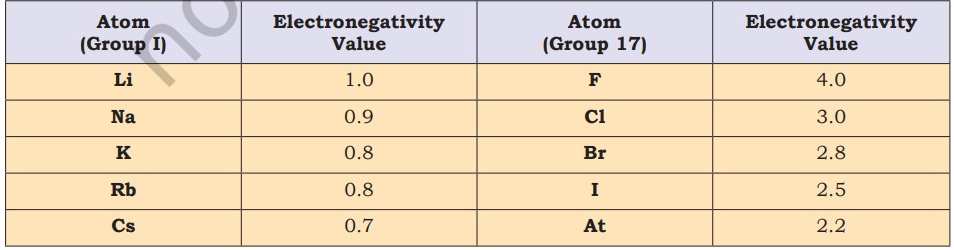
According to NCERT, electronegativity generally increases across a period from left to right like from lithium to fluorine) and decreases down a group (such as from fluorine to astatine) in the periodic table. The attraction between the outer (or valence) electrons and the nucleus increases as the atomic radius decreases in a period. Electronegativity also increases. On the same account electronegativity values decrease with the increase in atomic radii down a group. Non-metallic elements have a strong tendency to gain electrons. Therefore, electronegativity is directly related to the non-metallic properties of elements. Electronegativity is inversely related to the metallic properties of elements. Thus, the increase in electronegativities across a period is accompanied by an increase in non-metallic properties (or decrease in metallic properties) of elements. Similarly, the decrease in electronegativity down a group is accompanied by a decrease in non-metallic properties (or increase in metallic properties) of elements. Fluorine is the most electronegative element and cesium is the least electronegative element.
What is Covalent Bonding?
Covalent bonding is the process which occurs between two atoms with similar or identical electronegativity values. The atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to create a stable molecule. There are two types of covalent bonds: polar and nonpolar. In a polar covalent bond, the electrons are shared unequally between the two atoms while in a nonpolar covalent bond, the electrons are shared equally between the two atoms.
Also Check: CBSE Class 11 Science Video Courses
What are the Factors that Affect Electronegativity?
Nuclear charge- A higher nuclear charge results in a higher electronegativity value. This happens because an increase in nuclear charge leads to a stronger electron attraction.
Atom size- A greater atomic size results in decrease in electronegativity. The reason behind this is that electrons which are away from the nucleus experience less attraction.
Substituent effect- The electronegativity of an atom is influenced by the nature of the substituent attached to it. Thus substituents lead to change in an atom's electronegativity and chemical behavior.
Note: All images have been taken from NCERT Class 11 Chemistry Textbook.
Also, check
Pure and Mixed Substances: Definition, Characteristics and Example
Difference Between Cation and Anion: Definition, Characteristics and Example
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation