The difference between cation and anion mainly depends on the electrical charge of the ion. Furthermore, both cations and anions happen to be ions. Moreover, the ions are atoms or molecules that have either lost or gained one or multiple valence electrons.
Important difference between Cation and Anion
Parameter | Cation | Anion |
| Definition | A cation refers to an atom or a group of atoms that bear one or multiple positive electric charges. | An anion refers to an atom or a group of atoms that bear one or multiple negative electric charges. |
| Electric Charge | It has one positive charge or multiple positive charge | It has one negative charge or multiple negative charge |
| Electrons | The number of protons in cations is more than the number of electrons | The number of electrons in anions is more than the number of protons |
| Electric Field | Attraction of cations towards the negative terminal of an electric field | Attraction of cations towards the positive terminal of an electric field |
| Atoms | The formation of cations takes place from the metal atoms | Formation of cations takes place from the non-metal atoms |
Definition of Cation
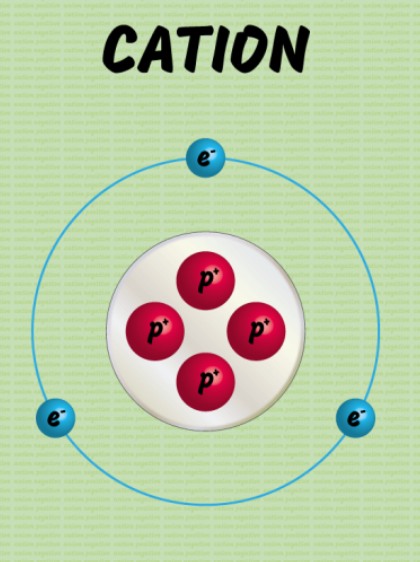
A cation refers to an ionic species that contains a positive charge. Therefore, there is a difference between cation and anion as the latter has a negative charge. Moreover, the number of protons in cation is more than the number of electrons.
Behavior and Characteristics:
- Charge: Cations have a positive charge due to an excess of protons compared to electrons.
- Size: Cations are generally smaller in size than their parent atoms because they lose electrons from their outermost shell, reducing the electron cloud's size.
- Chemical Reactivity: Cations exhibit specific chemical properties based on their charge and electronic structure. They often participate in reactions where they interact with anions (negatively charged ions) to form compounds.
Examples of Common Cations:
- Sodium ion (Na⁺): Found in table salt (NaCl) and essential for nerve function.
- Potassium ion (K⁺): Involved in muscle contraction and nerve signaling.
- Calcium ion (Ca²⁺): Essential for bone strength and many cellular processes.
- Magnesium ion (Mg²⁺): Found in chlorophyll and involved in enzyme reactions.
Importance: Understanding cations is crucial in various scientific disciplines, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science. Cations play essential roles in biological processes, such as cell signaling, muscle contraction, and nutrient absorption. In chemistry, they are central to the formation of ionic compounds, electrolysis processes, and the study of electrochemistry.
Definition of Anion
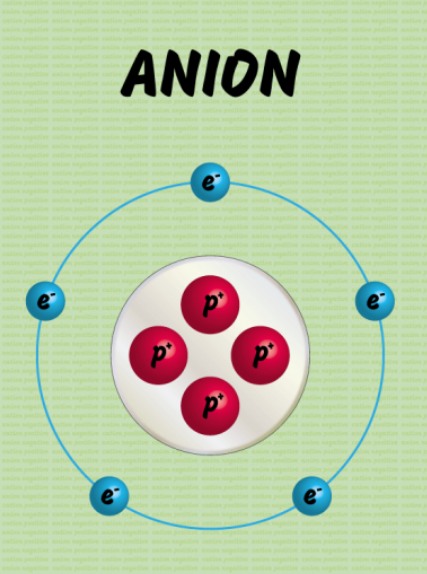
An anion refers to an ionic species that contains a negative charge. Anion is larger than cation due to it having extra electrons around it. This is another difference between cation and anion.
Behavior and Characteristics:
- Charge: Anions have a negative charge due to an excess of electrons compared to protons.
- Size: Anions are generally larger in size than their parent atoms because they gain electrons in their outermost shell, increasing the electron cloud's size.
- Chemical Reactivity: Anions exhibit specific chemical properties based on their charge and electronic structure. They often participate in reactions where they interact with cations (positively charged ions) to form compounds.
Examples of Common Anions:
- Chloride ion (Cl⁻): Found in table salt (NaCl) and various other compounds.
- Nitrate ion (NO₃⁻): Present in fertilizers and naturally occurring in soil.
- Sulfate ion (SO₄²⁻): Found in minerals and used in chemical industries.
- Carbonate ion (CO₃²⁻): Involved in the formation of limestone and coral reefs.
Importance: Understanding anions is crucial in various scientific disciplines, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science. Anions play essential roles in chemical reactions, particularly in ionic bonding, precipitation reactions, and electrolysis processes. They also influence biological processes such as cellular signaling and metabolism.
Related:
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation