118 Elements and Their Symbols and Atomic Numbers:The Periodic Table is a well-organized chart that contains all 118 known elements in the universe. These elements are the building blocks of matter, meaning everything around us is made up of them.
Each element in the periodic table has:
-
A unique symbol – a one or two-letter abbreviation used to represent the element.
-
An atomic number – the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of the element.
Check| Important Chemical Reactions for Class 12 Chemistry: Quick Revision for 2026 Board Exams
Check| CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Half Yearly Sample Paper 2025 with Solution, Download PDF
The Rules for Chemical Symbols
These rules help in identifying and writing chemical symbols consistently across all elements. The symbol serves as a shorthand notation for each element's name in formulas and equations, making communication more efficient and precise in the field of chemistry.
- The first letter of the chemical symbol of an element is always capitalized. Example: Carbon → C
- If the chemical symbol consists of more than one letter, any subsequent letters are lowercase. Example: Hydrogen → H, Helium → He
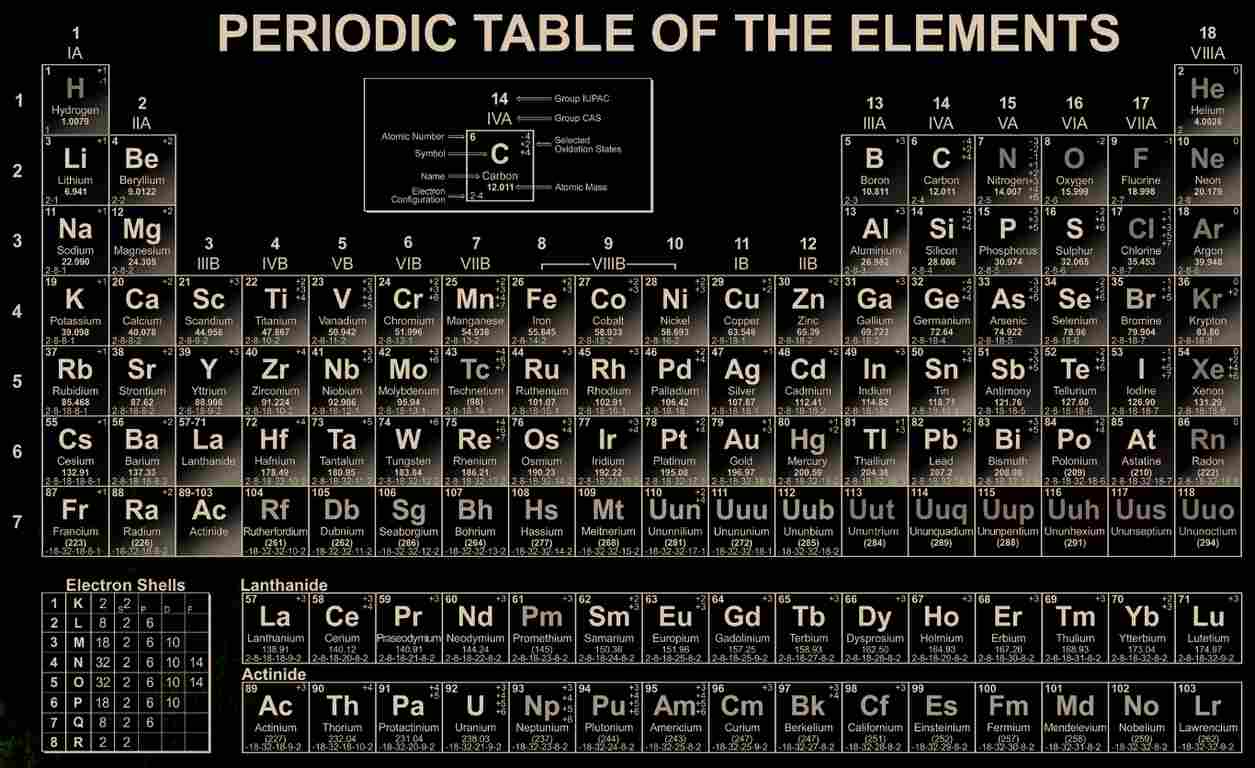
118 Elements and Their Symbols and Atomic Numbers
Here is a list of the 118 elements along with their symbols and atomic numbers:
- Hydrogen - H (Atomic number 1)
- Helium - He (Atomic number 2)
- Lithium - Li (Atomic number 3)
- Beryllium - Be (Atomic number 4)
- Boron - B (Atomic number 5)
- Carbon - C (Atomic number 6)
- Nitrogen - N (Atomic number 7)
- Oxygen - O (Atomic number 8)
- Fluorine - F (Atomic number 9)
- Neon - Ne (Atomic number 10)
- Sodium - Na (Atomic number 11)
- Magnesium - Mg (Atomic number 12)
- Aluminum - Al (Atomic number 13)
- Silicon - Si (Atomic number 14)
- Phosphorus - P (Atomic number 15)
- Sulfur - S (Atomic number 16)
- Chlorine - Cl (Atomic number 17)
- Argon - Ar (Atomic number 18)
- Potassium - K (Atomic number 19)
- Calcium - Ca (Atomic number 20)
- Scandium - Sc (Atomic number 21)
- Titanium - Ti (Atomic number 22)
- Vanadium - V (Atomic number 23)
- Chromium - Cr (Atomic number 24)
- Manganese - Mn (Atomic number 25)
- Iron - Fe (Atomic number 26)
- Cobalt - Co (Atomic number 27)
- Nickel - Ni (Atomic number 28)
- Copper - Cu (Atomic number 29)
- Zinc - Zn (Atomic number 30)
- Gallium - Ga (Atomic number 31)
- Germanium - Ge (Atomic number 32)
- Arsenic - As (Atomic number 33)
- Selenium - Se (Atomic number 34)
- Bromine - Br (Atomic number 35)
- Krypton - Kr (Atomic number 36)
- Rubidium - Rb (Atomic number 37)
- Strontium - Sr (Atomic number 38)
- Yttrium - Y (Atomic number 39)
- Zirconium - Zr (Atomic number 40)
- Niobium - Nb (Atomic number 41)
- Molybdenum - Mo (Atomic number 42)
- Technetium - Tc (Atomic number 43)
- Ruthenium - Ru (Atomic number 44)
- Rhodium - Rh (Atomic number 45)
- Palladium - Pd (Atomic number 46)
- Silver - Ag (Atomic number 47)
- Cadmium - Cd (Atomic number 48)
- Indium - In (Atomic number 49)
- Tin - Sn (Atomic number 50)
- Antimony - Sb (Atomic number 51)
- Tellurium - Te (Atomic number 52)
- Iodine - I (Atomic number 53)
- Xenon - Xe (Atomic number 54)
- Cesium - Cs (Atomic number 55)
- Barium - Ba (Atomic number 56)
- Lanthanum - La (Atomic number 57)
- Cerium - Ce (Atomic number 58)
- Praseodymium - Pr (Atomic number 59)
- Neodymium - Nd (Atomic number 60)
- Promethium - Pm (Atomic number 61)
- Samarium - Sm (Atomic number 62)
- Europium - Eu (Atomic number 63)
- Gadolinium - Gd (Atomic number 64)
- Terbium - Tb (Atomic number 65)
- Dysprosium - Dy (Atomic number 66)
- Holmium - Ho (Atomic number 67)
- Erbium - Er (Atomic number 68)
- Thulium - Tm (Atomic number 69)
- Ytterbium - Yb (Atomic number 70)
- Lutetium - Lu (Atomic number 71)
- Hafnium - Hf (Atomic number 72)
- Tantalum - Ta (Atomic number 73)
- Tungsten - W (Atomic number 74)
- Rhenium - Re (Atomic number 75)
- Osmium - Os (Atomic number 76)
- Iridium - Ir (Atomic number 77)
- Platinum - Pt (Atomic number 78)
- Gold - Au (Atomic number 79)
- Mercury - Hg (Atomic number 80)
- Thallium - Tl (Atomic number 81)
- Lead - Pb (Atomic number 82)
- Bismuth - Bi (Atomic number 83)
- Polonium - Po (Atomic number 84)
- Astatine - At (Atomic number 85)
- Radon - Rn (Atomic number 86)
- Francium - Fr (Atomic number 87)
- Radium - Ra (Atomic number 88)
- Actinium - Ac (Atomic number 89)
- Thorium - Th (Atomic number 90)
- Protactinium - Pa (Atomic number 91)
- Uranium - U (Atomic number 92)
- Neptunium - Np (Atomic number 93)
- Plutonium - Pu (Atomic number 94)
- Americium - Am (Atomic number 95)
- Curium - Cm (Atomic number 96)
- Berkelium - Bk (Atomic number 97)
- Californium - Cf (Atomic number 98)
- Einsteinium - Es (Atomic number 99)
- Fermium - Fm (Atomic number 100)
- Mendelevium - Md (Atomic number 101)
- Nobelium - No (Atomic number 102)
- Lawrencium - Lr (Atomic number 103)
- Rutherfordium - Rf (Atomic number 104)
- Dubnium - Db (Atomic number 105)
- Seaborgium - Sg (Atomic number 106)
- Bohrium - Bh (Atomic number 107)
- Hassium - Hs (Atomic number 108)
- Meitnerium - Mt (Atomic number 109)
- Darmstadtium - Ds (Atomic number 110)
- Roentgenium - Rg (Atomic number 111)
- Copernicium - Cn (Atomic number 112)
- Nihonium - Nh (Atomic number 113)
- Flerovium - Fl (Atomic number 114)
- Moscovium - Mc (Atomic number 115)
- Livermorium - Lv (Atomic number 116)
- Tennessine - Ts (Atomic number 117)
- Oganesson - Og (Atomic number 118)
These elements are organized in the periodic table based on their atomic numbers, which increase sequentially from 1 (Hydrogen) to 118 (Oganesson). Each element has unique chemical properties and is fundamental to understanding the composition and behavior of matter in the universe.
The periodic table that we follow for our studies is the Modern Periodic Table, which is based on atomic number rather than atomic mass. This arrangement was established by the British physicist Henry Moseley in 1913, who discovered that the atomic number (the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom) is the fundamental property that determines an element's position in the periodic table, rather than its atomic mass.
Mnemonics for Periodic Table
Here are some popular mnemonics to help you remember the first 20 elements of the periodic table:
For the first 20 elements:
H - Hydrogen
He - Helium
Li - Lithium
Be - Beryllium
B - Boron
C - Carbon
N - Nitrogen
O - Oxygen
F - Fluorine
Ne - Neon
Na - Sodium
Mg - Magnesium
Al - Aluminum
Si - Silicon
P - Phosphorus
S - Sulfur
Cl - Chlorine
Ar - Argon
K - Potassium
Ca - Calcium
Mnemonic: "Happy Harry Hates Being Bored. Could Not Obtain Free, Nice, Magical Apples. Silly People Should Consider All Kinds."
For remembering groups like Alkali Metals (Group 1):
Li - Lithium
Na - Sodium
K - Potassium
Rb - Rubidium
Cs - Cesium
Fr - Francium
Mnemonic: "Little Naughty Kids Rub Cute Frogs."
For remembering the Noble Gases (Group 18):
He - Helium
Ne - Neon
Ar - Argon
Kr - Krypton
Xe - Xenon
Rn - Radon
Mnemonic: "He Never Arrives, Krypton Xpects Really New."
For remembering Halogens (Group 17):
F - Fluorine
Cl - Chlorine
Br - Bromine
I - Iodine
At - Astatine
Mnemonic: "Foolish Clowns Bring In Apples."
Key Features of the Modern Periodic Table:
- Arranged by Atomic Number: Elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number (number of protons) across periods (rows) and groups (columns).
- Periods: There are 7 periods (rows) in the table. Each period represents a new energy level (shell) being filled with electrons.
- Groups: There are 18 groups (columns). Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons.
- Metals, Non-metals, and Metalloids: The table is divided into metals, non-metals, and metalloids (elements with properties in between metals and non-metals). Metals are on the left side, non-metals are on the right side, and metalloids are along a zig-zag line.
- Block Structure: The periodic table is divided into s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block elements, based on the electronic configurations of the elements.
- Lanthanides and Actinides: The elements in the f-block are known as the lanthanides (rare earth elements) and actinides (many of which are radioactive), and they are typically placed below the main body of the table to keep it more compact.
The modern periodic table allows us to understand the relationships between elements and their properties, and also to predict the behavior of new or undiscovered elements, and classify elements into categories based on their electronic configurations and chemical reactivity. This version of the table is widely used in chemistry and other sciences today.
Related:
Also Check:
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation