A homogeneous mixture is also known as a solution. It is a substance composed of two or more substances that are distributed uniformly at a molecular level or microscopic. In easier terms, homogeneous mixture components are distributed completely into the mixture and are difficult to distinguish from each other. Basically, mixtures can be classified into two: Homogeneous and Heterogeneous mixture.
What is a homogeneous mixture?
A Homogeneous mixture, whether it exists as a liquid, solid and gas. It maintains a consistent proportion of its compounds throughout the mixture. This uniformity ensures that the mixture appears uniform and seamless, showing only one phase of matter throughout its entirety.

Image Source: Quora
Also Read:
Quantum Numbers: Principal Quantum Number, Azimuthal, Magnetic And Electron Spin Quantum Number!
Examples of Homogeneous Mixture
- Liquid Solutions: Such as salt dissolved in water (saltwater), sugar dissolved in water (sugar water).
- Gas Mixtures: Air is considered a homogeneous mixture of gases (mainly nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, etc.).
- Alloys: Homogeneous mixtures of metals, like brass (copper and zinc), and steel (iron and carbon)
Important Terms to Know:
- Solutions
- Suspension
- Colloids
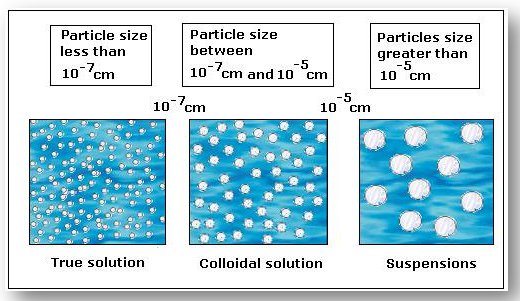
Image Source: Quora
Read: Atomic Mass of Elements
Solutions
Salt or sugar dissolved in water is a perfect example of a solution. The particles are less than 2 x 10-9 m in size. They are so tiny that you cannot differentiate between the solute and the solvent.
Suspension
The particles here are greater than 5 x 10-7 m in size, which means that the person can see the particles with the naked eye. Fine sand mixed in water is a basic example of a suspension. Over the period of time, the particles tend to settle (or float) and have to be mixed again to restore the suspended state.
Colloids
Colloids are the ones whose particle sizes range from 2 x 10-9 m to 5 x 10-7 m. The particles are sufficiently small to remain evenly distributed without settling or floating due to gravitational force. The stability is maintained due to intermolecular force within colloids. They are strong enough to overcome the tendency of particles to separate or aggregate.
Related:
118 Elements and Their Symbols and Atomic Numbers
What Is Enthalpy: Definition, Importance And Applications!
Now, that the concept is covered, we are also providing the video links for students to learn the concepts easily.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation