Rising temperatures on Earth are driving climate change. Methane and carbon dioxide, among other gases, help to cause this warming.
These gases keep heat from escaping from the atmosphere. Burning gas, oil, and coal mostly produces them. Additionally compounding the issue is deforestation.
We observe major alterations as the earth warms. The Arctic is melting ice. Rising sea levels are happening. The weather is getting more severe.
While some regions suffer protracted droughts, others get too much rain. Plants and animals find it hard to live in fresh settings. Floods, heat waves, and food shortages also have an impact on people.
In this article, we will examine the facts behind climate change. We will look at how greenhouse gases work, what researchers have found, and how human actions aggravate the problem.
What is Climate Change?

Source:The Weather Guys
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns, primarily driven by human activities.
Key Concepts:
1. Greenhouse Gases:
- Naturally occurring gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO₂) and methane, trap heat in the atmosphere.
- Human activities, especially the burning of fossil fuels, have significantly increased the concentration of these gases.
2. Human Contributions:
- Fossil Fuel Combustion: The burning of coal, oil, and natural gas for energy is the largest source of CO₂ emissions.
- Deforestation: Trees absorb CO₂; cutting them down reduces this natural carbon sink.
- Agricultural Practices: Livestock and certain fertilisers release methane and nitrous oxide, which are more potent greenhouse gases than CO₂.
Observed Effects:
1. Temperature Rise:
- Global temperatures have increased, with the last decade being the warmest on record.
- Heatwaves are becoming more frequent and severe.
2. Extreme Weather Events:
- Increased intensity and frequency of storms, floods, and droughts.
- Changes in precipitation patterns lead to water scarcity in some regions.
- Melting Ice and Rising Sea Levels:
- Glaciers and polar ice caps are melting, contributing to rising sea levels.
- Coastal areas face increased flooding and erosion.
What is the Science Behind Climate Change
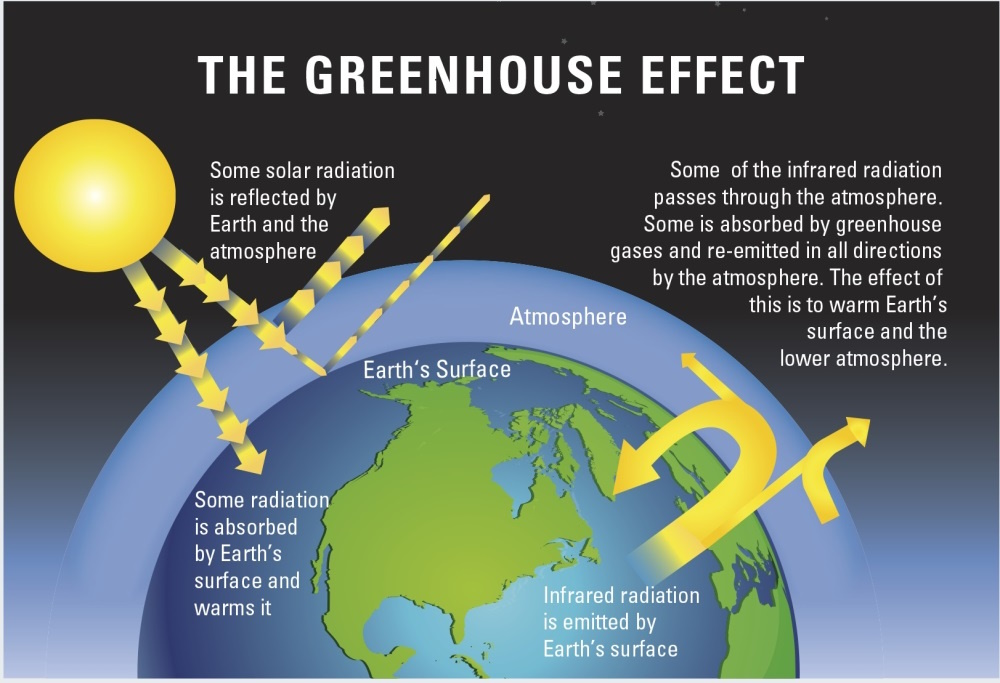
Source: Royal Society
The science behind climate change involves understanding how the Earth's climate system works and how human activities are altering it. Here's a structured overview:
1. The Earth's Climate System
- Components: The climate system includes the atmosphere, oceans, land surface, and ice. These components interact with each other and influence the Earth's climate.
- Energy Balance: The Earth receives energy from the sun, which is absorbed, reflected, or re-radiated. The balance between incoming solar energy and outgoing heat determines the planet's temperature.
2. Greenhouse Effect
Natural Process: The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon where certain gases in the atmosphere trap heat, keeping the Earth warm enough to support life.
Greenhouse Gases: Key greenhouse gases include:
-
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Released from burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and other human activities.
- Methane (CH₄): Emitted during the production and transport of coal, oil, and natural gas, as well as from livestock and other agricultural practices.
- Nitrous Oxide (N₂O): Released from agricultural and industrial activities, as well as during the combustion of fossil fuels and solid waste.
3. Human Contributions to Climate Change
- Fossil Fuel Combustion: The burning of coal, oil, and natural gas for energy is the largest source of CO₂ emissions.
- Deforestation: Cutting down forests reduces the number of trees that can absorb CO₂, increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Agricultural Practices: Certain farming practices release significant amounts of methane and nitrous oxide, contributing to climate change.
4. Evidence of Climate Change
- Rising Temperatures: Global average temperatures have increased significantly over the past century, with the last few decades being the warmest on record.
- Melting Ice: Glaciers and polar ice caps are melting, contributing to the rise in sea levels.
- Extreme Weather: The increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and heat waves, are linked to climate change.
5. Impacts of Climate Change
- Ecosystems: Climate changes affect biodiversity, leading to habitat loss and species extinction.
- Human Health: Climate change can exacerbate existing health problems, increase the incidence of heat-related illnesses, and facilitate the spread of diseases.
- Economy: Agriculture, fisheries, and tourism are impacted by changing climate conditions, resulting in economic challenges.
6. Mitigation and Adaptation
- Mitigation: Efforts to reduce or prevent the emission of greenhouse gases, such as transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and reforestation.
- Adaptation: Strategies to cope with the effects of climate change, such as building resilient infrastructure, developing drought-resistant crops, and improving water management.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation