Satellites are man-made artificial objects that orbit around other celestial bodies in space, playing a crucial role in communication, navigation, weather forecasting, and scientific research. The concept of artificial satellites was first proposed by Sir Isaac Newton in the 17th century.
The first successful artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, was launched by the Soviet Union on October 4, 1957, marking the beginning of the space age. Since then, thousands of satellites have been developed and deployed, revolutionizing various fields and enabling advancements in technology, exploration, and global connectivity.
Named after the renowned Indian astronomer, the Aryabhata spacecraft was India's first satellite. Entirely designed and built in India, it was launched aboard a Soviet Kosmos-3M rocket from Kapustin Yar on April 19, 1975.
Also read: National Space Day: India’s Space Achievements Timeline (1962 – 2024)
What is a Satellite?
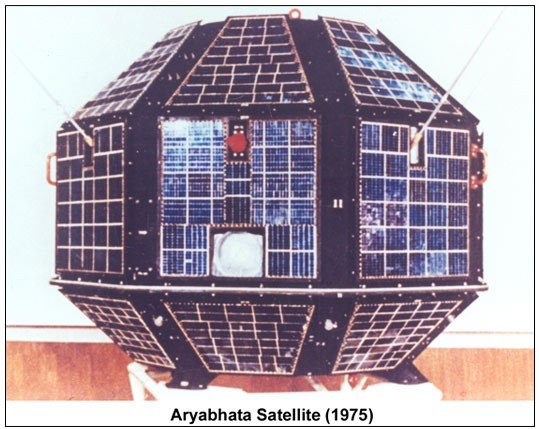
India's first satellite, Aryabhata; Image: U R Rao Satellite Centre
A satellite is an object that revolves around another object in space. Satellites are categorized into two types: natural and artificial. Natural satellites, such as the Earth and the Moon, are celestial bodies that naturally orbit larger objects; for example, the Earth orbits the Sun, and the Moon orbits Earth.
Artificial satellites, on the other hand, are machines launched into space to orbit a celestial body. Examples of artificial satellites include the Hubble Space Telescope and the International Space Station, both of which are designed to perform specific tasks while orbiting the Earth.
Also read: Types of Orbits and their applications
Types of Satellites
Space-based technology extends far beyond just providing communication and television services. In recent years, satellites have been launched for a diverse array of scientific purposes. These include Earth observation, meteorological studies, navigation, examining the effects of spaceflight on living organisms, and exploring the cosmos. Today, the most prevalent types of satellites, categorised by their functions, are:
- Communication Satellites
- Earth Observation Satellites
- Navigation Satellites
- Astronomical Satellites
Below, we delve deeper into the characteristics and functions of these various satellite types.
Communication Satellites
A communication satellite, typically positioned in Geostationary Orbit (GEO) and Low Earth Orbit (LEO), is equipped with a transponder — a combined receiver and transmitter of radio signals — that can receive signals from Earth and send them back to the planet. This functionality establishes communication links between regions that were previously isolated due to vast distances or other barriers. These communication satellites support a range of media transmissions, including radio, television, telephone, and Internet services.
Orbit of Communication Satellites
Communication satellites are mostly placed in the GEO or LEO due to their functionality.
Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO): Communication satellites are typically positioned in GEO, approximately 35,786 kilometres above the Earth's surface. This orbit is favoured for telecommunications and broadcasting due to its minimal interference and stable position relative to the Earth. GEO satellites offer several advantages, including extensive coverage areas, consistent bandwidth, and efficient power usage. For instance, the GSAT series by ISRO operates in GEO to provide various telecommunication services such as broadcasting and internet connectivity. However, a notable drawback of GEO satellites is their high latency, which can affect real-time communication.
Low Earth Orbit (LEO): Satellites in Low Earth Orbit, ranging from 160 to 1,000 kilometres above the Earth's surface, benefit from lower latency and increased bandwidth, facilitating faster data transmission. This makes LEO a preferred choice for deploying satellite constellations designed for high-speed internet services. For example, SpaceX's Starlink project utilizes a constellation of over 4,200 satellites positioned at approximately 550 kilometres in LEO to deliver high-speed internet across the globe.
Applications of Communication Satellites
Indian National Satellite (INSAT) System: The INSAT system is one of the largest communication satellite networks in the Asia-Pacific region. It supports a wide range of communication and broadcasting services across India.
Meteorology: Satellites equipped with transponders such as C-band, Extended C-band, and Ku-band play a crucial role in meteorology. They provide essential services including weather forecasting, disaster warnings, and search and rescue operations.
High-Speed Internet Services: Contemporary communication satellites are now offering high-speed internet services, providing fast and reliable connectivity for various applications.
Also read: Science Quiz On Space Debris With Answers
Earth Observation Satellites
Earth observation satellites are crucial for monitoring our planet from space, providing valuable data on environmental changes and aiding in rapid response during emergencies such as natural disasters and conflicts. These satellites enable consistent and repeatable monitoring of the Earth's surface and atmosphere. Examples of different Earth observation satellites include ISRO’s CARTOSAT series, OCEANSAT, EOS-04, ESA’s EUMETSTAT, etc.
Earth Observation satellites are categorised into the following types:
Weather Satellites: These satellites are used for tracking and forecasting weather patterns. Positioned primarily in geostationary orbits (GEO), they offer a continuous view of the Earth, allowing scientists to monitor cloud formation, track weather systems, and predict changes with high accuracy.
Remote Sensing Satellites: These satellites aid in detecting and monitoring the physical characteristics of an area by measuring its reflected and emitted radiation at a distance. Remote sensing satellites orbit the Earth in different paths—polar, non-polar low Earth orbit (LEO), or GEO—depending on their specific functions. Among these, Geographical Information System (GIS) satellites are a subset of remote sensing satellites, providing high-resolution images used for GIS mapping and spatial analysis.
Orbit of Earth Observation Satellites
Earth observation satellites often utilize a synchronous sub-recurrent orbit, a specialized type of polar orbit. This orbit combines elements of both a sun-synchronous orbit and a sub-recurrent orbit.
Sun-Synchronous Orbit: In this orbit, the satellite's orbit plane maintains a constant angle relative to the Sun as observed from the Earth, ensuring that the satellite passes over the same region at the same local solar time consistently.
Sub-Recurrent Orbit: This orbit allows the satellite to revisit the same location on the Earth's surface at fixed intervals, maintaining the same local solar time.
The synchronous sub-recurrent orbit enables satellites to observe the same region at regular intervals, as the angle of sunlight incident on the Earth's surface remains nearly constant.
Applications of Earth Observation Satellites
Based on the sensors onboard Earth observation satellites, these provide data in diversified spatial, spectral and temporal resolutions. As per ISRO, the data from these satellites are used for agriculture, water resources, urban planning, rural development, mineral prospecting, environment, forestry, ocean resources and disaster management.
As per JAXA, the data from Earth observation satellites is also utilised for aerosol forecast, studying greenhouse gas emissions, typhoon and rainfall updates, marine pollution, drift ice situation, sea surface temperature and phytoplankton density, earthquake, inundated area caused by flood and tsunami, volcano activity, deforestation, land use, vegetation, topography, and land surface temperature.
Also read: What is Space Junk (Debris) and why is it a global threat?
Navigation Satellites
Navigation system constellations are positioned at altitudes between 20,000 and 37,000 kilometres above the Earth’s surface. These satellites transmit signals that provide information about their time, spatial position, and operational status. There are two primary types of space-based navigation systems:
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) consist of satellites that transmit signals, which are received and used by GNSS receivers for geolocation, offering global coverage. Prominent GNSS systems include GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (Europe), and BeiDou (China).
Regional Navigation Satellite Systems (RNSS), on the other hand, are autonomous systems designed to provide navigation services over a specific region.
Orbit of Navigational Satellite
Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) hosts GPS satellites positioned at an altitude of around 20,200 km.
Geostationary and geosynchronous orbits are key components of NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation), which comprises a constellation of seven satellites. Three of these satellites are situated in geostationary orbit, while the remaining four are placed in inclined geosynchronous orbit.
Applications of Navigation Satellites
To meet the positioning, navigation and timing requirements of the nation, ISRO has established a regional navigation satellite system called Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC). NavIC was erstwhile known as the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), as per ISRO.
Also read: What Is Thirty Meter Telescope? Know India’s Role In It
Astronomical Satellites
An astronomical satellite is essentially a giant telescope in orbit, offering a clear view without interference from the Earth's atmosphere. Its infrared imaging technology operates effectively, unaffected by the planet's surface temperature. This type of satellite provides vision that is up to ten times sharper than even the most powerful ground-based telescopes.
The Hubble Space Telescope is an example of an astronomy satellite positioned in low Earth orbit.
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) stands as the largest and most powerful telescope to date, designed to observe distant regions of the universe.
AstroSat, India's first dedicated astronomy mission, is a space telescope focused on studying celestial objects across X-ray, optical, and UV spectral bands simultaneously.
Applications of Astronomical Satellites
Astronomy satellites are utilized to explore various celestial bodies and phenomena in space, ranging from creating star and planetary surface maps to capturing images of planets in our solar system and studying black holes.
Climate research satellites, equipped with specialized sensors, enable scientists to collect extensive, multifaceted data on Earth's oceans, ice, land, biosphere, and atmosphere.
Biosatellites facilitate space-based research on plant and animal cells and structures, playing a vital role in advancing medicine and biology by enabling collaboration among scientists worldwide.
Also read: Why Are There Stones On Railway Tracks?
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation