Budget 2025 Summary: The Union Budget is released by the Finance Minister on February 1, 2025, in the Parliament. The government's plan for the next fiscal year is laid out in the budget. The budget provides a general road map for the government's revenue and expenditure strategy.
Candidates preparing for UPSC or any other government exam must not miss the key highlights of Budget 2025. The budget is prepared by the Department of Economic Affairs (DEA), Ministry of Finance and has two components, such as the revenue budget and the capital budget. It will provide essential information about the government’s financial planning, tax policies, and reforms.
Income Tax has been revised to Rs 12 lakh, and there will be no in tax upto Rs 12 Lakh
Budget 2025 Summary, Key Takeways for UPSC and Other Sarkari Exams
Budget 2025 focused on youth, women, and farmers. The Finance Minister mentioned this budget continues government efforts to a) accelerate growth b) secure inclusive development c) invigorate private sector investments d) uplift household sentiments e) enhance spending power of India’s rising middle class.
The Economic Survey, which was presented a day before the budget, highlights the point that despite the global instability, the economy of India will remain stable between 6.3% and 6.8%, The unemployment rate of the country remains declines to 3.2%. Continue reading this article for key highlights for Budget 2025
The budget 2025 focused on
- Furthering Make In India
- Supporting MSMEs
- Enabling employment-led development
- Investing in people economy and innovation
- Securing energy supplies
- Supporting exports
- Nurturing innovation
The government will launch the Export Support Mission with sectoral and ministerial targets. The mission will be driven jointly by the ministries of commerce, MSMEs, and finance. The Export Support Mission will facilitate easy access to export credit, cross-border factoring support, and support to MSMEs to tackle non-tariff measures in overseas markets
The Personal Income Tax slab has been revised and now up to 12 lakh there will be no tax. Check the table below for updated tax regimes
| Annual Income | Tax rate |
| Rs 0-4 lakh | NIL |
| Rs 4-8 lakh | 5 percent |
| Rs 8-12 lakh | 10 percent |
| Rs 12-16 lakh | 15 percent |
| Rs 16-20 lakh | 20 percent |
| Rs 20-24 lakh | 25 percent |
| Above Rs 24 lakh | 30 percent |
Jal Jeevan Mission: To achieve 100 % coverage, the mission extended till 2028 with an enhanced total outlay
Asset Monetization Plan 2025-30: launched to plough back capital of ₹ 10 lakh crore in new projects
Check the table below for major expenditures planned.
| Major Items |
Expenditure (₹ Crore) |
| Defence | 4,91,732 |
| Rural Development | 2,66,817 |
| Home Affairs | 2,33,211 |
| Agriculture and Allied Activities | 1,71,437 |
| Education | 1,28,650 |
| Health | 98,311 |
| Urban Development | 96,777 |
| IT and Telecom | 95,298 |
| Energy | 81,174 |
| Commerce & Industry | 65,553 |
| Social Welfare | 60,052 |
| Scientific Departments | 55,679 |
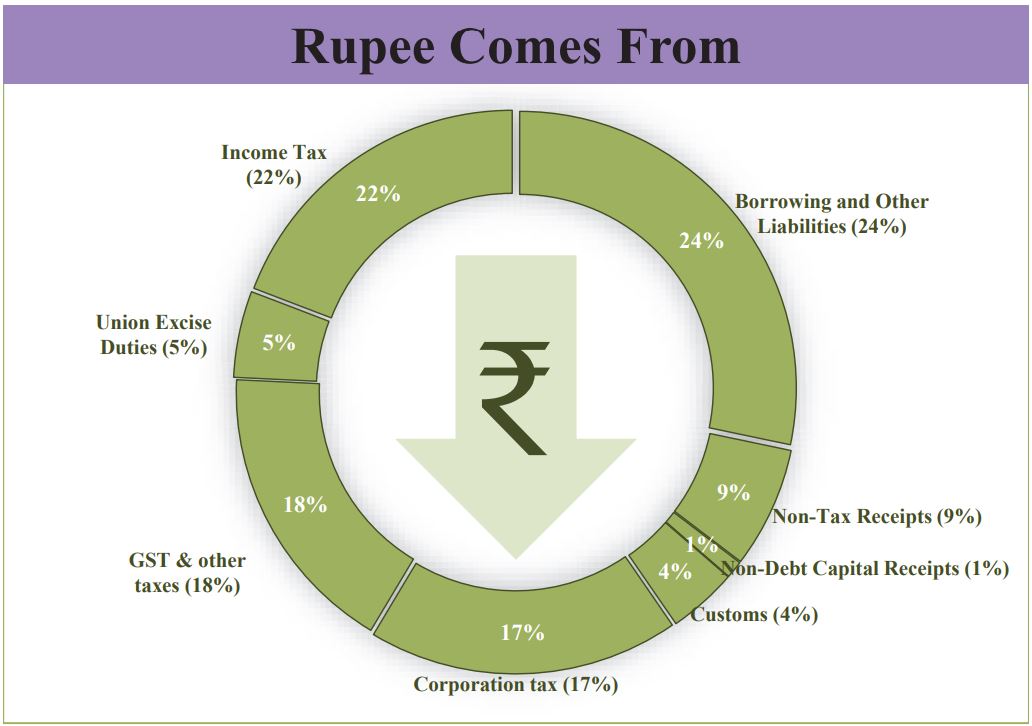
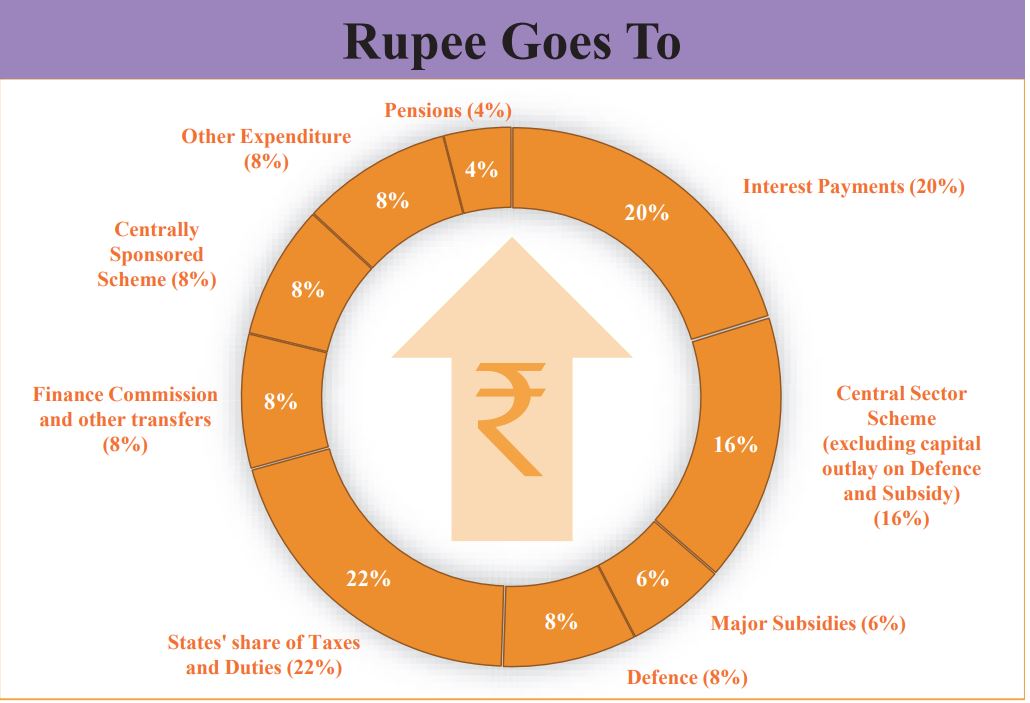
Check the chart below to know about form where government will earn money and where its is going to invest
Also Check,
| UPSC and State PCS Ancient History Questions |
|
| Top YouTube Channel for UPSC |
|
| UPSC Strategic Preparation Guide | UPSC IAS Syllabus 2025 |
| NCERT Books for UPSC Preparation | IAS Officer Salary |
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation