Key Points
- CBSE Class 10 Science Exam held on Feb 20, 2025.
- Answer key helps estimate scores and identify weak areas.
- Question paper had 39 questions for 80 marks in 3 hours.
CBSE Class 10th Science Answer Key 2025: The CBSE Class 10 Science Exam 2025 was held on February 20, 2025. As per the initial student reactions, the paper was of moderate difficulty level. To help the students in assessing their performance, we have provided the CBSE Class 10 Science Answer Key 2025 in this article. The answer key has been prepared by subject experts and serves as an important resource for students to cross-check their answers and estimate their scores. Using the answer key allows students to learn from their mistakes and improve their preparation for future exams.
This answer key will also help the students to prepare for the comapartment exam which will be held tomorrow. It is an amazing oppurtunity for the students to perform thier best and get promoted to the next class.
Check| CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2025 For Compartment Exam (All Sets)
Check| CBSE Class 10 Science Paper Analysis 2025 (All Sets)
CBSE Class 10th, 12th Syllabus 2025-26
CBSE Class 10 Science Exam Answer Key- Highlights
The CBSE Class 10 Science question paper had 39 questions for 80 marks. The time allowed to write the paper was 3 hours. All questions were compulsory with some questions having internal choices.
| Feature | Highlights |
| Board Name | Central Board Of Secondary Education (CBSE) |
| Exam Name | CBSE Class 10th Science Exam |
| Exam Date | February 20, 2025 |
| Duration | 10:30 AM to 1:30 PM (3 hours) |
| Total Marks | 80 |
| Mode | Offline (Pen and Paper) |
| Time Duration | 3 Hours |
| Question Paper Sets: | Multiple Sets (Set 1, Set 2, Set 3, Set 4) |
Features Of CBSE Class 10th Science Answer Key
1. Self-Evaluation:
Students can compare their answers with the official solutions to understand their performance.
2. Score Estimation:
By checking the answer key, students can predict their approximate marks before the official results are announced.
3. Identify Mistakes:
Analysing incorrect answers helps students understand their weak areas for improvement in future exams.
CBSE Class 10 Science Course Structure 2025
| S. No. | Unit | Marks |
| 1. | I. Chemical Substances-Nature and Behaviour | 25 |
| 2. | II. World of Living | 25 |
| 3. | III. Natural Phenomena | 12 |
| 4. | IV. Effects of Current | 13 |
| 5. | V. Natural Resources | 05 |
|
| Total | 80 |
CBSE Class 10 Science Answer Key 2025
Get here the CBSE Class 10th Science Answer Key 2025 which is curated by the subject matter experts. Students can access below the answers to all questions asked in the CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2025:
SECTION-A
In this section, Question Nos. 1 to 20 are Multiple-Choice Questions.
1. In the following experimental setup of electrolysis of water, if P and Q are the gases collected in the test tubes enclosing the electrodes R and S, then select the option/options in which the matching is correct:
(i) P-Oxygen gas, R-Anode
(ii) P-Hydrogen gas, R-Cathode
(iii) Q-Hydrogen gas, S-Cathode
(iv) Q-Oxygen gas, S-Anode
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (iii) and (iv)
(C) (i) and (iii)
(D) (ii) and (iv)
Answer: (D) (ii) and (iv)
Explanation: During the electrolysis process, water breaks down into its constituent gases, hydrogen and oxygen. The positive electrode (anode, R) attracts negatively charged ions (hydroxide ions – OH-) and generates oxygen gas (O2). The negative electrode (cathode, S) attracts positively charged ions (hydrogen ions – H+) and produces hydrogen gas (H2).
2. You have three aqueous solutions A, B and C as given below:
A - Potassium nitrate
B - Ammonium chloride
C - Sodium carbonate
The ascending order of the pH of these solutions is:
(A) A<B<C
(B) B<C<A
(C) C<A<B
(D) B<A<C
Answer: (D) B<A<C
3. Select from the following a statement which is not true about burning of magnesium ribbon in air:
(A) It burns with a dazzling white flame.
(B) A white powder is formed on burning.
(C) It is an endothermic reaction.
(D) It is an example of a combination reaction.
Answer: (C) It is an endothermic reaction.
Explanation:
- Burning of magnesium ribbon is an exothermic reaction, as it releases heat and light.
- It burns with a dazzling white flame, forming magnesium oxide (white powder).
- It is a combination reaction because Mg + O2 → MgO involves the combination of magnesium and oxygen.
4. A Hydrocarbon which does not belong to the same homologous series of carbon compounds is
(A) C4H10
(B) C7H14
(C) C6H14
(D) C10H22
Answer: (B) C7H14
Explanation:
(A), (C) and (D) belong to the alkane homologous series (CnH2n+2) while C7H14 belongs to the alkene homologous series (CnH2n), which is different.
5. The colour of the solution observed after about 1 hour of placing iron nails in copper sulphate solution is
(A) Blue
(B) Pale green
(C) Yellow
(D) Reddish brown
Answer: (B) Pale green
Explanation:
- Copper sulfate (CuSO4) solution is blue.
- When iron nails are placed in it, iron displaces copper, forming iron sulfate (FeSO4), which is light green or pale green in colour.
6. Juice of tamarind turns blue litmus to red. It is because of the presence of a chemical compound called
(A) Acetic acid
(B) Methanoic acid
(C) Oxalic acid
(D) Tartaric acid
Answer: (D) Tartaric acid
Explanation:
- Tamarind contains tartaric acid, which is responsible for its sour taste and acidic nature.
- Acids turn blue litmus to red.
7. The water of crystallization is present in
(i) Bleaching Powder
(ii) Plaster of Paris
(iii) Washing Soda
(iv) Baking Soda
(A) (ii) and (iv)
(B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (i) and (iii)
(D) (i) and (iv)
Answer: (B) (ii) and (iii)
Explanation:
- Plaster of Paris (CaSO4·½H2O) has water of crystallization.
- Washing Soda (Na2CO3·10H2O) also has water of crystallization.
- Bleaching Powder and Baking Soda do not.
8. A tall pea plant with round seeds (TTRR) is crossed with a short pea plant with wrinkled seeds (ttrr). The F1 generation will be
(A) 25% tall with round seeds
(B) 50% tall with wrinkled seeds
(C) 75% tall with wrinkled seeds
(D) 100% tall with round seeds
Answer: (D) 100% tall with round seeds
Explanation: TTRR (Tall, Round) × ttrr (Short, Wrinkled) will result in TtRr in F1 generation, which will show Tall and Round traits as Tall (T) and Round (R) are dominant traits.
9. A pair of endocrine glands located in the human brain is
(A) Parathyroid and Pituitary
(B) Pineal and Thymus
(C) Hypothalamus and Thymus
(D) Hypothalamus and Pineal
Answer: (D) Hypothalamus and Pineal
Explanation: Only three endocrine glands are located in the region of the brain which are hypothalamus, pituitary, and pineal glands.
10. Select the option having correct matching of the organism given in Column I with the mode of reproduction in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| P Leishmania | 1. Regeneration |
| Q Spirogyra | 2. Multiple Fission |
| R Planaria | 3. Binary Fission |
| S Plasmodium | 4. Fragmentation |
|
| 5. Budding |
(A) P-4, Q-2, R-1, S-3
(B) P-3, Q-4, R-5, S-2
(C) P-3, Q-4, R-1, S-2
(D) P-4, Q-3, R-2, S-1
Answer: (C) P-3, Q-4, R-1, S-2
Explanation:
- Leishmania → Binary Fission (with a longitudinal plane of division)
- Spirogyra → Fragmentation (algae breaking into pieces to grow)
- Planaria → Regeneration (ability to regrow body parts)
- Plasmodium → Multiple Fission (malaria-causing parasite reproduces by multiple fission)
11. The basic filtration unit of the excretory system in human beings is:
(A) Nephron
(C) Neuron
(B) Urethra
(D) Urinary bladder
Answer: (A) Nephron
Explanation: Nephron is the functional unit of the kidney, responsible for filtration and formation of urine.
12. In human alimentary canal, the digestive juice secreted by the gastric glands are
(A) Bile, Trypsin, Pepsin
(B) Hydrochloric acid, Pepsin, Mucus
(C) Lipase, Bile, Mucus
(D) Salivary amylase, Pepsin, Bile
Answer: (B) Hydrochloric acid, Pepsin, Mucus
Explanation:
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl): Creates an acidic environment.
- Pepsin: Enzyme that digests proteins.
- Mucus: Protects the inner lining of the stomach.
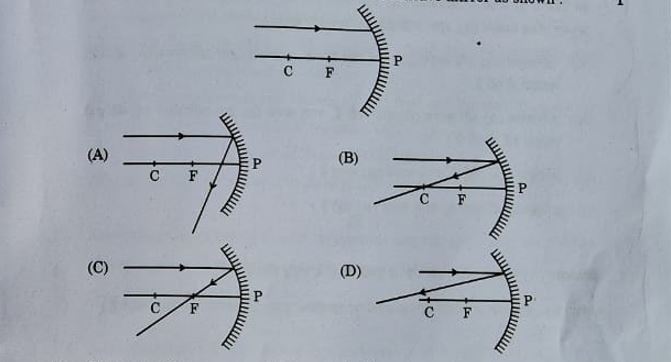
13. Identify from the following the ray diagram which shows the correct path of the reflected ray for the ray incident on a concave mirror as shown:
Answer: Option (c)
Explanation: For an incident ray, parallel to the principal axis, the reflected ray passes through the focus for a concave mirror.
14. The part of human eye which controls the amount of light entering into it.
(A) Iris
(B) Cornea
(C) Ciliary muscles
(D) Pupil
Answer: (A) Iris
Explanation:
- Iris: Regulates the amount of light entering the eye by controlling the size of the pupil.
- Pupil: Opening that allows light into the eye, but it’s controlled by the iris.
- Cornea: Transparent layer that helps in focusing light.
- Ciliary Muscles: Change the shape of the lens to focus on near or distant objects.
15. Consider the following food chain:
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle
If the amount of energy available at third trophic level is 50 kJ, the available energy at the producer level was:
(A) 0.5 kJ
(B) 5 kJ
(C) 500 kJ
(D) 5000 kJ
Answer: (D) 5000 kJ
Explanation: Energy transfer follows the 10% law: Only 10% of energy is transferred to the next level.
Applying the 10% rule:
- Energy at Frog level = 50 kJ.
- Grasshopper level = 50 kJ × 10 = 500 kJ.
- Grass level (producer) = 500 kJ × 10 = 5000 kJ.
16. The incorrect statement about ozone is
(A) It is a deadly poisonous gas.
(B) It shields the surface of the earth from UV radiation from sun.
(C) It is used as a refrigerant and in fire-extinguishers.
(D) It is formed by combining oxygen molecule with free oxygen atom.
Answer: (C) It is used as a refrigerant and in fire extinguishers.
Q.Nos. 17 to 20, two statements are given labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C) and (D) as given below:
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
17. Assertion (A): Carbon and its compounds are our major sources of fuels.
Reason (R): Most of the carbon compounds on burning release a large amount of heat and light.
Answer: (A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Explanation: Carbon and its compounds are used as fuels because they release a large amount of heat and light when burned.
18. Assertion (A): Xylem tissue moves water and minerals obtained from the soil by the roots.
Reason (R): Xylem tissue is found only in the roots of a plant.
Answer: (C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Explanation: Xylem tissue transports water and minerals from the roots to different parts of the plant, but it is not found only in the roots—it is present throughout the plant.
19. Assertion (A): In the common domestic circuits the earth wire is connected to a metallic plate buried deep inside the earth.
Reason (R): Earth wire ensures that any leakage of current to the metallic body of the appliance keeps its potential to that of the earth, so the user may not get a severe electric shock.
Answer: (A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Explanation: The earth wire is connected to a buried metallic plate to ensure safety by directing leakage current into the ground, preventing electric shocks.
20. Assertion (A): The food web is a network of several food chains operating in an ecosystem.
Reason (R): The food web decreases the stability of an ecosystem.
Answer: (C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Explanation: The food web is indeed a network of interconnected food chains, but it increases the stability of an ecosystem rather than decreasing it.
Section B
21. A light green-coloured solution of the sulfate salt of metal ‘P’ is taken in a beaker, and a rod of another metal ‘Q’ is put in this solution, as shown in the following figures:
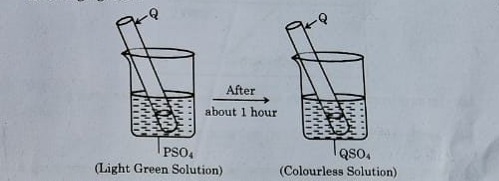
Identify the metals ‘P’ and ‘Q’ and write the chemical equation for the reaction that occurs. State the conclusion of this reaction in terms of the reactivity series of metals.
Answer:
Metal 'P' is Iron (Fe)
Metal 'Q' is Zinc (Zn)
Reaction: FeSO4+ Zn→ZnSO4+Fe
Conclusion:
Since zinc is more reactive than iron, it displaces iron from its sulfate solution. This confirms the reactivity order: Zn > Fe.
22. (a) How is the brain protected in our body?
(b) A doctor finds in one of his patients that he is not maintaining a proper posture and balance of his body. State the region of the brain and also the part of the brain which is responsible for it.
Answer:
(a)The brain is protected by the skull (cranium) and three protective membranes called meninges. A fluid called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cushions the brain from shocks.
(b)The region of the brain responsible for maintaining posture and balance is the hindbrain. The specific part of the brain that controls body posture and balance is the cerebellum.
23. (a) "Proteins control the expression of various characters." Explain this statement by taking an example of "tallness" as a characteristic in plants.
OR
(b) Explain the mechanism of inheritance used by sexually reproducing organisms to ensure the stability of the DNA of the species.
Answer: (a) Proteins are encoded by genes, which determine traits. In tall plants, the gene responsible for tallness produces a protein that influences plant height by regulating growth hormones like gibberellins.
OR
(b) Each gene is present on chromosomes, which are separate, independent pieces of DNA. Each cell in an organism contains two copies of each chromosome—one from the male parent and one from the female parent.
During gamete formation (in germ cells):
- Each gamete receives one chromosome from each pair, either maternal or paternal.
- When fertilization occurs, the two gametes combine, restoring the normal chromosome number in the progeny.
This process ensures the stability of DNA in a species and maintains genetic information across generations.
Q24. Study the figure in which the path of a ray of light going from Medium 1 to Medium 2 is shown.
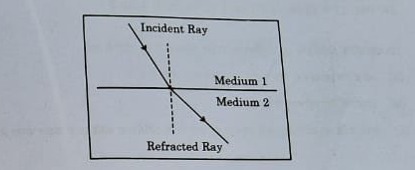
(a) Out of the two Media – Medium 1 and Medium 2, in which is the speed of light more?
Answer:
Thus, the speed of light is more in Medium 2 compared to Medium 1.
(b) State the reason for the bending of the refracted ray away from the normal.
Answer:
The bending occurs when light travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium. Since Medium 1 is denser than Medium 2, the speed of light increases in Medium 2, causing the ray to bend away from the normal.
(c) Express the refractive index of Medium 2 with respect to Medium 1 in terms of the speed of light in two media.
Answer:
Refractive index of Medium 2 with respect to Medium 1 is given as,
n21=Speed of light in Medium 2/Speed of light in Medium 1
Q25. (a) Give reasons:
(i) The sky appears dark to passengers flying at a very high altitude.
(ii) 'Danger' signal lights are red in color.
Answer:
- The sky appears dark at high altitudes due to the thin atmosphere and less scattering of light.
- Danger signals are red because red light has the longest wavelength and is least scattered, making it visible from a distance.
OR
(b) What is a rainbow? "We see a rainbow in the sky only after the rainfall." Why?
Answer:
A rainbow is a natural spectrum of light appearing in the sky when sunlight passes through raindrops.
A rainbow forms when sunlight is refracted, internally reflected, and dispersed by water droplets in the air. Rainwater droplets act as prisms, breaking white light into its spectrum of colors.
Q26. We do not clean natural ponds or lakes whereas an aquarium or a swimming pool needs to be cleaned regularly. Why?
Answer:
Natural ponds or lakes do not require regular cleaning because they have a self-sustaining ecosystem. They contain microorganisms, plants, and aquatic animals that maintain a natural balance by decomposing organic waste and recycling nutrients.
In contrast, an aquarium or a swimming pool lacks such a natural ecosystem.
SECTION-C
27. Write balanced chemical equations for the reactions that occur when:
(a) Steam is passed over red-hot iron.
(b) Natural gas is burnt in air.
(c) Glucose reacts with oxygen in the cells of our body and provides energy.
Answer:
(a) 3Fe+4H2O→Fe3O4 + 4H2
(b)CH4+2O2→CO2+2H2O
(c) C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O+Energy(ATP)
28. (a) State the chemical property in each case on which the following uses of baking soda are based:
(i) As an anti-acid
(ii) As a constituent in making baking powder
(iii) In soda-acid fire extinguishers
Answer:
(i) As an antacid: It is weakly basic and neutralizes stomach acid.
(ii) In making baking powder: It releases CO₂ when heated, making cakes fluffy.
(iii) In soda-acid fire extinguishers: It reacts with acid to produce CO₂, which puts out the fire.
29. Name the blood vessel that brings
(i) oxygenated blood
(ii) deoxygenated blood, to the human heart.
Also, name the chamber of the heart which receives deoxygenated blood and state how deoxygenated blood from this chamber is sent to the lungs for oxygenation.
Answer:
(i) Oxygenated blood vessel: Pulmonary vein
(ii) Deoxygenated blood vessel: Vena cava
Heart chamber receiving deoxygenated blood is Right atrium.
30. The gene combination of purple-flowered pea plants is denoted as (WW) and that of white-flowered pea plants as (ww). When these two plants are crossed, F₂ generation is obtained.
(a) List two observations made by Mendel in F₂ generation plants.
(b) Give the
(i) percentage of white-flowered plants and
(ii) ratio of the gene combinations WW, Ww, and ww in F₂ generation.
(c) Write one difference between dominant and recessive traits.
Answer:
(a) Mendel’s observations in F₂ generation:
- Dominant traits appear in a 3:1 ratio in F₂ generation.
- Recessive traits reappear in 25% of offspring.
(b) (i) Percentage of white-flowered plants: 1/4x100=25%
(ii) Gene ratio in F₂: WW: Ww: ww = 1:2:1
(c) Difference between dominant and recessive traits:
- Dominant trait: Expressed even if one allele is present (e.g., Purple flower).
- Recessive trait: Expressed only if both alleles are recessive (e.g., White flower).
Q31. A student placed a candle flame at different distances from a convex lens and focused its image on a screen. He recorded his observation in tabular form as given below:
| S.No. | Distance of flame from the lens (cm) | Distance of the image from the lens (cm) |
| 1 | -90 | 18 |
| 2 | -60 | 20 |
| 3 | -40 | 24 |
| 4 | -30 | 30 |
| 5 | -24 | 40 |
| 6 | -20 | 60 |
| 7 | -18 | 90 |
| 8 | -12 | 120 |
Analyse the observation table and, on the basis of your analysis only, answer the following questions (without doing any calculations):
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens used? Give reason to justify your answer.
(b) Which one of the set of observations is not correct and why?
(c) Draw a ray diagram to show image formation for any correct set of observations.
Answer: (a) Focal length of the convex lens:
- The data suggests focal length = 30 cm.
- Reason: Image is inverted and magnified when the object is beyond 2F.
(b) Incorrect observation:
- When object is at -12 cm, image should not be at +120 cm.
- A virtual, erect, and magnified image forms when the object is within focal length.
(c) Ray diagram for convex lens image formation:
Draw ray diagram for object beyond 2F, forming an image between F and 2F.
Q32. A person uses lenses of +2.0 D power in his spectacles for the correction of his vision.
(a) Name the defect of vision the person is suffering from.
(b) List two causes of this defect.
(c) Determine the focal length of the lenses used in the spectacles.
Answer:
(a) Defect of vision: Hypermetropia (Far-sightedness)
(b) Causes:
- Eyeball too short
- Lens too weak to focus near objects
(c) Focal length of +2.0 D lens: f= 1/d = ½ = 0.5m
Q33. (a) Explain the statement "Potential difference between two points is 1 volt."
(b) What do the symbols given below represent in an electric circuit? Write one function of each.
(Image contains two circuit symbols: one for an ammeter and another for a resistor.)
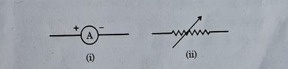
Answer: (a) Potential difference of 1V Definition: 1 volt is when 1 joule of work is done to move 1 coulomb of charge.
(b) Symbols and functions:
(i) Ammeter (A): Measures current in a circuit.
(ii) Resistor: Controls the flow of current.
More answers are being updated here, stay tuned!
Download | CBSE Class 10 Science Answer Key 2025 PDF (Link To Be Active Soon) |
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation