Centripetal force: The force that keeps an object fixed in its circular path is the centripetal force. Moreover, this topic deals with the definition, example and formula of it. Centripetal force is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the force that keeps an object moving in a circular path, directing it towards the center of that path. Here's a comprehensive explanation of centripetal force. Read the complete article for better understanding and vision.
Meaning and Definition Centripetal force?
Centripetal force is derived from the Latin words "centrum" (center) and "petere" (to seek or go towards). It refers to the inward force that acts on an object moving along a curved path, preventing it from moving in a straight line tangent to the circle. Essentially, it keeps the object continually changing direction towards the center of the circle.
.png)
Factors Determining Centripetal Force:
- Velocity of the Object: The speed at which the object moves along its circular path affects the magnitude of the centripetal force. Higher velocities require greater centripetal force to keep the object in the same circular trajectory.
- Distance from the Center: The radius of the circular path (distance from the center) also plays a crucial role. A smaller radius requires a larger centripetal force to maintain the object's motion at a given speed.
- Mass of the Object: The mass of the object moving in the circular path influences the centripetal force required. Greater mass requires a stronger force to keep it on the circular path.
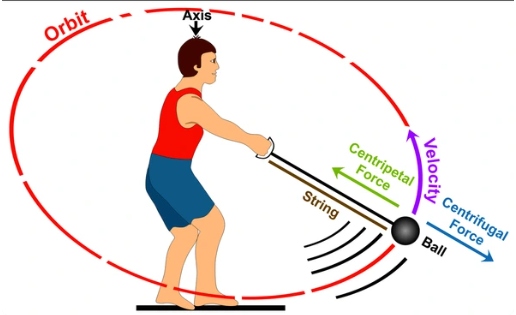
Example of Centripetal force
- Planetary Orbits: The gravitational force exerted by the Sun on planets keeps them in their elliptical orbits.
- Rotating Objects: Objects tied to a string and spun around, like a tetherball or a stone in a sling, experience centripetal force due to tension in the string.
Centripetal Force is crucial in understanding circular motion and its fundamentals in various fields such as physics, engineering and astronomy.
Example Calculation of Centripetal Force:
Calculating centripetal force involves using a specific formula that relates the mass of an object, its velocity, and the radius of the circular path it follows.
Let's say an object with a mass m=10 kg moves in a circular path with a speed v=5 m/s and a radius r=2 meters.
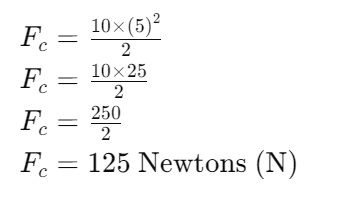
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation