Law Of Conservation Of Mass: Did you know that in water the ratio of the mass of hydrogen to the mass of oxygen is always 1:8? This led to one of the laws of chemical combination, the law of constant proportions. In this article, we will find out about the law of conservation of mass, atoms, molecules along with Dalton’s atomic theory.
What is the Law of Conservation of Mass?
The law of conservation of mass states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. The law also states that it can be transformed into another form. It was given by Antoine L. Lavoisier in 1789. The law of conservation of mass is one of the laws of chemical combination, the other being the law of constant proportions.
Also Check: CBSE Class 9 Science Notes for Chapter 3 - Atoms and Molecules
What is the Formula of the Law of Conservation of Mass?
The formula of the law of conservation of mass is as follows:
∂ρ/∂t +⛛(ρv) = 0
Where,
ρ = density
t = time
v = velocity
⛛ = divergence
What is the Law of Constant Proportions?
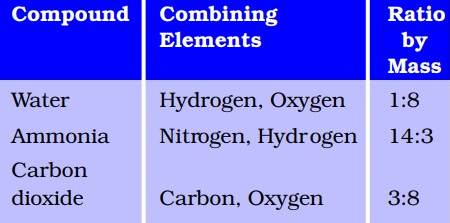
The law of constant proportions (also called the law of definite proportions) states that in a chemical substance the elements are always present in definite proportions by mass. It was given by Joseph Proust in 1797.
What is Dalton’s Atomic Theory?
It was John Dalton’s atomic theory that provided an explanation for the laws of chemical combination. According to this theory, all matter, whether an element, a compound or a mixture is composed of small particles called atoms.
The postulates of the theory are as follows:
All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms.
Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical properties.
Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
Also Check: CBSE Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Solutions: Chapter 1, Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
What is an Atom?
Atoms are the building blocks of matter and are very small in size. They are the smallest particles of matter. Example- Sodium (Na), Hydrogen (H)etc.

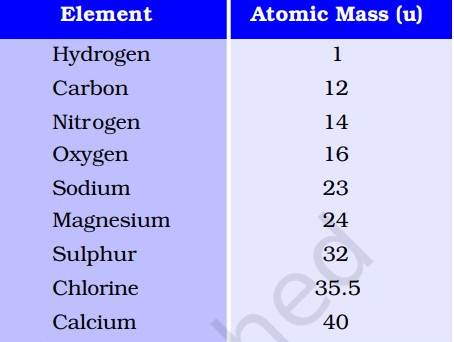
What is Atomic Mass?
NCERT defines atomic mass as 'the average relative mass of an atom of the element as compared with the mass of an atom of carbon (C-12 isotope)'.
What is a Molecule?
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together. Example-two atoms of hydrogen) and one atom of oxygen react with each other and form one molecule of water.
Note: All images have been taken from NCERT Class 9 Science textbook.
Also, check
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation