Astronomers have made a fascinating discovery, showing that massive black holes can "cook" for themselves. Using advanced data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and the Very Large Telescope (VLT), scientists observed how black holes in galaxy clusters generate a cycle of gas cooling and self-sustenance.
Key Points:
- Black Hole Feeding Mechanism:
- Black holes, some millions to billions of times the mass of the Sun, reside at the centers of galaxy clusters.
- These black holes produce powerful jets that cool the surrounding hot gas, forming filaments of warm gas.
- Some of this warm gas flows back into the black hole, continuing the cycle and fueling further outbursts.
- Observations and Data:
- The study was based on observations of seven galaxy clusters, including Perseus and Centaurus.
- The data combined X-ray images (blue) from Chandra and optical light (red) from the VLT, revealing hot and warm gas filaments.
What role do Jets and Gas Filaments play?
Here is the description:
| Gas Type | Description |
| Hot Gas | X-ray emitting, shown in blue, representing high-temperature gas. |
| Warm Gas | Filaments formed when the hot gas cools, shown in pink and red, visible through optical data. |
- Cooling Process:
- Jets from black holes trigger cooling in the hot gas, causing it to condense into warm filaments.
- These filaments then flow toward the black hole, feeding it, and the cycle repeats.
- Turbulence plays an important role in initiating this cooling process.
What are the New Findings & Evidence from NASA about these observations?
These observations made by NASA’s Chandra X-ray and Very Large Telescope (VLT) are:
- Brightness Link: The brightness of the hot gas in the center of galaxy clusters is directly related to the brightness of the warm filaments. This confirms the self-feeding process of black holes.
- Unexpected Cosmic Connections:
- The filaments found in galaxy clusters bear a striking resemblance to "jellyfish galaxies" – galaxies that lose gas as they move through their surroundings, forming similar structures.
- This connection implies a shared cosmic mechanism between these phenomena.
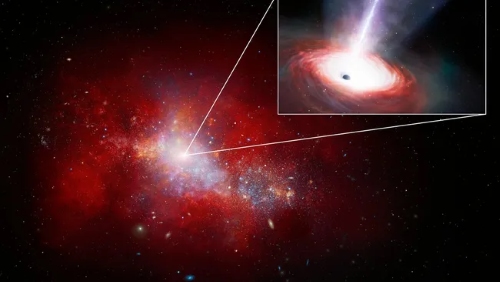
Source: NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/J. da Silva/M. Zamani/Space.com
What are the Notable Observations of Galaxy Clusters by NASA?
Notable observations of Galaxy Clusters is:
- Perseus Cluster:
- X-ray Gas: Appears bluish-purple.
- Warm Gas Filaments: Bright pink, solid.
- Visual Effect: Surrounding galaxies shine brightly, making them easily discernible.
- Centaurus Cluster:
- X-ray Gas: Softer, diffuse purple.
- Warm Gas Filaments: Feathery texture, transitioning from pale pink to neon red.
What is the Significance of the Study?
This breakthrough supports a model where black holes do not only feed on external gas but also regulate their own feeding cycles. By cooling and condensing the surrounding gas, black holes can sustain their growth indefinitely.
What are the Research Methodology & Collaboration by others University and Countries?
- Lead Researcher: Valeria Olivares from the University of Santiago, Chile.
- International Team: Collaboration with experts from the US, Chile, Australia, Canada, and Italy.
- Key Tools:
- MUSE (Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer) on the VLT – for 3D cosmic views.
- Chandra X-ray Observatory – for detailed X-ray observations.
Visual Representation of the Findings:
.jpg)
Source: AI Genrated
- The images show central black holes surrounded by glowing gas filaments.
- Perseus Cluster (left): Bright galaxies and solid pink filaments.
- Centaurus Cluster (right): Diffuse, softer gas and feathery filaments.
Black Holes: Key Facts & Insights
- Definition:
- Extremely dense objects in space with intense gravitational pull, preventing even light from escaping.
- Types: Stellar, Supermassive, Intermediate.

Source: NASA
Formation of Black Holes:
- Stellar Black Holes:
- Formed from the collapse of massive stars (8-10 times the mass of the Sun).
- The resulting mass is a few times that of the Sun.
- Supermassive Black Holes:
- Found at the center of galaxies (e.g., Sagittarius A* in the Milky Way).
- Can be millions or billions of times the mass of the Sun.
- Intermediate Black Holes:
- Medium-sized, discovered through research into smaller and larger black holes.
Discovery & Milestones:
- Theoretical Prediction:
- Black holes were predicted by Einstein's general theory of relativity (1916).
- First image captured in 2019 by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) of M87’s supermassive black hole.
- First Detected:
- Cygnus X-1: The first identified black hole, located in the Milky Way.
What are the Characteristics of Black Hole?
- Event Horizon:
- Boundary beyond which nothing, not even light, can escape.
- Singularity:
- Core where the black hole’s mass is concentrated, causing extreme gravitational forces.
- Accretion Disk:
- A disk of gas and dust spiraling into the black hole, emitting X-rays.
Notable Black Holes:
- Sagittarius A*:
- Supermassive black hole at the center of our galaxy, 26,000 light-years away.
- M87 Black Hole:
- First-ever black hole image released in 2019 by the EHT.
What are the Theories & Concepts behind Black Hole?
- Hawking Radiation:
- Theoretical prediction that black holes slowly lose mass over time due to quantum effects.
- Wormholes:
- Not proven, though some theories suggest black holes could contain wormholes to other universes or parts of spacetime.
Conclusion:
This study sheds new light on the dynamic relationship between black holes and their environment. By demonstrating the role of jets and gas filaments, astronomers have uncovered a cosmic cycle where black holes feed themselves through a unique process of gas cooling and refeeding.
For more informations on NASA, space explorartins, Click on the links given below:
Read| Interstellar Object May Have Reshaped Our Solar System's Planetary Orbits
Read| How Light Pollution Is Threatening the Very Large Telescopes in Chile: An Expert’s Warning
Read| Who is Janet Petro? Meet the First Woman to Lead NASA as Acting Administrator
Read| List of Administrators of NASA
Read| GJ 1214 b: A Mysterious ‘Super-Venus’ Exoplanet Unveiled by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope
Read| NASA-ISRO Mission: How Earth Satellite NISAR will see the Earth?
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation