Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) Udyog Bharat 4.0 is an initiative by the Department of Heavy Industry (DHI) under the aegis of Ministry of Heavy Industries and Public Enterprises, Government of India.
The initiative by the Department of Heavy Industry aims to raise awareness about Industry 4.0 among the Indian manufacturing industry to reach 25% of the total GDP by 2025 with the help of demonstration centres.
Centres of SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0
1- Center for Industry 4.0 (C4i4) Lab Pune
2- IITD-AIA Foundation for Smart Manufacturing
3- I4.0 India at IISc Factory R & D Platform
4- Smart Manufacturing Demo & Development Cell at CMTI.
Features of SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0:
1- Awareness Campaigns
2- Master Trainers to be trained
3- Start-up/ incubators to be provided
4- Hand-holding of SMEs to plan and implement relevant Industry 4.0 projects to be done through consultancy services on chargeable basis
5- Collaborating with neighbourhood Universities for student training/internship programmes
6- Involving industry in SPV membership model for sustainability
7- Participating in a Government formed platform for Industry 4.0 on a common agenda
8- To make adequate provisions for e-waste management
9- Involving as many clusters of Capital Good as possible
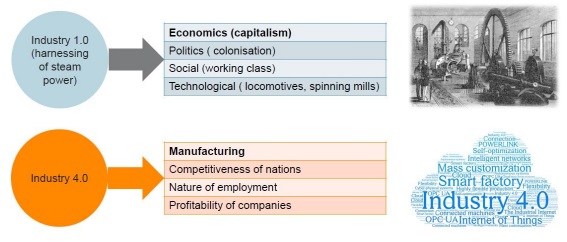
About Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 will happen on a global scale taking the automation of the manufacturing process to a new level by linking the cyber & physical, incorporating AI and enabling customized and flexible mass production technologies. It aims at minimizing wasteful processes and actions, optimizing the use of energy and other inputs.
Timeline of the Industrial Revolution:
Industry 1.0:
1- Introduced in the 1800s.
2- Mechanization
3- Water Power
4- Steam Power
Industry 2.0:
1- Introduced at the beginning of the 20th century.
2- Primary source of power-- electricity.
3- Machines were designed with their own power source.
4- Development of management programs.
5- Mass production and assembly lines.
Industry 3.0:
1- Introduced in the last few decades of the 20th century.
2- Invention and manufacturing of electronic devices.
3- CNC and Robotics-- integrated circuit chips-- to automate individual machines.
4- Software system development to capitalise electronic hardware.
5- ERP (Enterprise resource planning) systems were introduced.
Industry 4.0:
1- Introduced in the 21st century.
2- It is also known as the digital revolution.
3- Internet Of Things (IOT)-- enable the system to share the information which is used to guide intelligent actions.
4- Additive Manufacturing - 3D printers.
5- Collaborative Robotics
Nations such as Germany, France, China, USA etc. have created platforms for pre-competitive cooperation in Industry 4.0 and are looking forward to the automation and control to replace expensive manpower and attain lower cost of conversion, thereby regaining their share in manufacturing economy from emerging economies.
The focus of the Indian programme for Industry 4.0 is to utilize the technology to make products for the global markets at competitive rates and to be embrace Industry 4.0 technology with latest technological advancements.
List of Important Government Schemes Launched in India in 2020
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation