"Normally, in India, a majority of the people have accepted Hindi as a national language and many people speak Hindi and write in Devanagari script but there is nothing on record to suggest that any provision has been made or order issued declaring Hindi as a national language of the country," Gujarat High Court while dismissing a PIL seeking direction for mandatory printing of details of goods such as price, ingredients used and date of manufacturing in Hindi on the grounds that it was the National Language of India.
Official Languages of India
English, Urdu and Hindi were the official languages of Colonial India. In 1950, when the Constitution of India came into effect, it envisaged that English would be phased out in favour of Hindi over a period of 15 years. It also gave the Indian Parliament the power to provide for the continued use of English even thereafter by law. In 1964, the Government of India faced resistance in the non-Hindi speaking belt of the country over its plans to make Hindi the sole official language of the country. Since then, both Hindi and English are used as the official languages of the country.
India has no National Language as per the Constitution but has Hindi and English as the official languages. As per Article 343 of the Indian Constitution:
(1) The official language of the Union of India shall be Hindi written in Devanagari script.
(2) Notwithstanding anything mentioned in clause (1), for a period of fifteen years from the commencement of this Constitution, the English language shall continue to be used for all the official purposes of the Union of India for which it was being used immediately before such commencement:
President may, during the said period, by order authorise the use of the Hindi language in addition to the English language and of the Devanagari form of numerals in addition to the international form of Indian numerals for any of the official purposes of the Union.
(3) Notwithstanding anything in this article, Parliament may by law provide for the use, after the said period of fifteen years, of— (a) the English language, or (b) the Devanagari form of numerals, for such purposes as may be specified in the law.
The Official Languages Act, 1963, allowed for the continuation of English alongside Hindi in the Indian Government indefinitely until legislation is passed to change it.
| The Official Languages Act, 1963 It is an Act to provide for the languages which may be used for the official purpose of the Union of India, for the transaction of business in Parliament, for Central and State Acts and for a certain purpose in High Courts. |
Read- 10 Most Spoken Languages in India by Number of Speakers
Scheduled Languages of India
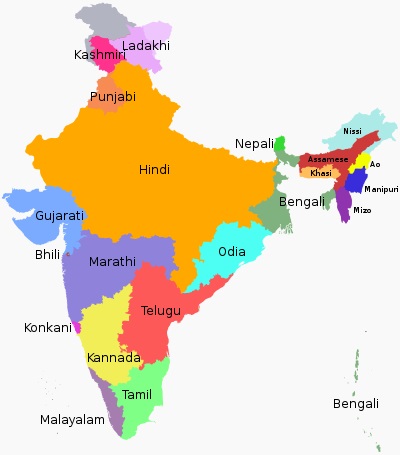
As per the Eighth Schedule to the Indian Constitution, 22 languages have been granted the status of scheduled languages of India. These are-- Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Oriya, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu, Bodo, Santhali, Maithili and Dogri.
Schedules Languages of India: Areas where they are spoken and year of recognition
| S.No. | Language | Area | Year of Recognition |
| 1. | Assamese | Assam | 1950 |
| 2. | Bengali | West Bengal | 1950 |
| 3. | Gujarati | Gujarat | 1950 |
| 4. | Hindi | North India | 1950 |
| 5. | Kannada | Karnataka | 1950 |
| 6. | Kashmiri | Jammu and Kashmir | 1950 |
| 7. | Konkani | Goa | 1992 |
| 8. | Malayalam | Kerala | 1950 |
| 9. | Manipuri | Manipur | 1992 |
| 10. | Marathi | Maharashtra | 1950 |
| 11. | Nepali | Sikkim, Assam, and Arunachal Pradesh | 1992 |
| 12. | Odiya | Odisha | 1950 |
| 13. | Punjabi | Punjab | 1950 |
| 14. | Sanskrit | Karnataka (Shivamogga District) | 1950 |
| 15. | Sindhi | Rajasthan, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh | 1967 |
| 16. | Tamil | Tamil Nadu | 1950 |
| 17. | Telugu | Andhra Pradesh, Telangana | 1950 |
| 18. | Urdu | Jammu & Kashmir, Telangana and Uttar Pradesh | 1950 |
| 19. | Bodo | Assam and Meghalaya | 2004 |
| 20. | Santhali | West Bengal, Jharkhand and Odisha | 2004 |
| 21. | Maithili | Bihar and Jharkhand | 2004 |
| 22. | Dogri | Jammu and Himachal Pradesh | 2004 |
Of these languages, 14 were initially included in the Indian Constitution. The Sindhi language was added in 1967. Thereafter, three more languages-- Konkani, Manipuri and Nepali were included in 1992. Subsequently, Bodo, Dogri, Maithili and Santhali were added in 2004.
At present, there are increased demands for the inclusion of 38 more languages in the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution. These are as follows:
(1) Angika
(2) Banjara
(3) Bazika
(4) Bhojpuri
(5) Bhoti
(6) Bhotia
(7) Bundelkhandi
(8) Chhattisgarhi
(9) Dhatki
(10) English
(11) Garhwali (Pahari),
(12) Gondi
(13) Gujjar/Gujjari
(14) Ho
(15) Kachachhi
(16) Kamtapuri
(17) Karbi
(18) Khasi
(19) Kodava (Coorg)
(20) Kok Barak
(21) Kumaoni (Pahari)
(22) Kurak
(23) Kurmali
(24) Lepcha
(25) Limbu
(26) Mizo (Lushai)
(27) Magahi
(28) Mundari
(29) Nagpuri
(30) Nicobarese
(31) Pahari (Himachali)
(32) Pali
(33) Rajasthani
(34) Sambalpuri/Kosali
(35) Shaurseni (Prakrit)
(36) Siraiki
(37) Tenyidi
(38) Tulu
“As the evolution of dialects and languages is dynamic, influenced by socio eco-political developments, it is difficult to fix any criterion for languages, whether to distinguish them from dialects, or for inclusion in the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India. Thus, both attempts, through the Pahwa (1996) and Sitakant Mohapatra (2003) Committees to evolve such fixed criteria have not borne fruit. The Government is conscious of the sentiments and requirements for inclusion of other languages in the Eighth Schedule and will examine the requests keeping in mind these sentiments, and other considerations such as the evolution of dialects into language, widespread use of a language etc.," Ministry of Home Affairs on the inclusion of languages in the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation