On the most important bilateral meeting held between India & China, China’s Ambassador to India, Xu Feihong, shared a post on X on February 23, highlighting the significance of the historic Tea Horse Road. This ancient trade route, spanning over 2,000 km, served as a vital link between China and India through Tibet.
Tea from across China was transported to Xizang, then shipped to Kolkata, India, via the Himalayan passes, and sold in Europe and Asia on a massive… pic.twitter.com/pYclUyrVCr
— Xu Feihong (@China_Amb_India) February 23, 2025
While the Silk Road is more widely recognised for connecting China to Europe, the Tea Horse Road played an equally important role in commerce for centuries. It facilitated the movement of Chinese tea to Tibet, from where it was transported through Himalayan passes to Kolkata and subsequently distributed to markets in Europe and Asia.
What is the Ancient Tea Horse Road?
The Ancient Tea Horse Road was a major trade route connecting Yunnan, Sichuan, and Tibet regions in China. From the 6th to the 20th century, this route facilitated tea exchange from Sichuan and Yunnan for horses from Tibet. Due to its function in the trade, it became widely known as the Tea Horse Road.
Source:tibetantrekking
What are its features?
Ancient Tea Horse Road has significant features, which include its historical remnants, religious symbols, and its geographical challenges
- Historical Remnants: Deep ruts (about 70 cm) in stone slabs, created by the continuous movement of pack horses over centuries, remain visible today.
- Religious Symbols: Ancient roadside altars engraved with Buddhist scriptures and mottos serve as a testament to the cultural and spiritual significance of the road.
- Geographical Challenges: One of the highest and most perilous ancient trade routes, it spanned diverse terrains, carrying commerce, culture, and civilisation across vast landscapes.
What is the importance of the Tea Horse Road?
The Ancient Tea Horse Road rivalled the Silk Road in importance and was one of the longest trade routes in the world, extending over 10,000 kilometres. It passed through treacherous landscapes like the Hengduan mountain range, the Tibetan plateau, and wild forests. Despite its significance, it was also one of the most treacherous routes, and only a few traders could complete the entire journey.
What is the Origin of the Tea Horse Road?
The trade route originated from the tea-horse trade markets, where Han and Tibetan people exchanged goods. The trade dates back to the Tang Dynasty (618–907 CE) and became more organised during the Song Dynasty (960–1279 CE) when the government established Tea Horse Trade Offices to regulate and oversee transactions.
What are the Two Main Routes of the Ancient Tea Horse Road?
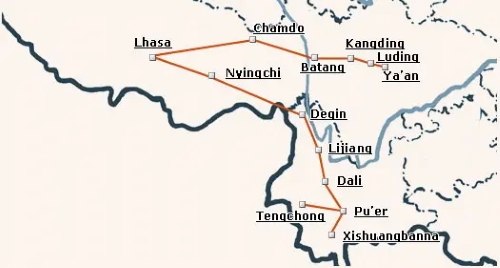
Source:chinahighlights
The Ancient Tea Horse Road was divided into two primary routes:
1. Sichuan-Tibet Tea Horse Road
- Length: Over 4,000 kilometers
- Route: Ya'an (Sichuan)→ Luding→ Kangding→ Batang → Chamdo (Tibet)→ Lhasa
- Extension: Reached Nepal, Myanmar, and India
- Development: During the Ming Dynasty (1368–1644 CE), this route was officially recognised, leading to urban and economic expansion along the path.
2. Yunnan-Tibet Tea Horse Road
- Origin: Late 6th century
- Route: Simao (Yunnan)→ Pu'er→ Dali→ Lijiang→ Shangri-La→ Lhasa
- Extensions: Connected Nepal, Burma, and India, making it a crucial trade link to South Asia.
What was the role of Kangding?
Kangding was the largest trading post along the Tea Horse Road. It served as a crucial meeting point where traders from different regions exchanged goods. In 1696, Emperor Kangxi of the Qing Dynasty officially approved the tea-for-horse trade in Kangding, further solidifying its role as a key commercial hub. Goods such as silk and tea flowed westward, while products from South Asia, Europe, and America were introduced to China.
How Did the Tea Horse Road Contribute to Development?
Tea Horse Road boosted the local economy and expanded trade networks. It has contributed to economic growth, cultural exchange, and played an important role in infrastructure development. Here are all the contributing factors in detail:
- Economic Growth: The flourishing trade along the route boosted local economies and contributed to the expansion of commercial towns.
- Cultural Exchange: The route facilitated cross-cultural interactions between the Han, Tibetans, and other ethnic groups.
- Infrastructure Development: The necessity of transport led to the creation of roads, bridges, and trade stations, which later evolved into towns and cities. For instance, Lijiang remains a well-preserved example of a town that thrived due to its location along the Tea Horse Road.
What were the reasons for the decline of Tea Horse Road?
With the development of modern transportation in the late 20th century, the Ancient Tea Horse Road gradually became obsolete. Today, modern highways such as the Sichuan-Tibet Highway have replaced these ancient pathways. Here is given in detail:
- Political Instability (1912): The fall of the Qing Dynasty disrupted governance, weakening control over traditional trade routes.
- Advancements in Transportation: The expansion of modern roads and railways reduced reliance on old caravan paths.
- Impact of World War II: While briefly used for military supply chains, the rise of industrial production and mechanised transport diminished its significance.
- Post-1949 Reforms: With the establishment of modern China, land reforms and infrastructure development rendered the traditional porter-based trade system obsolete.
Challenges and Transportation
The journey along the Ancient Tea Horse Road was highly perilous due to:
- High-altitude terrains and precipitous mountain paths
- Fast-flowing rivers and treacherous crossings
- Lack of wheeled or waterway transport, making pack horses the only viable option
Despite these challenges, traders played a vital role in connecting remote villages and facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas.
Can You Explore the Tea Horse Road Today?
Yes! The Ancient Tea Horse Road remains a fascinating destination for travellers. Although no longer an active trade route, the Tea Horse Road remains a popular destination for travellers. Visitors can experience:
- Stunning landscapes and wildlife.
- Rich cultural experiences with ethnic communities.
- A chance to explore historical trade centres and religious sites.
Conclusion
The Ancient Tea Horse Road played an instrumental role in fostering trade, cultural exchange, and economic growth across China and neighbouring regions. Though abandoned, it remains an iconic symbol of history, adventure, and human resilience. Exploring this ancient route today offers an enriching journey into China’s past, highlighting the deep-rooted connection between commerce, nature, and culture.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation