Principles of Inheritance and Variation CBSE Notes: Revision notes are the short textual content that summarises the chapter. Such notes are helpful for students and teachers to quickly revise the topic. For board students who have to complete a huge syllabus for their exams, revision notes work as an effective piece of information.
Here, revision notes for CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 are provided which are based on the information given in NCERT Class 12 Biology Principles of Inheritance and Variation chapter. These Principles of Inheritance and Variation revision notes will help you prepare for the test or exams quickly. A few minutes before the exam if given to these notes, will help you refresh the concepts and thus increase your chances of scoring well. Read and download Principles of Inheritance and Variation CBSE notes from below.
CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Revision Notes
Chapter: Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Introduction:
- Inheritance is the process by which traits or characteristics are passed from parents to offspring.
- Gregor Mendel is known as the father of genetics for his experiments on pea plants, which laid the foundation for understanding the principles of inheritance.
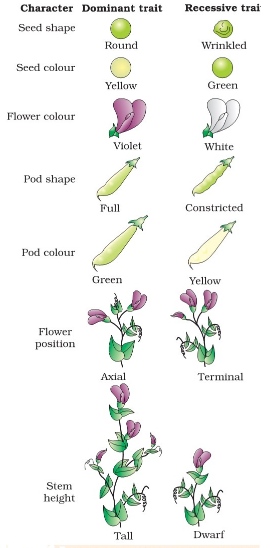
Mendel's Laws of Inheritance:
Law of Segregation:
- Mendel proposed that individuals possess two factors (alleles) for each trait, and these segregate during gamete formation.
- The factors segregate randomly, and each gamete receives only one of the two alleles.
Law of Independent Assortment:
- Mendel observed that different traits segregate independently of each other during gamete formation.
- This law applies only to genes located on different chromosomes or genes located far apart on the same chromosome.
Extensions to Mendelian Genetics:
Incomplete Dominance:
- In some cases, neither allele is completely dominant over the other, resulting in an intermediate phenotype.
Co-dominance:
- In co-dominance, both alleles are expressed simultaneously, leading to the expression of both traits.
Multiple Alleles:
- Some genes have more than two alleles in a population, creating multiple possible phenotypes.
Pleiotropy:
- A single gene can influence multiple traits or phenotypes.
Polygenic Inheritance:
- Many traits are controlled by multiple genes, resulting in a continuous range of phenotypes.
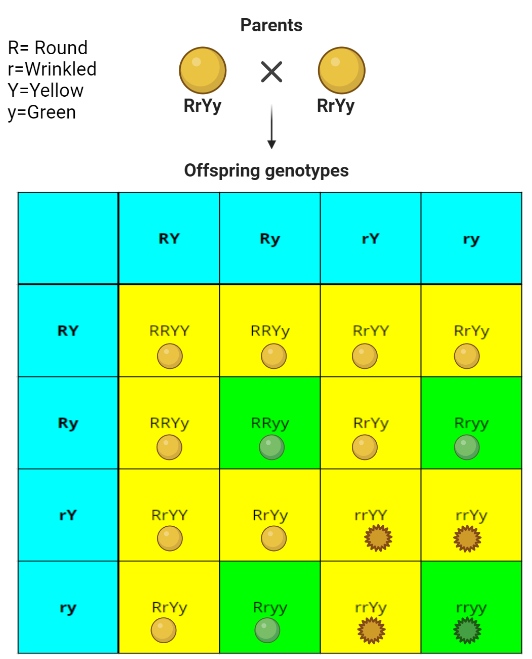
Genotypic ratio: 1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1
Phenotypic ratio: 9:3:3:1
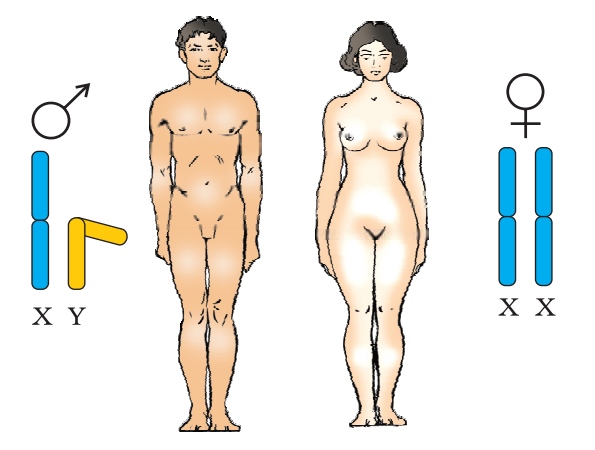
Sex-linked Inheritance:
- Certain genes are located on the sex chromosomes (X and Y), leading to distinct inheritance patterns.
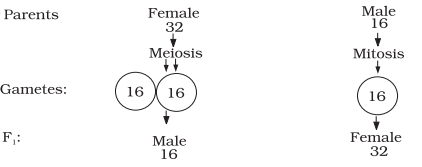
Sex-determination in Honey Bee
Human Genetic Disorders:
- Genetic disorders can result from mutations in genes or abnormalities in chromosome structure or number.
- Examples include Down syndrome, haemophilia, sickle cell anaemia, Klinefelter’s Syndrome, Turner’s Syndrome and colour blindness.
Read:
| Download NCERT Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Revision Notes PDF |
Read: NCERT Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter-Wise
Related:
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation