Check the CBSE Class 12 Biology Sample Paper 2025 designed by subject matter experts for effective board exam preparation. This sample paper follows the latest CBSE exam pattern and includes expert-curated questions based on past exams and key syllabus topics. With provided solutions, you can evaluate your answers and improve your understanding. Whether for last-minute revision or thorough practice, this CBSE Class 12 Biology Sample Paper is a must-have resource to boost your confidence and improve your scores in the exam tomorrw. Download the sample paper ans solutions in PDF.
Key Features of the CBSE Class 12 Biology Sample Paper 2025:
- Expert-Curated Questions: Based on past exam trends and key CBSE syllabus topics.
- Latest Exam Pattern: Designed as per the CBSE Board Exam 2025 format.
- With Solutions: Includes answers to help students assess their performance.
- PDF Download Available: Practice anytime, anywhere with the downloadable file.
- Effective for Last-Minute Revision: Covers important topics to ensure high scores.
CBSE Class 12 Biology Sample Paper 2025: Marking Scheme
Marking scheme shows what marks are allotted to each type of question. Both, the exam pattern and marking distribution for CBSE Class 12 Biology have been presented here, for your reference. The exact same exam pattern will be followed in the upcoming CBSE Class 12 Biology Board Exam 2025.
| Section | Type of Question | No of Questions | Total Marks |
| A | Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs)/ Assertion-Reasoning | 16 | 1 x 16 = 16 |
| B | Short Answer Questions | 5 | 2 x 5 = 10 |
| C | Short Answer Questions | 7 | 3 x 7 = 21 |
| D | Case-based/Source-based/Passage-based/Integrated Assessment Questions | 2 | 4 x 2 = 8 |
| E | Long Answer Questions | 3 | 5 x 3 = 15 |
|
| TOTAL |
| 70 |
|
| Practical: |
|
|
|
| Identification/Familiarity with the apparatus |
| 5 |
|
| Written test (Based on given / prescribed practicals) |
| 10 |
|
| Practical Records |
| 5 |
|
| Viva |
| 10 |
|
| TOTAL |
| 30 |
Important: CBSE Class 12 Biology Top 50 mcqs
CBSE Class 12 Biology Sample Paper 2025 for Board Exam 2025
Check and download the sample paper with solutions below:
General Instructions
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has five sections and 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 16 questions of 1 mark each; Section-B has 5 questions of 2 marks each; Section-C has questions of 3 marks each; Section-D has 2 casebased questions of 4 marks each; and Section-E has 3 questions of 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. 5. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions. 6. Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
SECTION – A
- Select the type of inheritance mismatched with an example from the list given below:
(a) Incomplete dominance: Antirrhinum
(b) Codominance: 'AB' blood group.
(c) Polygenic inheritance: Mirabilis jalapa
(d) Pleiotropy: phenylketonuria disease
- What would be the number of chromosomes in the cells of the Aleurone layer in a plant species with 8 chromosomes in its synergids?
(a) 16
(b) 24
(c) 32
(d) 4
- Which of the following refer to correct example(s) of organisms which have evolved due to changes in environment brought about by anthropogenic action.
(A) Drawin's finches of Galapagos Islands
(B) Herbicides resistant weeds
(C) Antibiotic resistance in eukaryotes
(D) Man created breeds of domesticated animals like dogs.
(a) (A) & (B)
(b) (B), (C) & (D)
(c) Only (D)
(d) Only (A)
- Gynoecium of Michelia is
(a) Monocarpellary
(b) Multicarpellary syncarpous
(c) Multicarpellary apocarpous
(d) Absent.
5.10 E.coli cells with 15 N-ds DNA are incubated in a medium containing 14 N (normal NHCI). After 80 minutes, how many E.coliv will have DNA totally free from 15N?
(a) 80 cells
(b) 60 cells
(c) 140 cells
(d) 160 cells
- In E.coli, the lac Operon gets switched on when :
(a) Repressor binds to operator
(b) Lactose is present and binds to repressor
(c) Lactose is present in binds to RNA polymerase
(d) RNA polymers bind to the operator.
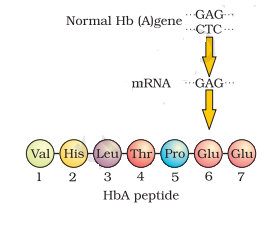
- In the figure given below what does (a) and (b) represents :
![]()
(a) GAG, Glutamic acid
(b) GUG, Valine
(c) GAG, Valine
(d) GUG, Glutamic acid
- Flippers of Penguins and Dolphins are examples of:
(a) Conversion evolution
(b) Industrial evolution
(c) Natural selection
(d) Adaptive radiation
- Cry gene(s) that controls the Corn borer.
(a) Cry 1 Ac & Cry II Ab
(b) Cry I Ab & Cry II Ac.
(c) Cry I Ab.
(d) Cry II Ab
- DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis are shown in the figure. Mark the correct statement.
(a) B and 3 contains more positively charged DNA molecule than band 1
(b) B and 3 indicates more charge density than bands 1 and 2
(c) B and 1 have longer DNA fragments than bands 2 and 3.
(d) All bands have equal length and charges but differ in base composition.
- Monascus purpureus is a yeast used commercially in the production of
(a) Ethanol
(b) Streptokinase for removing clots from the blood vessels.
(c) Blood cholesterol lowering statins.
(d) Lipase to formulate detergents.
- Read the following statements and select the correct statement(s)
(A) India has only 2.4% of the world's land area.
(B) India's share of global species diversity is less than 5%.
(C) India is one of the 12 mega diversity countries of the world.
(D) Nearly twice the plant species as many as animals species have been recorded in India.
(a) A, B, C
(b) A, B, C, D
(c) Only D
(d) A, C
Question No. 13 to 16 consist of two statements - Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
- Assertion: Unlike mammals, desert lizards lack the physiological ability required to deal with the high temperature.
Reason: Desert lizards change their body temperature in accordance to ambient conditions by behavioural means.
- Assertion: tRNA is an adaptor molecule that on one hand read the code and on other hand would bind to specific amino acid.
Reason: RNA Polymerase III is responsible for transcription of tRNA.
- Assertion: The regions inside the seminiferous tubules contains leydig cells
Reason: Leydig cells synthesise and secrete androgens.
- Assertion: Insertion of recombinant DNA within the coding sequence of -galactosidase results in colourless colonies.
Reason: Presence of insert results in inactivation of enzyme -galactosidase known as insertional inactivation.
SECTION - B
- Differentiate between spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
- DNA is a hydrophilic molecule and can't pass through a cell membrane. So, the bacterial cell is made competent to take up the plasmid.
(a) What is the role of CaCl2 in making the cell competent?
(b) How one can introduce alien DNA into host plant cell directly?
- Lymphoid organs are the main component of human immune system.
(a) Name the primary lymphoid organs present in human body.
(b) Expand MALT.
- Study the figure given below and answer the following questions:
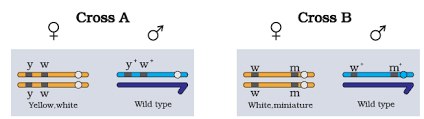
(a) Identity in which of the above given crosses is the strength of linkage between the genes is higher and why?
(b) Out of cross 'A' and cross 'B', when would the proportion of non-parental gene combinations be higher?
- What will be the amount of energy available to the organisms of tertiary consumer level of a food chain, if the energy available at the producer level is 20,000 joules?
OR
"Decomposition is an Oxygen requiring process". Comment.
SECTION-C
- (a) Name the primates that lived about 15 million years ago.
(b) Write the order in which Neanderthals, Homo habilis and Homo appeared on the earth, State the brain capacity of each of them erectus?
(c) How Homo habilis were different from Homo erectus?
- (a) Mention the relationships between pituitary and ovarian hormones during a menstrual cycle. (b) How many primary follicles are left in each ovary in a human female at puberty.
- (a) "A mother of 1 year old daughter wanted to space her second child. Which contraceptive method may be suggested by the doctor to her?
(b) How the action of LNG 20 is different from Cu-T?
(c) Name one non-medicated IUD.
- (a) Write two ways of development of apomictic seeds.
(b) Write one advantage of apomictic seeds.
- (a) Mention the relationships between pituitary and ovarian hormones during a menstrual cycle.
(b) How many primary follicles are left in each ovary in a human female at puberty.
- Describe how do 'flocs' and 'activated sludge help in sewage treatment.
- (a) Why are mango trees unable to grow in temperate climates?
(b) Give an example of a crop that shows genetic diversity.
(c) Write the use of sacred grooves.
- A vector is engineered with three features, which facilitate its cloning within the host cell. List down and mention the three features and explain each of them.
OR
Explain with example how transgenic animals proved to be beneficial in:
(i) Production of biological products.
(ii) Chemical safety testing.
SECTION-D
Q. No. 29 and 30 are case-based questions. Each question has 3 subparts with internal choice in one subpart.
- In a study to test a new vaccine against the viral disease, mouse model testing is done. In this process, mice were vaccinated and their blood samples were tested. After a few days those mice were again infected with the virus. This time they do not show any disease symptoms. Their blood samples were tested. Two graphs show antibody concentration for the first and second infection in mice blood.
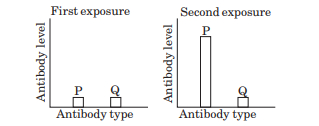
(a) Why the antibody concentration is high during second infection in mice?
(b) Which of the following cells is involved in humeral immunity?
(i) T-cells
(ii) B-cells
(iii) Mast cells
(iv) Both T & B cells.
(c) Which type of immunity is gained by the mice after second exposure with virus?
OR
Draw the labelled diagram of antibody.
30.
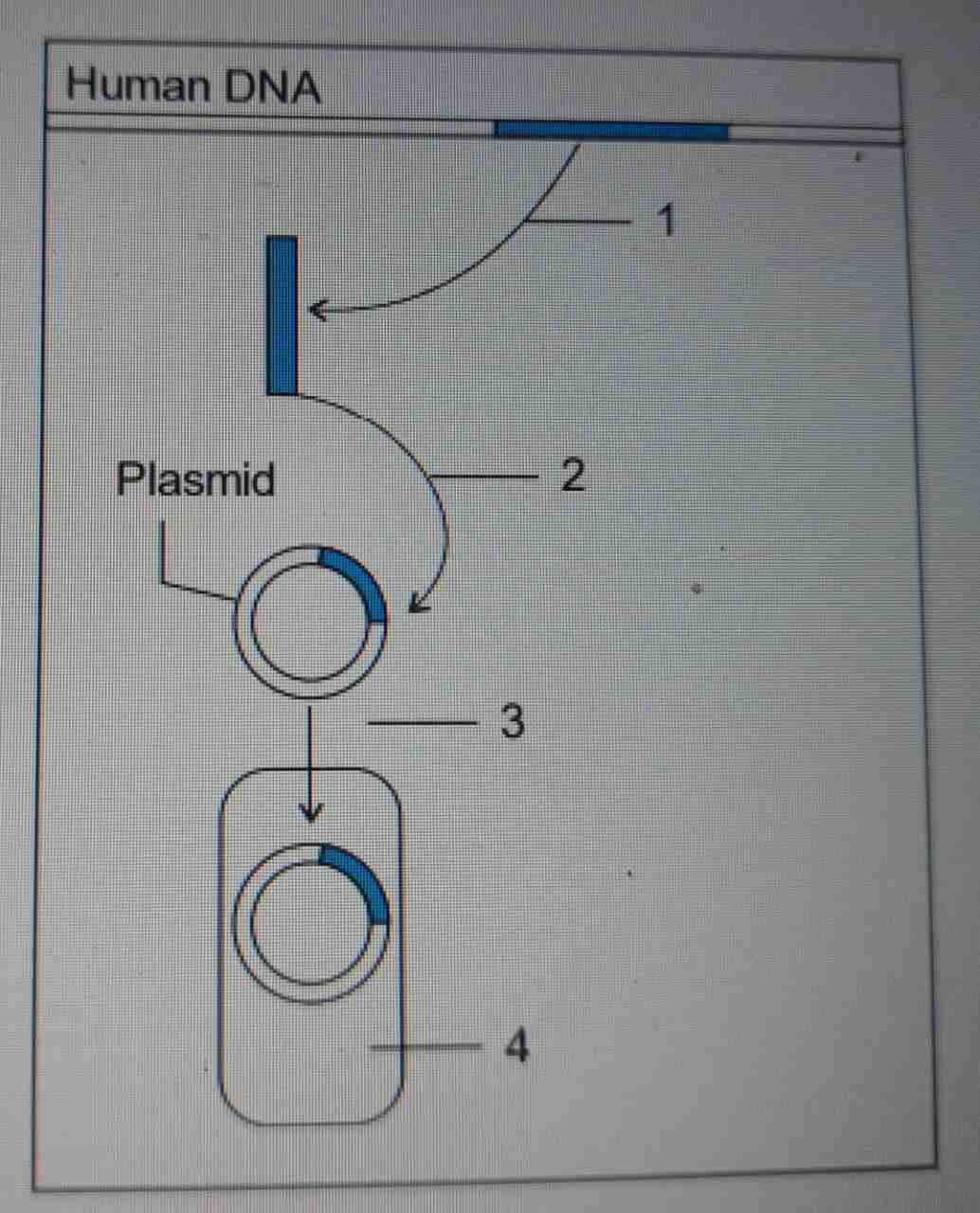
(a) Name the technique in biotechnology whose steps are shown in the above figure.
(b) Name the steps 1 to 4 marked in the figure.
(c) Give an example where a human gene product is obtained from transgenic bacteria
OR
Draw the structure of immature insulin.
SECTION-E
31.(a) Tropical regions in the world account for greater biological diversity. Justify with two reasons.
(b) Why habitat loss and alien species invasion considered as the cause of biodiversity loss? Explain each with an example.
OR
(a) Name the cells that act as HIV factory in humans when infected by HIV.
(b) Explain the events that occur in thses infected cells.
(c) How HIV causes the immune deficiency?
- (a) State the reasons for which Hershey and Chase used different radioactive isotopes and explain how they used them.
(b) What is the use of blending and centrifugation of culture?
(c) Write the observation and conclusion they arrived at.
OR
Given below is a stretch of DNA showing the coding strand of a structural gene of a transcription unit. 5- ATG ACC GTA TTT TCT GTA GTG CCC GTA CTT CAG GCA TAA - 3
(a) Write the corresponding template strand and the mRNA strand that will be transcribed, along with its polarity.
(b) If GUA of the transcribed mRNA is an intron, depict the sequence involved in the formation of hnRNA/the mature processed mRNA strand.
(i) In a bacterium
(ii) In humans
(c) Upon translation, how many amino acids will the resulting polypeptide have in case of humans?
- (a) Where does microsporogenesis occur in an angiosperm? Describe the process of microsporogenesis.
(b) Draw a labelled diagram of the two-celled male gametophyte of an angiosperm. How is the three celled male gametophyte different from it?
OR
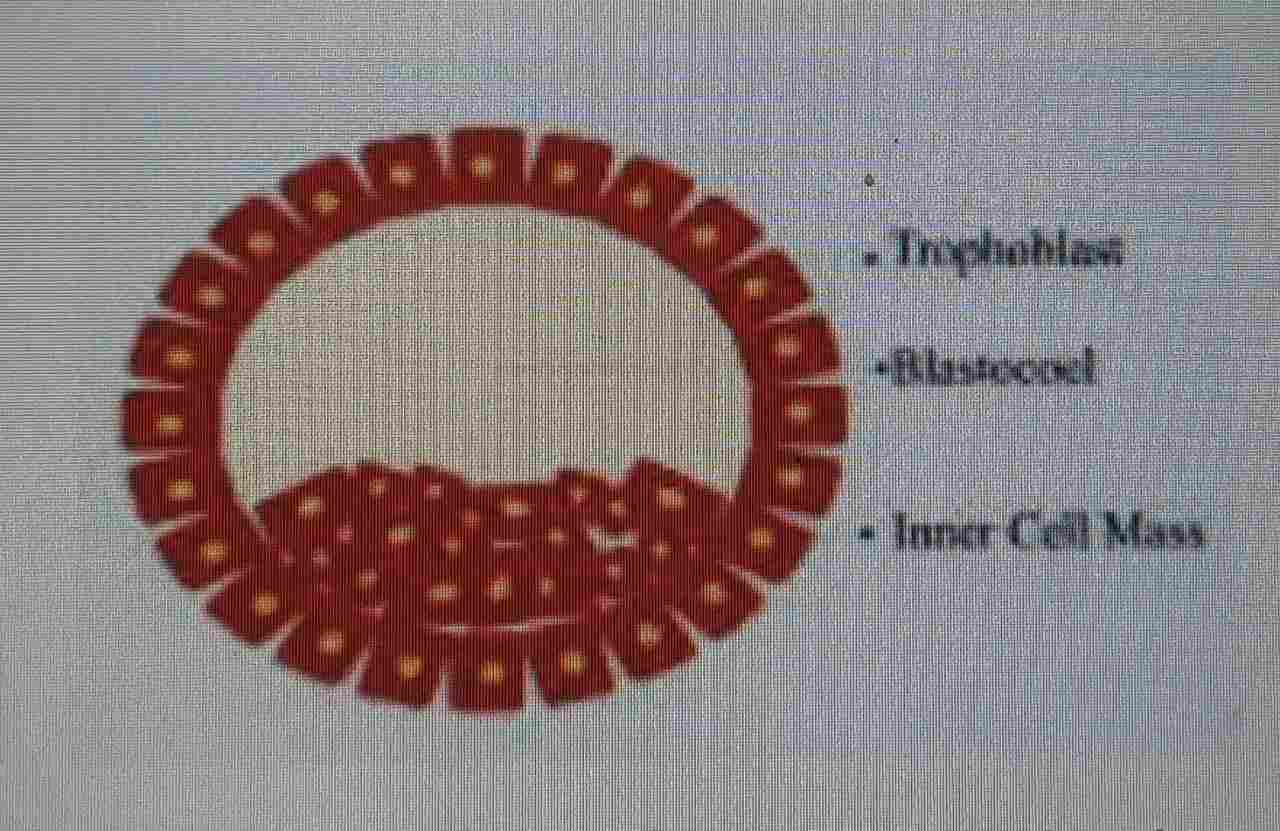
(a) Explain the events taking place at the time of fertilization of an ovum in human female.
(b) Name and draw a labelled sectional view of the embryonic stage that gets implanted.
Also Check: CBSE Class 12 Biology Syllabus 2024-25
SOLUTIONS
SECTION - A
- (c) Polygenic inheritance: Mirabilis jalapa
- (b) 24
- (b) (B), (C) & (D)
- (c) multicarpellary apocarpus.
- (c) 140 cells
- (b) lactose is present in binds to repressor
- (b) GUG, Valine
- (a) Convergent evolution
- (c) Cry I Ab
- (c) band I has longer DNA fragment than bands 2 and 3
- (c) blood cholesterol lowering statins
- (b) A, B, C, D
- (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- (b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
- (d) A is false but R is true.
- (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
SECTION - B
17.
| Spermatogenesis | Oogenesis |
|
|
- (a) increases the efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium through pores in its cell wall.
(b) By gene gun (biolistics): cells are bombarded with high velocity micro-particles of gold or tungsten coated with DNA.
- (a) Bone marrow & Thymus
(b) Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue.
- (a) In cross 'A' as genes are closely placed. Less the distance between the jeans greater is the strength of linkage.
(b) Non parental combinations be higher in case of cross 'B' as the distance between jeans is more and chance of crossing over will be more which leads to new combinations.
- According to 10% law of energy entering a particular trophic level of organism is available for transfer to the next trophic level. Producer level = 20,000 Joules Primary Consumer level 10% of 20,000 = 2,000 Joules Secondary Consumer level = 10% of 2,000 = 200 Joules Tertiary consumer level = 10% of 200 = 20 Joules.
OR
Detritus is composed of nitrogen and water-soluble substances like sugars. In the presence of oxygen, complex carbon compounds are oxidized to produce carbon dioxide.
SECTION-C
- (a) Dryopithecus & Ramapithecus
(b) Homo habilis (brain capacity-650-800cc) - Homo erectus (brain capacity - 900cc) - Neanderthal man (brain capacity - 1400cc).
- (a) FSH stimulate follicular development and secretion of estrogen. LH induces ovulation and development of corpus luteum which secrets progesterone.
(b) 60000-80000 primary follicles
- (a) IUDs (Intra Uterine Devices)
(b) LNG-20, a hormone releasing IUD make the uterus unsuitable for implantation and cervix hostile to sperms. While Cu ions of Cu-T suppress the motility of sperms.
(c) Lippes loop 25
- (a) • Apomictic seeds developed by diploid egg cell if it is formed without reduction division. • In some species like of citrus and mango, nucellar cells develop into embryos
(b) If hybrids are made into apomictic seeds, there is no segregation of characters in the hybrid and farmers can keep on using these seeds.
(c) Homo habilis probably did not eat meat while Homo erectus probably ate meat.
- 'Flocs' are masses of aerobic bacteria as associated with fungal filaments to form mesh like structures. These aerobic microbes consume the major part of the organic matter in the effluent. This significantly reduces biological oxygen demand (BOD) of the effluent. A small part of the activated sludge is used as inoculum and pumped back to aeration tank. The remaining major part of the sludge is pumped into anaerobic digester where microbes or bacteria grow anaerobically to produce CH4 , H2S and CO2 or biogas.
- (a) Temperature affects the kinetics of enzymes and through it the metabolic activity and other physiological functions of the organisms.
(b) Rice/ Mango/ Rauwolfia vomitoria.
(c) Sacred grooves are tracts of forests which are regenerated around places of worship. This is in situ conservation of forests.
- Features that facilitate cloning of vectors
- Origin of Replication (Ori): sequence of DNA from where replication starts. Piece of foreign DNA linked to it is made to replicate within the host cell. It also decides copy number of linked DNA.
- Selectable Marker: Antibiotic resistant genes that helps in selecting the host cells, which are transformants / recombinants from the non- recombinant ones.
- Cloning Site : unique recognition site in a vector to link the foreign DNA. It helps the particular restriction enzyme to cut the vector DNA.
- Small size of the vector : it facilitates the introduction of the DNA into the host easily.
OR
(i) Transgenic animals produced by the introduction of the portion of DNA which codes for a particular product such as human protein (-1- antitrypsin) used to treat emphysema, phenyl ketonuria and cystic fibrosis.
(ii) Animals are made to carry genes which make them more sensitive to toxic substances or chemicals than non-transgenic animals and when they are exposed to the toxic substances, the effects can be studied. Toxicity testing takes less time in such animals.
SECTION - D
- (a) Second encounter shows the secondary response. Memory of the first encounter leads to the production of higher amount of antibodies.
(b) (b) B-cells
(c) Acquired Active immunity
OR
Diagram on pg no. 151 of NCERT
- (a) Recombinant DNA technology/ genetic engineering
(b) 1 - cutting & isolation of human gene 2 - incorporation of human gene into plasmid to produce recombinant DNA. 3 - transformation of plasmid into bacteria 4 - transformant bacteria with rDNA
(c) Insulin obtained from transgenic bacteria
OR
Diagram on pg no. 211 of NCERT
SECTION-E
- (a) • Tropical regions relatively undisturbed for millions of years and had long evolutionary time for species diversification.
- Environment less seasonal/more constant and predictable and promotes niche specialisation.
- More solar energy available in tropics leads to higher productivity.
(b) Habitat loss : Amazon forests is being cut for cultivation of soyabeans/ degradation by pollution/clearing of forest for commercial or tourism purpose.
Alien species invasion : Nile perch introduced in Lake Victoria leads to extinction of cichlid fish/Introduction of African catfish Clarias gariepinus threat to indigenous catfish/carrot grass and water hyacinth causes threat to indigenous species.
OR
(a) Macrophages
(b) Diagram on pg no. 155 of NCERT
(c) Progeny HIV enters into helper T-lymphocytes, replicates, released in blood attack other helper T-lymphocytes, leads to immune deficiency
- (a) Some bacteriophages grown on medium having radioactive (35S) to obtain radioactive protein coat and some bacteriophages grown on medium having radioactive (32P) to obtain radioactive DNA.
(b) Blending or agitating to remove viral coats from bacteria. Centrifugation to separate““virus particles from bacteria by spinning them.
(c) Bacteria which was infected with viruses that had radioactive DNA were radioactive, indicating that DNA was the material that passed from virus to bacteria/ bacteria that were infected with viruses that had radioactive proteins were not radioactive; indicating that protein did not enter the bacteria from viruses. Thus DNA is genetic material.
OR
(a) Template strand
3-TAC TGG CAT AAA AGA CAT CAC GGG CAT GAA GTC CGT ATT—
5’mRNA Strand 5’-- AUG ACC GUA UUU UCU GUA GUG CCC GUA CUU CAG GCA UAA - 3’
(b) GUA is intron““mRNA in bacterium““5-AUG ACC GUA UUU UCU GUA GUG CCC GUA CUU CAG GCA UAA-3'
Processed mRNA in humans after removal of introns :
5'-AUG ACC GUA UUU UCU GUA GUG CCC GUA CUU CAG GCA UAA -3' 5'-AUG ACC UUU UCU GUG CCC CUU CAG GCA UAA -3'
(c) 9 amino acids forms polypeptide as UAA is stop codon.
- (a) In pollen sacs or microsporangia of each another lobe.
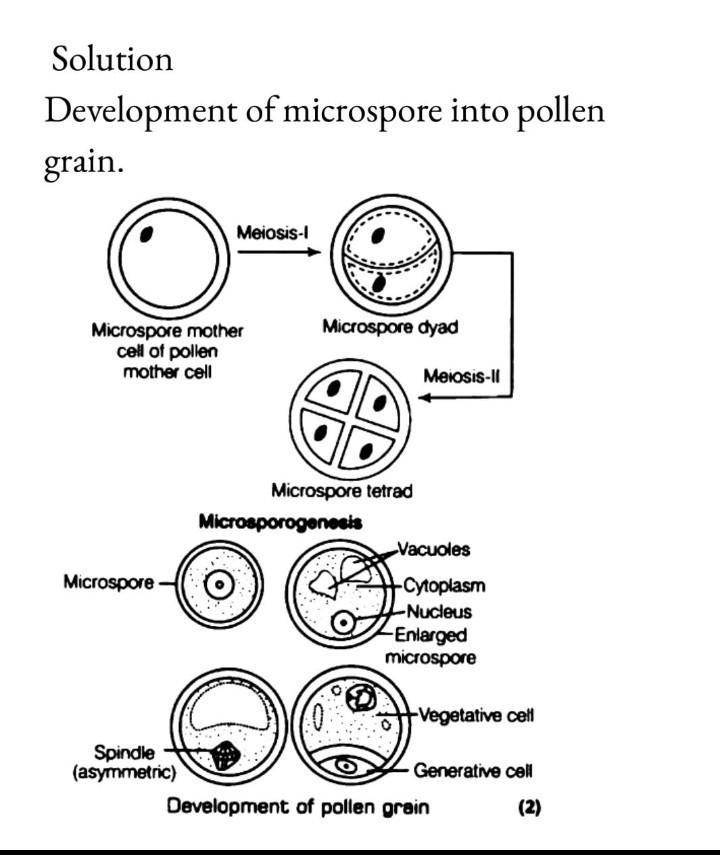
(b) In Over 60% of angiosperms, pollen grains are shed at two-celled stage (one generative and other vegetative). In others, the generative cell di- vides mitotically to give rise to 2 male gametes before pollen grains are shed, called 3-celled stage.
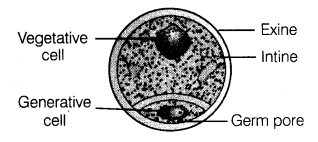
OR
(a) Sperms comes in contact with zona pellucida layer of ovum, induces the changes in the membrane of ovum and block the entry of other sperms (prevent polyspermy), lytic enzymes/secretions of acrosome helps the entry of sperm head, completion of meiotic division of secondary oocyte, formation of second polar body and ovum/ootid, fusion of nuclei of sperm and ovum forming zygote.
(b) Blastocyst
CBSE Class 12 Biology Sample Paper 2025: Download PDF
Also Check:
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Marking Scheme 2024-25
- CBSE Class 12 COMPLETE Study Material
- CBSE Class 10 COMPLETE Study Material
- CBSE Class 12 Deleted Syllabus 2025
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2024-2025: Download PDF of All Subjects
- CBSE Class 12 Subject Wise Exam Pattern And Marking Scheme 2025
- CBSE Class 12 Competency-Based Questions 2025
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation