New CBSE Syllabus 2021-22 for Class 12 Biology is available here for download. Link to download CBSE Class 12 Biology Syllabus 2021-22 is given at the end of this article. Besides CBSE class 12 Biology Syllabus 2021-22, here students will also get details about paper pattern & links to access other important articles for upcoming CBSE board exam preparation.
Also Check: NCERT Books for Class 12 (PDF): All Subjects - Subject-wise & Chapter-wise
CBSE Class 12 Biology Syllabus 2021-22:
Theory Paper - Time: 03 Hours, Max. Marks: 70
| Unit | Title | No. of Periods | Marks |
| VI | Reproduction | 30 | 14 |
| VII | Genetics and Evolution | 40 | 18 |
| VIII | Biology and Human Welfare | 30 | 14 |
| IX | Biotechnology and its Applications | 30 | 10 |
| X | Ecology and Environment | 30 | 14 |
|
| Total | 160 | 70 |
NCERT Solutions for CBSE Class 12 Biology ‒ All Chapters
Unit-VI Reproduction
Chapter-1: Reproduction in Organisms
Reproduction, a characteristic feature of all organisms for continuation of species; modes of reproduction - asexual and sexual reproduction; asexual reproduction - binary fission, sporulation, budding, gemmule formation, fragmentation; vegetative propagation in plants; events in sexual reproduction.
Chapter-2: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Flower structure; development of male and female gametophytes; pollination - types, agencies and examples; outbreeding devices; pollen-pistil interaction; double fertilization; post fertilization events - development of endosperm and embryo, development of seed and formation of fruit; special modes- apomixis, parthenocarpy, polyembryony; Significance of seed dispersal and fruit formation.
Chapter-3: Human Reproduction
Male and female reproductive systems; microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary; gametogenesis - spermatogenesis and oogenesis; menstrual cycle; fertilisation, embryo development upto blastocyst formation, implantation; pregnancy and placenta formation (elementary idea); parturition (elementary idea); lactation (elementary idea).
Chapter-4: Reproductive Health
Need for reproductive health and prevention of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs); birth control - need and methods; medical termination of pregnancy (MTP); amniocentesis; infertility and assisted reproductive technologies - IVF, ZIFT, GIFT, AI (brief overview).
Unit-VII Genetics and Evolution
Chapter-5: Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Heredity and variation, Mendelian inheritance; deviations from Mendelism – incomplete dominance, co-dominance, multiple alleles and inheritance of blood groups, pleiotropy; elementary idea of polygenic inheritance; chromosome theory of inheritance; chromosomes and genes; linkage and crossing over; Sex determination - in human being, birds, grasshopper and honey bee; Mutation, Pedigree analysis, sex linked inheritance - haemophilia, colour blindness; Mendelian disorders in humans –sickle cell anaemia, Phenylketonuria, thalassemia; chromosomal disorders in humans; Down's syndrome, Turner's and Klinefelter's syndromes.
Chapter-6: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Structure of DNA and RNA; DNA packaging; Search for genetic material and DNA as genetic material; DNA replication; Central Dogma; transcription, genetic code, translation; gene expression and regulation - lac operon; Human genome project; DNA fingerprinting.
Chapter-7: Evolution
Origin of life; biological evolution and evidences for biological evolution (paleontology, comparative anatomy, embryology and molecular evidences); adaptive radiation; Biological evolution: Lamarck’s theory of use and disuse of organs, Darwin's theory of evolution; mechanism of evolution - variation (mutation and recombination) and natural selection with examples, types of natural selection; Gene flow and genetic drift; Hardy - Weinberg's principle; brief account of evolution; human evolution.
Unit-VIII Biology and Human Welfare
Chapter-8: Human Health and Diseases
Pathogens; parasites causing human diseases (malaria, dengue, chikungunya, filariasis, ascariasis, typhoid, pneumonia, common cold, amoebiasis, ringworm) and their control; Basic concepts of immunology - vaccines; cancer, HIV and AIDS; Adolescence - drug and alcohol abuse.
Chapter-9: Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Animal husbandry, Plant breeding, tissue culture, single cell protein.
Chapter-10: Microbes in Human Welfare
Microbes in food processing, industrial production, Antibiotics; production and judicious use, sewage treatment, energy generation and microbes as biocontrol agents and bio-fertilizers.
Unit-IX Biotechnology and its Applications
Chapter-11: Biotechnology - Principles and Processes
Genetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology).
Chapter-12: Biotechnology and its Application
Application of biotechnology in health and agriculture: genetically modified organisms - Bt crops; RNA interference, Human insulin, gene therapy; molecular diagnosis; transgenic animals; biosafety issues, biopiracy and patents.
Unit-X Ecology and Environment
Chapter-13: Organisms and Populations
Organisms and environment: Habitat and niche, abiotic factors, ecological adaptations; population interactions - mutualism, competition, predation, parasitism, commensalism; population attributes - growth, birth rate and death rate, age distribution.
Chapter-14: Ecosystem
Ecosystem: structure and function; productivity and decomposition; energy flow; pyramids of number, biomass, energy; nutrient cycles (carbon and phosphorous); ecological succession; ecological services - carbon fixation, pollination, seed dispersal, oxygen release (in brief).
Chapter-15: Biodiversity and Conservation
Biodiversity - Concept, levels, patterns, importance; loss of biodiversity; biodiversity conservation; hotspots, endangered organisms, extinction, Red Data Book, Sacred Groves, biosphere reserves, national parks, wildlife, sanctuaries and Ramsar sites.
Chapter-16: Environmental Issues
Air pollution and its control; water pollution and its control; agrochemicals and their effects; solid waste management; radioactive waste management; greenhouse effect and climate change impact and mitigation; ozone layer depletion; deforestation; case study exemplifying success story addressing environmental issue(s).
CBSE Class 12 Biology Practical: 2021-22
Time allowed: 3 Hours, Max. Marks: 30
| Evaluation Scheme | Marks | |
| One Major Experiment 5, 6, 8, 9 | 5 | |
| One Minor Experiment 2, 3, 4 | 4 | |
| Slide Preparation 1, 7 | 5 | |
| Spotting | 7 | |
| Practical Record + Viva Voce | Credit to the students’ work over the academic session may be given | 4 |
| Investigatory Project and its Project and its Record + Viva Voce | 5 | |
| Total | 30 | |
A. List of Experiments, 60 Periods
1. Prepare a temporary mount to observe pollen germination.
2. Collect and study soil from at least two different sites and study them for texture, moisture content, pH and water holding capacity. Correlate with the kinds of plants found in them.
3. Collect water from two different water bodies around you and study them for pH, clarity and presence of any living organism.
4. Study the presence of suspended particulate matter in air at two widely different sites.
5. Study the plant population density by quadrat method.
6. Study the plant population frequency by quadrat method.
7. Prepare a temporary mount of onion root tip to study mitosis.
8. Study the effect of different temperatures and three different pH on the activity of salivary amylase on starch.
9. Isolate DNA from available plant material such as spinach, green pea seeds, papaya, etc.
B. Careful observation of the following (Spotting):
1. Flowers adapted to pollination by different agencies (wind, insects, birds).
2. Pollen germination on stigma through a permanent slide or scanning electron micrograph.
3. Identification of stages of gamete development, i.e., T.S. of testis and T.S. of ovary through permanent slides (from grasshopper/mice).
4. Meiosis in onion bud cell or grasshopper testis through permanent slides.
5. T.S. of blastula through permanent slides (Mammalian).
6. Mendelian inheritance using seeds of different colour/sizes of any plant.
7. Prepared pedigree charts of any one of the genetic traits such as rolling of tongue, blood groups, ear lobes, widow's peak and colourblindness.
8. Controlled pollination - emasculation, tagging and bagging.
9. Common disease causing organisms like Ascaris, Entamoeba, Plasmodium, any fungus causing ringworm through permanent slides, models or virtual images. Comment on symptoms of diseases that they cause.
10. Two plants and two animals (models/virtual images) found in xeric conditions. Comment upon their morphological adaptations.
11. Two plants and two animals (models/virtual images) found in aquatic conditions. Comment upon their morphological adaptations.
CBSE Class 12 Biology: Prescribed Books
1. Biology, Class-XII, Published by NCERT
2. Other related books and manuals brought out by NCERT (including multimedia)
3. Biology Supplementary Material (Revised). Available on CBSE website.
Practical Examination for Visually Impaired Students of Classes XI and XII Evaluation Scheme
Time Allowed: Two hours, Max. Marks: 30
| Topic | Marks |
| Identification/Familiarity with the apparatus | 5 |
| Written test (Based on given / prescribed practicals) | 10 |
| Practical Records | 5 |
| Viva | 10 |
| Total | 30 |
General Guidelines
· The practical examination will be of two-hour duration. A separate list of experiments is included in the curriculum.
· The written examination in practicals for these students will be conducted at the time of practical examination of all other students.
· The written test will be of 30 minutes duration.
· The question paper given to the students should be legibly typed. It should contain a total of
15 practical skill based very short answer type questions. A student would be required to answer any 10 questions.
· All questions included in the question paper should be related to the listed practicals. Every question should require about two minutes to be answered.
· Questions may be generated jointly by the external/internal examiners and used for assessment.
· A writer may be allowed to such students as per CBSE examination rules.
· These students are also required to maintain a practical file. A student is expected to record at least five of the listed experiments as per the specific instructions for each subject. These practicals should be duly checked and signed by the internal examiner.
· The format of writing any experiment in the practical file should include aim, apparatus required, simple theory, procedure, related practical skills, precautions etc.
· The viva questions may include questions based on basic theory / principle / concept, apparatus / materials / chemicals required, procedure, precautions, sources of error etc.
CBSE Class 12 Biology Paper Pattern 2021-22:
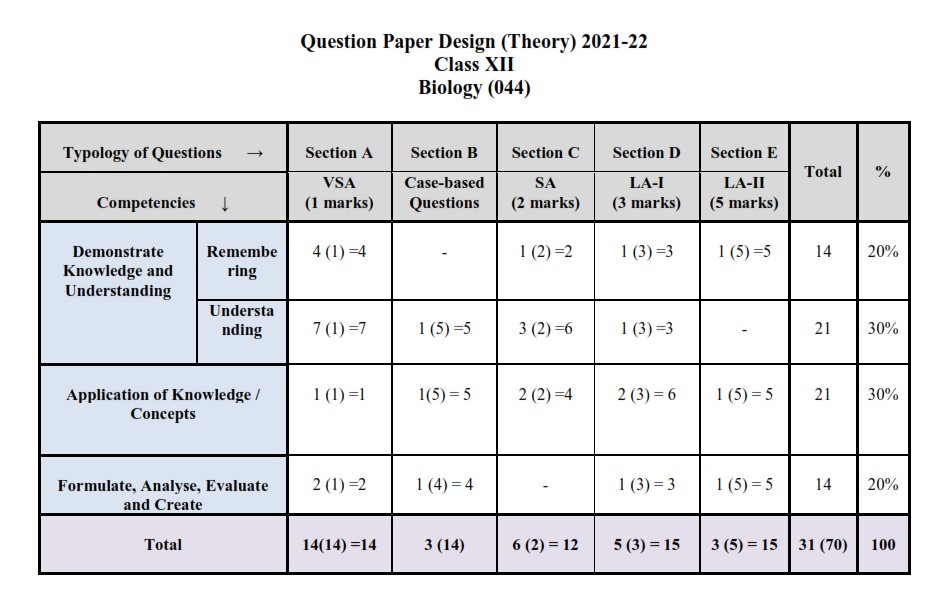
Note:
All questions would be compulsory. However, an internal choice of approximately 33%
would be provided.
⇒ Section ‘A’ would have 10 MCQs (including matching type MCQs) and 04 Assertion-
Reasoning type questions of one mark each.
⇒ Section ‘B’ would have 3 source-based/case-based /passage-based/integrated assessment questions: 2 questions of 5 marks each and 1 question of 4 marks with sub parts of the values 1/2/3 marks each.
⇒Section ‘C’ would have 6 Short Answer (SA) type questions carrying 2 marks each.
⇒ Section ‘D’ would have 5 Long Answer-I (LA-I) type questions carrying 3 marks each.
⇒Section ‘E’ would have 3 Long Answer-II (LA-II) type questions carrying 5 marks each.
⇒Internal Choice would be provided in 3 questions of Section ‘C’, in 2 questions of Section ‘D’
and in all three questions of Section ‘E’.
Suggestive verbs for various competencies
· Demonstrate Knowledge and Understanding
State, name, list, identify, define, suggest, describe, outline, summarize, etc.
· Application of Knowledge/ConceptsCalculate
illustrate, show, adapt, explain, distinguish, etc.
· Formulate, Analyze, Evaluate and Create
Interpret, analyse, compare, contrast, examine, evaluate, discuss, construct, etc.
Download CBSE Class 12 Biology Syllabus 2021-22 PDF
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation