CBSE Class 12 Informatics Practices Syllabus 2022-2023: CBSE Class 12 students can check and download here the new CBSE Syllabus of Informatics Practices. The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has released the revised CBSE Class 12 Informatics Practices Syllabus for the current academic session, 2022-23. Students must go through the full syllabus to know the details of the course structure and evaluation scheme.
Check CBSE Class 12 Informatics Practices (Code 065) Syllabus 2022-23 below:
1. Prerequisite: Informatics Practices – Class XI
2. Learning Outcomes
At the end of this course, students will be able to:
- Create Series, Data frames and apply various operations.
- Visualize data using relevant graphs.
- Design SQL queries using aggregate functions.
- Import/Export data between SQL database and Pandas.
- Learn terminology related to networking and internet.
- Identify internet security issues and configure browser settings.
- Understand the impact of technology on society including gender and disability issues.
Also Check CBSE Class 12 Syllabus of All Subjects for 2022-2023 Session (PDF)
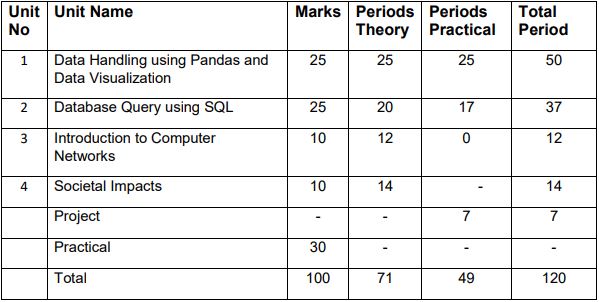
3. Distribution of Marks and Periods
4. Unit Wise syllabus
Unit 1: Data Handling using Pandas -I
Introduction to Python libraries- Pandas, Matplotlib. Data structures in Pandas - Series and Data Frames.
Series: Creation of Series from – array, dictionary, scalar value; mathematical operations; Head and Tail functions; Selection, Indexing and Slicing.
Data Frames: creation - from dictionary of Series, list of dictionaries, Text/CSV files; display; iteration; Operations on rows and columns: add, select, delete, rename; Head and Tail functions; Indexing using Labels, Boolean Indexing;
Importing/Exporting Data between CSV files and Data Frames.
Data Visualization
Purpose of plotting; drawing and saving following types of plots using Matplotlib – line plot, bar graph, histogram
Customizing plots: adding label, title, and legend in plots.
Unit 2: Database Query using SQL
Math functions: POWER (), ROUND (), MOD ().
Text functions: UCASE ()/UPPER (), LCASE ()/LOWER (), MID ()/SUBSTRING ()/SUBSTR (), LENGTH (), LEFT (), RIGHT (), INSTR (), LTRIM (), RTRIM (), TRIM ().
Date Functions: NOW (), DATE (), MONTH (), MONTHNAME (), YEAR (), DAY (), DAYNAME ().
Aggregate Functions: MAX (), MIN (), AVG (), SUM (), COUNT (); using COUNT (*).
Querying and manipulating data using Group by, Having, Order by.
Unit 3: Introduction to Computer Networks
Introduction to networks, Types of network: LAN, MAN, WAN.
Network Devices: modem, hub, switch, repeater, router, gateway
Network Topologies: Star, Bus, Tree, Mesh.
Introduction to Internet, URL, WWW, and its applications- Web, email, Chat, VoIP.
Website: Introduction, difference between a website and webpage, static vs dynamic web page, web server and hosting of a website.
Web Browsers: Introduction, commonly used browsers, browser settings, add-ons and plug-ins, cookies.
Unit 4: Societal Impacts
Digital footprint, net and communication etiquettes, data protection, intellectual property rights (IPR), plagiarism, licensing and copyright, free and open source software (FOSS), cybercrime and cyber laws, hacking, phishing, cyber bullying, overview of Indian IT Act.
E-waste: hazards and management.
Awareness about health concerns related to the usage of technology.
Project Work
The aim of the class project is to create tangible and useful IT application. The learner may identify a real-world problem by exploring the environment. e.g. Students can visit shops/business places, communities or other organizations in their localities and enquire about functioning of the organization, and how data are generated, stored, and managed.
The learner can take data stored in csv or database file and analyze using Python libraries and generate appropriate charts to visualize.
If an organization is maintaining data offline, then the learner should create a database using MySQL and store the data in tables. Data can be imported in Pandas for analysis and visualization.
Learners can use Python libraries of their choice to develop software for their school or any other social good.
Learners should be sensitized to avoid plagiarism and violation of copyright issues while working on projects. Teachers should take necessary measures for this. Any resources (data, image etc.) used in the project must be suitably referenced.
The project can be done individually or in groups of 2 to 3 students. The project should be started by students at least 6 months before the submission deadline.
Practical Marks Distribution
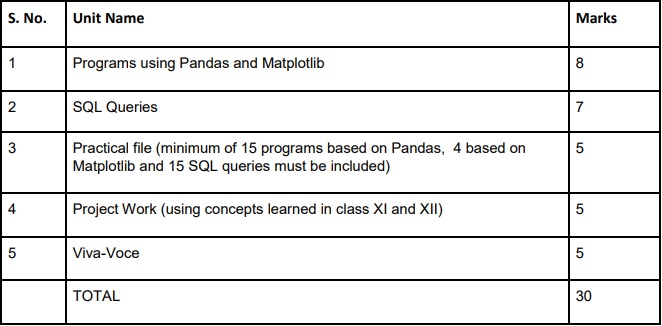
Download the full syllabus from the following link and check details of practical work:
CBSE Class 12 Informatics Practices Syllabus 2022-23: Download in PDF |
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation