BSEH Haryana Board Class 12 Economics Model Paper 2025: If you are a HBSE Class 12 student, looking for the Economics model paper, well then your search ends here. Students might be aware that the Haryana Board of School Education (HBSE) has released the model test papers for the students of class 12 for almost all the subjects. The model papers are for the session 2024-25 and 2025 board examination. Here we have given the HBSE Class 12 Economics Model Test Paper and marking scheme.
HBSE has also released the marking scheme for various subjects with the model paper. The model test papers will give students insights into typology of questions, marks pattern and question paper format. There are different types of questions such as multiple choice, short and long answer questions.
Why Solve Sample Papers?
Sample question papers are an important resource for students. Students should solve as many sample papers as they can to check their knowledge and preparation. Sample question papers help students to understand how much they have understood from what they have learned. In addition, solving sample papers help students to develop writing practice and get better at time management.
Download the HBSE Class 12 Economics Model Paper and Marking scheme in PDF format for free from the links in this article.
HBSE Class 12 Economics Question Paper Instructions 2024-25
1. The question paper has two parts; In Part A (Micro Economics) and Part B (Macro Economics). All questions are compulsory.
2. Marks prescribed for each question are given against it.
3. Question numbers 1 to 10 and 18 to 27 are objective questions. Each question carries one mark. Answer these questions as per instructions.
4. Question numbers 11 to 12 and 28 to 29 are very short answer type questions in which each question carries 3 marks and the answer to each should generally not exceed 30 words.
5. Question numbers 13 to 15 and 30 to 32 are short answer questions in which each question carries 4 marks. Answers to each should normally not exceed 60 words.
6. Question numbers 16 to 17 and 33 to 34 are long answer questions in which each question carries 6 marks. The answer to each should generally not exceed 130 words.
7. Internal relaxation is available in some questions. You have to attempt only one of these questions.
8. Word limit does not apply to questions containing numerical and graphical.
Also Read: NCERT Class 12 Revised Textbooks
HBSE Class 12 Economics Model Paper 2024-25
Check the questions from HBSE Class 12 Economics Model Test Paper 2024-25.
PART A
Q1. Which of the following is the study of microeconomics?
(A) Aggregate demand
(B) Business cycle
(C) Consumer equilibrium
(D) National income
Ans. (C)
Q2. Equilibrium point is the point at which the forces of demand and supply
(A) Not Equal
(B) Equal
(C) does not work
(D) goes back and forth
Ans. (B)
Q3. Opportunity cost is meant by:-
(A) cost of alternative use
(B) Actual cost
(C) total cost
(D) None of these
Ans. (A)
Q4. In perfect competition a firm is in a state of equilibrium when:
(A) MC= Zero
(B) MC=TR
(C) MC=MR
(D) AC=AR
Ans. (C)
Q5. Select the correct formula:
(A) MC=TC-TVC
(B) MC=TFC+TVC
(C) MC=TCN+1-TCN
(D) TFC=AFC/Q
Ans. (C)
Q6. When TP is maximum:
(A) MP= Zero
(B) MP= +ive
(C) MP= -ive
(D) AP= Zero
Ans. (A)
Q7. Economics is a ………………….. science. (social, natural).
Ans. Social
Q8. Support price is determined by the government..... the equilibrium price. (below/above)
Ans. Above
Q9. What is the shape of the demand curve?
Ans. -VE
Read the following statement- Assertion (A) and Reason (R) .
Choose one of the correct alternatives given below .
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(A) Assertion (A) is true , but Reason (R) is false.
(B) Assertion (A) is false , but Reason (R) is true.
Q10. Assertion (A) : The average variable cost curve is U shaped.
Reason (R) : AFC=TFC/Q
Ans. (B)
Q11. Mention about the central problems of the economy.
Ans. Central problems are the common problems of an economy. These problems are due to limited resources and unlimited wants of humans.
1. What to produce :-consumer goods or capital goods
2. How to produce :- labour intensive technique or capital intensive technique
3. For whom to produce :-for self consumption or market selling.
Q12. Describe the characteristics of indifference curves.
Ans. 1. ICs are slope –ve.
2. ICs are convex to origin.
3. ICs never intersect each others.
4. Higher ICs show higher level of satisfaction.
5. ICs never touch X-Axis or Y-Axis .
OR
A consumer spends Rs. 50 on a good when its price is Rs. 1 per unit and spends Rs.64 when its price is Rs. 2 per unit. Find the price elasticity of the good.
Ans. Ed < 1
As +Ve Relation b/w Price & Total Exp.
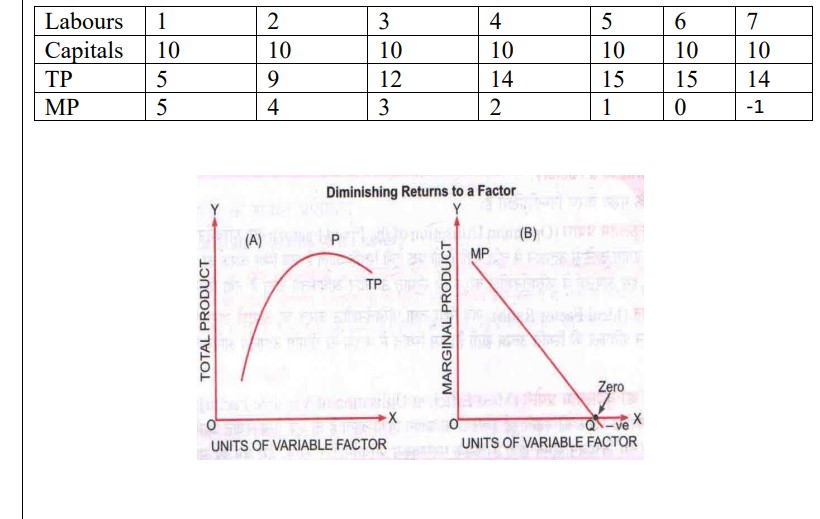
Q13. Explain the diminishing returns of factors with the help of table and graph.
Ans. Diminishing Return to Factor : In the short run with fixed factors if we increase variable factors then total products increase at decreasing rate and in this situation marginal product will decrease and cost will increase.
Q14. Explain with the help of a diagram how a farm can be earn supernormal profit in the short run in a perfectly competitive market.
Ans. Super Normal Profit under PC:
A firm will be in the equilibrium if
1. MC =MR
2. MC curve cut MR curve from below.
A firm will earned Super normal Profit if average revenue is more than average cost. i.e. AR > AC.
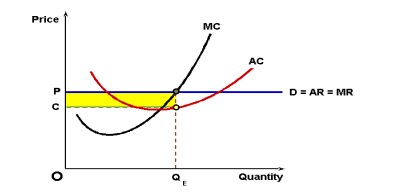
Here , SNP is shown by shaded area.
OR
Find the following from the table -
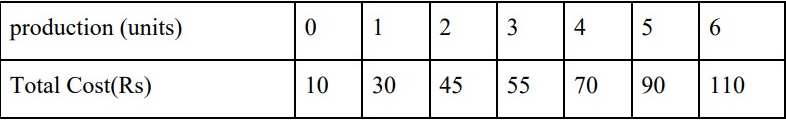
1. Total variable Cost (TVC)
2. Average Fixed Cost (AFC)
3. Average variable cost (AVC)
4. Marginal cost (MC)
Ans. 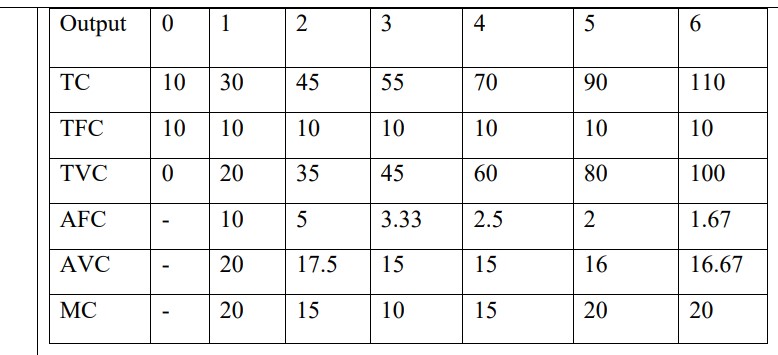
Q15. What is equilibrium price? How it is determined ?
Ans. Equilibrium Price: when market forces will be equal to each other i.e. market demand is equal to market supply then there will be price equilibrium.
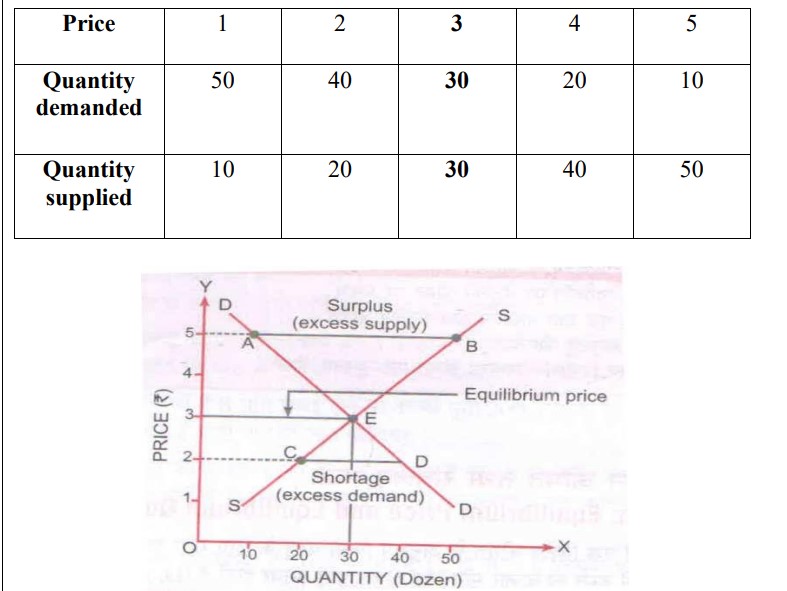
OR
Explain the difference between control price and support price.
Ans. 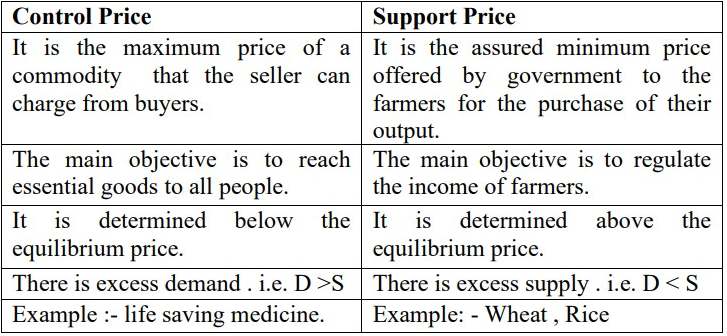
Q16. Describe total expenditure method of measuring price elasticity of demand.
Ans. It shows how much total expenditure of a good change and in which direction due to change in the price of a good.
1) If price ↑ or ↓ and TE remain constant then Ed= 1
2) If price ↑ and TE ↓ or price ↓ and TE ↑ then Ed > 1
3) If price ↑ and TE ↑ or price ↓ and TE↓ then Ed < 1
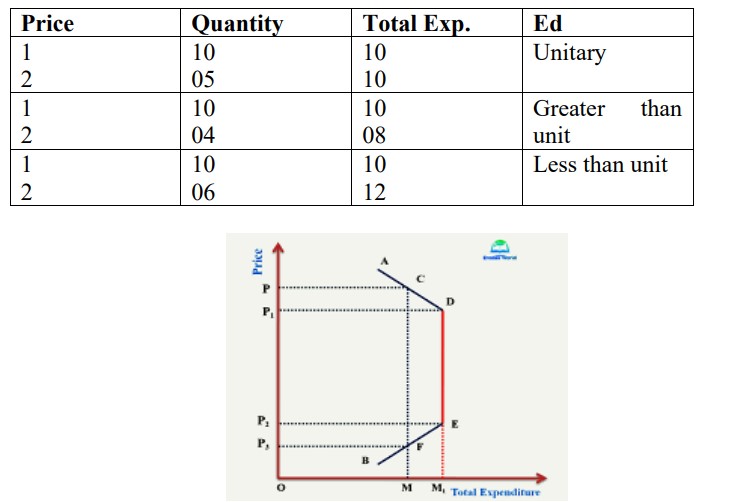
OR
What is the law of demand? Why does this law apply?
Ans. Law of Demand: Law of demand states that other things being equal, there is inverse relation between price and quantity demanded. The main causes of application of law of demand are given below: 1. Law of Diminishing Marginal Utilities. 2. Income Effects 3. Substitution effects 4. Size of consumers 5. Different Uses.
Q17. Explain the meaning and characteristics of a perfectly competitive market.
Ans. Meaning of Perfect competition: - Perfect competition is a market situation where large number of buyers and sellers are buying and selling homogenous products at equal price.
Main features:-
1. Large no. of buyers and sellers
2. Homogenous products
3. AR=MR
4. Firms is price taker and industry is price maker
5. Perfect knowledge
6. Perfect mobility
7. Lack of transportation cost
8. Lack of advertisement cost
OR
What is meant by producer equilibrium? Explain producer equilibrium by marginal method.
Ans. Meaning of marginal revenue and marginal cost then
i) If MR is greater than MC then firm will increase output
ii) If MR is less than MC then firm will decrease output
iii) If MR=MC and MC is rising ,then firm will be equilibrium
Conditions of equilibrium
a) MR=MC
b) MC cuts MR from below.
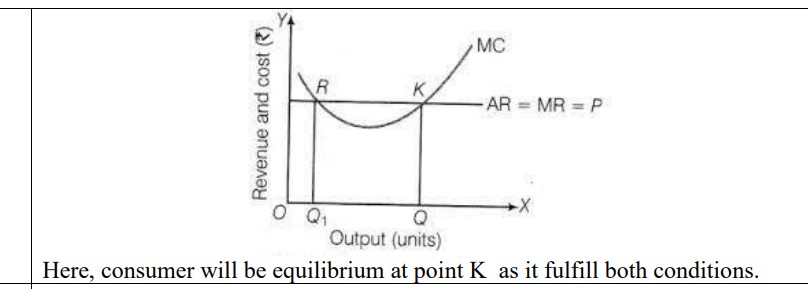
To get the complete sample paper and marking scheme, refer to the links given below:
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation