The ICSE Class 10 Chemistry exam is one of the most important exams for students aiming to excel in science. Understanding the exam pattern, question types, and solutions is crucial for effective preparation. This article provides the ICSE Class 10 Chemistry 2024 question paper along with solutions, helping students analyse their performance and gain clarity on complex topics.
By going through the solved question paper, students can identify important topics, understand the marking scheme, and improve their answering techniques. Whether you want to cross-check your responses or prepare for upcoming exams, this guide will serve as a valuable resource. Download the PDF and make the most of these expert-verified solutions.
ICSE Class 10 Chemistry 2024 Question Paper with Solutions
Question-1: Choose the correct answers to the questions from the given options.
(i) Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo:
(a) Addition reaction (b) Substitution reaction
(c) Oxidation reaction (d) Redox reaction
(ii) In the 2nd period, Neon has maximum Ionisation Potential because:
(a) It has unstable electronic configuration.
(b) It easily accepts electrons.
(c) It easily loses electrons.
(d) The outer most shell is completely filled.
(iii) Copper, Zinc, and Tin are the metals alloyed to form:
(a) Duralumin (b) Brass
(c) Bronze (d) Solder
(iv) The metal hydroxide which reacts with both acids and alkalis to form salt and water is:
(a) Calcium hydroxide
(b) Magnesium hydroxide
(c) Aluminium hydroxide
(d) Ferric hydroxide
(v) Reaction of an alcohol with a carboxylic acid in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 is termed as:
(a) Halogenation (b) Esterification
(c) Hydrogenation (d) Dehydrohalogenation
(vi) Conversion of Ethanol to Ethene by the action of concentrated sulphuric acid involves:
(a) Dehydration (b) Dehydrogenation
(c) Dehydrohalogenation(d) Hydrolysis
(vii) The oxidising agent in the equation, S + 2H2SO4 - 3SO2 + 2H2O is:
(a) Sulphur (b) Sulphuric acid
(c) Sulphur dioxide (d) Water
(viii) Electron Affinity is maximum in:
(a) Mg (b) Ar
(c) Li (d) Br
(ix) The compound that is not a constituent of the electrolytic mixture used in the Hall-Heroult's process is:
(a) Al2O3 (b) NaAlO2
(c) Na3AlF6 (d) CaF2
(x) On passing ammonia gas over heated copper oxide for some time, a reddish-brown residue is left behind. What property of ammonia is demonstrated here?
(a) Basic property
(b) Oxidising property
(c) Reducing property
(d) Acidic property
(xi) Rotten egg smell is due to the liberation of:
(a) HCl gas (b) H2S gas
(c) Cl2 gas (d) SO2 gas
(xii) Ammonia gas is collected by downward displacement of air since ammonia is:
(a) very slightly soluble in water.
(b) heavier than air.
(c) lighter than air.
(d) insoluble in water.
(xiii) Which of the following would occupy 22.4 litres at S.T.P.?
1. 32 g of oxygen gas
2. 2 moles of hydrogen gas
3. 6.022 × 1023 molecules of ammonia
(a) 1 and 2 (b) 1 and 3
(c) 2 and 3 (d) 1, 2 and 3
[Atomic weights: O = 16, H = 1, N = 14]
(xiv) In the molecule of water, oxygen atom has:
(a) One shared pair of electrons.
(b) Three shared pair of electrons.
(c) Two lone pairs of electrons.
(d) One lone pair of electrons.
(xv) A mineral from which the metal can be extracted economically and conveniently is known as:
(a) Matrix (b) Ore
(c) Flux (d) Alloy
Question-2
(i) The following sketch represents the electroplating of an Iron cup with Nickel metal. Study the diagram and answer the following questions.
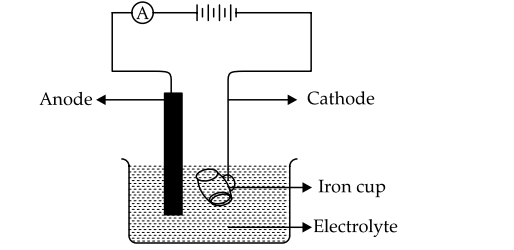
(a) During electroplating the iron cup is placed at the cathode. Why?
(b) Name the ion that must be present in the electrolyte.
(c) State one condition that is necessary to ensure that the deposit is smooth, firm and even.
(d) Write the reaction taking place at the cathode.
(e) What change would you observe at the anode?
(ii) Match the column A with Column B:
(a) Water 1. Lithium
(b) Alkali metal 2. Iodine
(c) Halogen 3. Covalent compound
(d) Calcium oxide 4. Acetic acid
(e) Weak acid 5. Ionic compound
6. Sulphuric acid
(iii) Complete the following sentence by choosing the correct answer from the brackets:
(a) The salt that can be prepared by Direct Combination is ................. . [FeCl3/FeCl2]
(b) The metallic oxide which can be reduced by using common reducing agents is ...................[Fe2O3/Al2O3]
(c) The metal nitrate which on thermal decomposition forms a black residue is .................[zinc nitrate/copper nitrate]
(d) During the electrolysis of copper sulphate solution, if ................ is used as electrode, the colour of the electrolyte does not fade.[copper/platinum]
(e) The process of heating the concentrated ore in a limited supply or absence of air is ................ [roasting/calcination]
(iv) State the terms for the following:
(a) The group obtained by removing one hydrogen atom from the parent alkane.
(b) Two metal plates or wires through which the current enters and leaves the electrolytic cell.
(c) The amount of substance which contains the same number of units as the number of atoms in carbon-12.
(d) The tendency of an atom to pull a shared pair of electrons towards itself in a compound.
(e) The formula which represents the simplest ratio between the atoms of elements present in a compound
(v) (a) Give the IUPAC names of the organic compounds represented by the structural formulae given below:
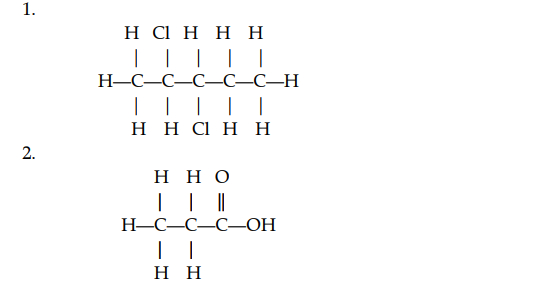
(b) Draw the structural diagram for the following organic compounds:
1. 3-methyl pentane
2. propyne
3. methanal
SECTION – B
Question-3
(i) Rewrite the following statements by adding the correct word as shown in the example:
| Example: Given Statement: Ammonia changes moist red litmus to blue. Correct statement: Aqueous ammonia changes moist red litmus to blue. |
(a) Sulphuric acid acts as a dehydrating agent.
(b) Ammonia reacts with chlorine to given ammonium chloride and nitrogen.
(ii) Identify only the anion present in the following compound:
(a) The compound on heating produces a colourless, odourless gas which turns lime water milky and
has no effect on acidified potassium dichromate solution.
(b) The solution of the compound which on treating with concentrated sulphuric acid and freshly prepared ferrous sulphate solution produces a brown ring.
(iii) Mohan has three solutions P, Q and R having a pH of 13, 5 and 2 respectively. Which of the above
solutions is P, Q or R:
(a) will react with Magnesium to liberate hydrogen gas?
(b) will liberate ammonia gas when it reacts with ammonium chloride?
(c) will contain molecules as well as ions?
(iv) The following table is related to an industrial process of an acid.
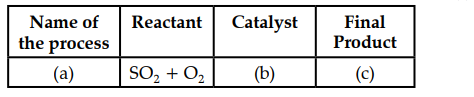
Identity (a), (b) and (c).
Question-4
(i) Define the following terms: [2]
(a) Molar volume
(b) Normal salt
(ii) Draw the electron dot structure of: [2]
(a) Methane molecule
(b) Nitrogen molecule
[Atomic number: N = 7, C = 6, H = 1]
(iii) Complete and balance the following equation:
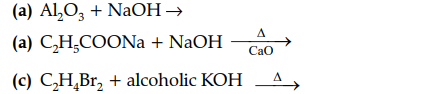
(iv) Choose the organic compound from the list given below to answer the following question: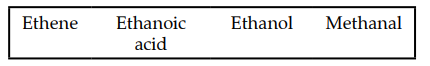
(a) The compound which does not have double bond in its structure.
(b) The compound which in its pure form turns into an ice like solid on cooling.
(c) The compound which is used for artificial ripening of fruits.
Answers
Answer-1
(i) Option (a) is correct
(ii) Option (d) is correct.
(iii) Option (d) is correct
(iv) Option (c) is correct.
(v) Option (b) is correct.
(vi) Option (a) is correct.
(vii) Option (b) is correct
(viii) Option (d) is correct.
(ix) Option (b) is correct
(x) Option (c) is correct
(xi) Option (b) is correct.
(xii) Option (c) is correct
(xiii) Option (b) is correct
(xiv) Option (c) is correct.
(xv) Option (b) is correct.
Answer-2.
(i) (a) The metal which is to be electroplated should always be at cathode in electroplating.
Therefore, the metal ion (Ni2+) in it gets reduced at the cathode and forms a layer on it.
(b) Cation: Ni2+ and anion depend upon the electrolyte taken.
(c) The passage of low current for long time is a necessary condition to ensure the deposit is smooth, even and firm.
(d) Ni2+ + 2e– ® Ni
(e) Negatively charge ions (depends upon the electrolyte) move toward the anode but do not discharged due to nature of the electrode. But Ni losses two electrons converted into Ni2+ in the solution. That results anode electrode get thinner and iron cup becomes thicker over the time of electrolysis.
(ii) Column A Column B
(a) Water 3. Covalent compound
(b) Alkali metal 1. Lithium
(c) Halogen 2. lodine
(d) Calcium oxide 5. lonic compound
(e) Weak acid 3. Acetic acid
(iii) (a) FeCl3
(b) Al2O3
(c) Copper nitrate
(d) Copper
(e) Calcination
(iv) (a) Alkyl group
(b) Electrodes (cathode and anode)
(c) Mole
(d) Electronegativity
(e) Empirical formula
Other questions and answers will be updated soon...
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation