Newton’s Second Law Of Motion: Newton's second law of motion is all about how forces affect the motion of objects. It talks about the acceleration of an object that depends on two key things that are the net force acting on it and the object’s mass. Keep reading the article to know about other details as well.
Here’s the breakdown of the law:-
- Net Force: This is the total force of an object after considering the individual forces acting on it in different directions.
- Mass: This is the measure of how much matter an object contains.
The Formula For Newton‘s Second Law of Motion
F = ma, where
F= force
m= mass of an object
a= acceleration
Important Points To Remember
- The greater the net force acting on an object, the greater its acceleration will be.
- The more massive an object, the less acceleration it will experience.
Newton’s Second Law Of Motion can be formally expressed as follows:-
The acceleration of an object as produced by the net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force and inversely proportional to the mass of an object.
The formula in equation form is:
Derivation For Newton’s Second Law Of Motion
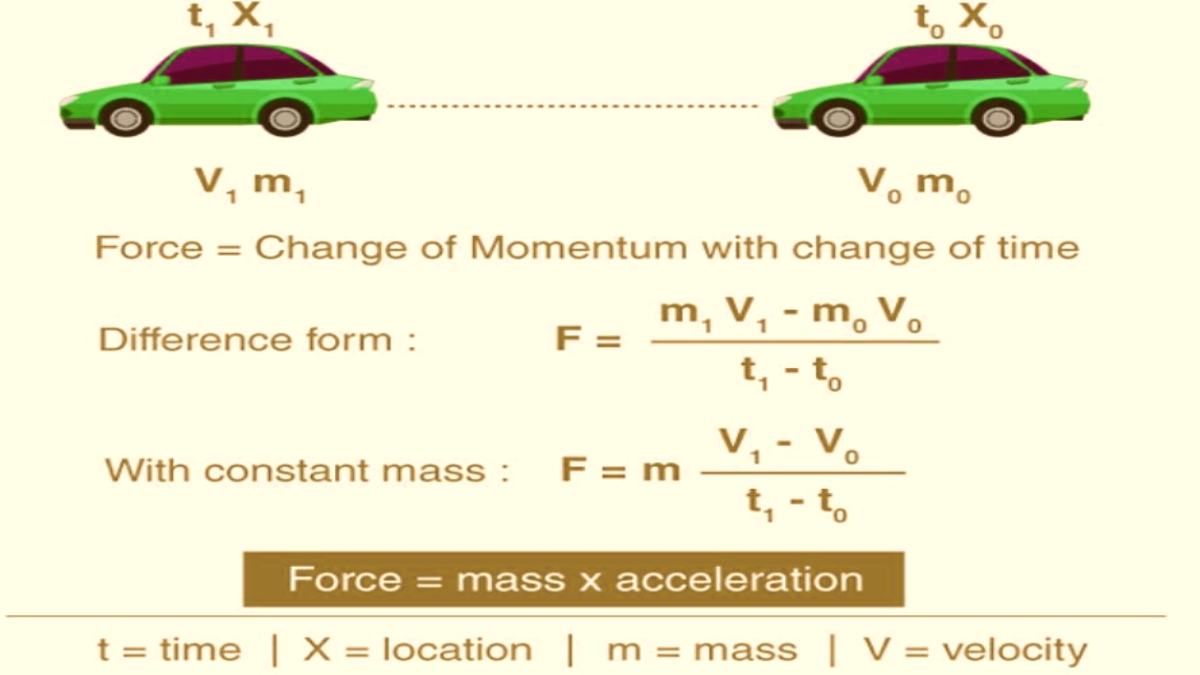
For Changing Mass
Let us assume we have a car at a point (0) defined by location X0 and the time t0. The car has mass m0 that travels with velocity v0. The car moves to point 1, defined by location X1 and the time t1. The mass and velocity of the car will be m1 and v1.
As we take the difference between point 1 and point 0, we get an equation for the force that is
For Constant Mass
For a constant mass, the equation is as follows:-
What Is Net Force?
The Net Force is the sum of all forces acting on the body. It is the vector sum of all the forces.
Applications Of Newton’s Second Law Of Motion
- Pushing a grocery cart: The more force you exert, the faster the cartwheel moves.
- Kicking A Soccer Ball: The force of the foot acting on the ball causes 9it to accelerate forward.
Other Related Links

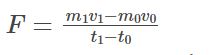
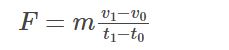
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation