5 Questions on DNA Answered: DNA or Deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule that is responsible for carrying genetic information which is responsible for the development and functioning of an organism.
Here we will be looking at the most asked questions on DNA and the answers to the same questions.
What is DNA Made of?
DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is composed of nucleotides. The nucleotides are a combination of two components which are deoxyribose sugar, phosphate groups and nitrogenous bases like Adenine, Cytosine, Thymine and Guanine. These are abbreviated as A, C, T and G respectively and make up the genetic code.
Adenine bonds with Thymine and Cytosine bonds with Guanine.
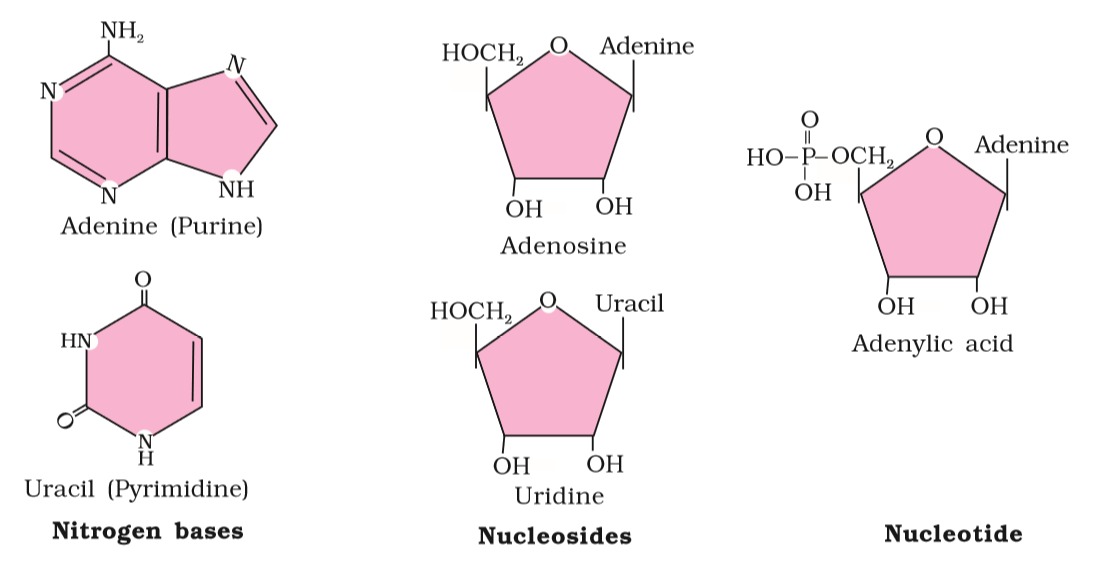
Source: NCERT
Who discovered DNA?
DNA was discovered by Swiss biologist Johannes Friedrich Miescher in 1869 while he was conducting research on white blood cells.

Source: Wikipedia
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA has a double helical structure which resembles a twisted ladder. It was discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick on February 28, 1953. Rosalind Franklin is also credited with identifying the double helical structure of DNA.
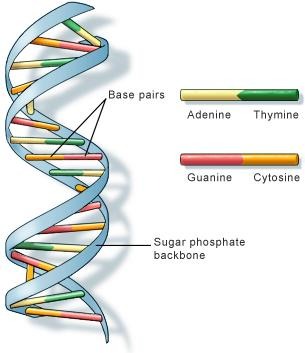
Who discovered the structure of DNA?
The structure of DNA was discovered by scientists James Watson and Francis Crick along with Maurice Wilkins. They were awarded the Nobel prize in 1962 for their discovery of DNA structure.
Rosalind Franklin is also credited with the discovery of DNA structure as she created the picture of the double helix structure of the DNA.

Source: BMC Biology
What is the function of DNA?
The function of DNA is to store genetic information which is required for the organism to develop, function and reproduce. Apart from storing genetic information, there are other functions of DNA which are as follows:
Replication: DNA needs to replicate to transfer genetic information from the parent cell to the daughter cell and also to ensure that there is equal distribution of DNA during the process of cell division.
It also helps in the production of other polymers like proteins
Mutations: The DNA plays a part in the mutations occurring in the body.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation