Black holes are interesting and fascinating objects in the universe. They are highly dense areas of space where gravity is so intense that even light cannot escape. While significant research has been conducted, many characteristics of black holes still remain unexplained.
Before starting the topic, Let's have fun facts about Black Hole
Is Black Hole is really like a Vaccume Cleaner? No!
A black hole has an 'event horizon,' a boundary beyond which nothing, not even light, can escape. Objects outside this horizon are safe from being pulled in. The gravitational pull near a black hole behaves just like any other object of the same mass until you cross the horizon.
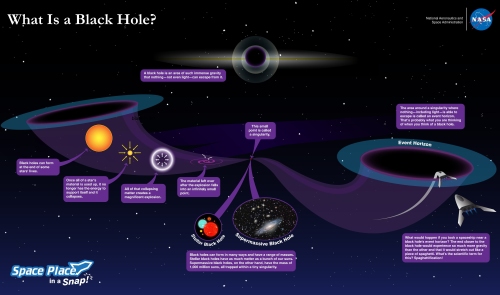
What is a Black Hole?
Source: spaceplace.nasa.gov
About Black Hole
Black holes are mysterious celestial bodies that have captivated scientists for years, yet many aspects of their nature remain elusive. Contrary to their name, black holes are not literal holes but are incredibly dense regions of space where vast amounts of matter are compressed into an extremely small volume. The gravitational force near a black hole's event horizon—the boundary surrounding it—is so intense that nothing, not even light, can break free.
Unlike conventional surfaces such as those of planets or stars, the event horizon is not a tangible surface but rather a boundary that demarcates the point beyond which matter is irrevocably drawn into the black hole. Although much is still unknown about the inner workings of black holes, such as the nature of matter within the event horizon, scientists have made significant progress in understanding their fundamental properties.
Here is description about Black Hole:
| Feature | Description |
| Definition | A region of space where gravity is so intense that nothing, including light, can escape. |
| Event Horizon | The boundary surrounding a black hole, beyond which escape is impossible. |
| Singularity | A point of infinite density at the center of a black hole where the laws of physics break down. |
How Black Holes Formed?
Black hole's forms through various processes:
- Stellar Collapse: When a massive star exhausts its nuclear fuel, it collapses under gravity, forming a stellar-mass black hole.
- Supermassive Black Holes: Found at the center of galaxies, possibly formed through the merger of smaller black holes or the collapse of massive gas clouds.
- Primordial Black Holes: Hypothetical black holes that may have formed in the early universe due to density fluctuations.
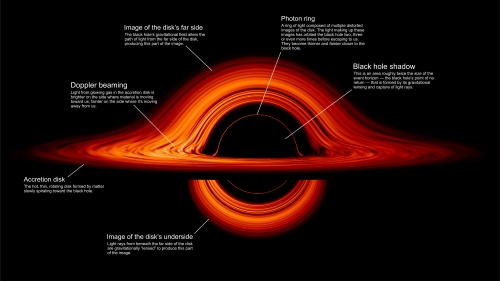
How Black Hole’s detected by scientists?
Since black holes do not emit light, scientists detect them through their interactions with surrounding matter. Methods include:
A. Accretion Disks
- Black holes are often surrounded by rings of gas and dust that emit radiation across multiple wavelengths, including X-rays.
B. Gravitational Effects on Nearby Stars
- A black hole's gravitational pull affects the orbits of nearby stars, helping astronomers identify its presence.
C. Gravitational Waves
- When massive objects accelerate, they create ripples in space-time, detected as gravitational waves.
D. Gravitational Lensing
- Black holes bend and distort light from background objects, revealing their presence.
- Real-World Example: The first direct image of a black hole, M87*, was captured by the Event Horizon Telescope in 2019, confirming many theoretical predictions about black holes.
Source: NASA
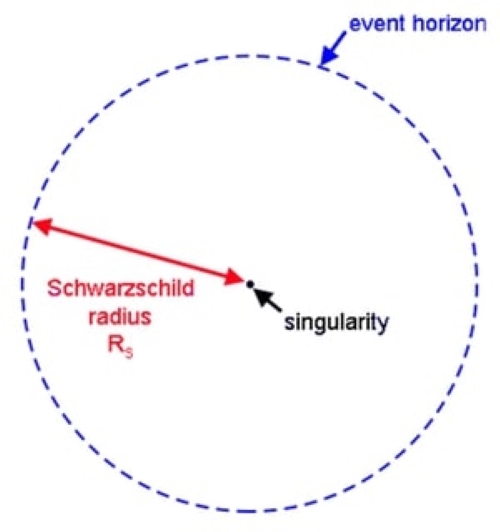
What is the Structure of a Black Hole?
Source: NASA's Imagine the Universe
Structure of Black Hole:
| Component | Description |
| Singularity | A point of infinite density where matter collapses. |
| Event Horizon | The edge of a black hole, known as the event horizon, is the point beyond which nothing can escape. |
| Schwarzschild Radius | The distance from the singularity where the escape velocity equals the speed of light. |
How many types of Black Hole are Exits?
Types of Black Hole:
| Type | Mass Range | Formation |
| Stellar-Mass Black Holes | 5–20 times the Sun’s mass | Formed from collapsing massive stars. |
| Intermediate-Mass Black Holes | 100–1000 times the Sun’s mass | Possibly formed from merging stellar-mass black holes. |
| Supermassive Black Holes | Millions to billions of times the Sun’s mass | Found at galaxy centers, origin remains under study. |
| Primordial Black Holes | Hypothetical | Thought to have formed in the early universe. |
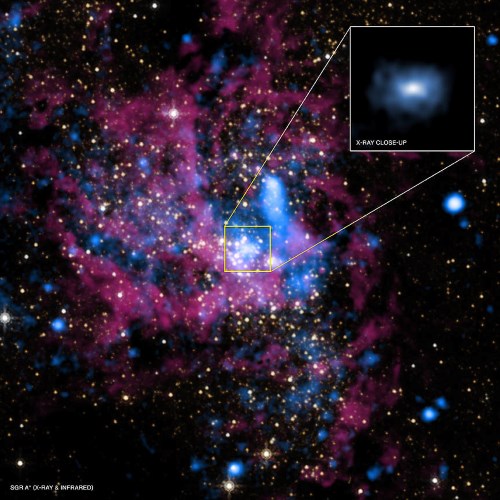
Real-World Example: Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way, was imaged in 2022.
Source: X-ray: NASA/UMass/D.Wang et al., IR: NASA/STScI
What are the Common Misconceptions about Black Hole?
There are various misconceptions on Black Hole which are:
- Black Holes Are Not Wormholes: They do not provide shortcuts to other parts of the universe.
- Black Holes Are Not Cosmic Vacuum Cleaners: They do not indiscriminately pull in matter; only objects that cross the event horizon are drawn in. Objects orbiting at a safe distance remain unaffected, much like planets around a star.
The Future of Black Hole Research
Scientists continue to study black holes using advanced telescopes and simulations. Some of the key areas of research include:
- Understanding what happens inside the event horizon.
- Exploring how black holes influence galaxy formation.
- Studying the connection between black holes and dark matter.
- Enhancing imaging techniques like the Event Horizon Telescope to capture more detailed black hole images.
- Investigating Hawking radiation and its implications for black hole evaporation.
Black holes remain one of the most fascinating subjects in astrophysics, continually challenging our understanding of space, time, and gravity.
In conclusion, black holes are the universe's most fascinating mysteries, challenging our understanding of space, time, and gravity.
These cosmic giants, with their powerful gravitational pull, shape galaxies and space-time itself. Ongoing research is unraveling their secrets, from the formation of stellar-mass black holes to the exploration of Hawking radiation.
Breakthroughs like the Event Horizon Telescope are bringing us closer to understanding these celestial wonders, promising even more groundbreaking discoveries that could redefine our view of the universe.
For more informations on Space explorations and NASA, Vist the link given below:
Read| How Black Hole's Cook for themselves? NASA Reveal the Chandra X-ray Shows
Read| Interstellar Object May Have Reshaped Our Solar System's Planetary Orbits
Read| How Light Pollution Is Threatening the Very Large Telescopes in Chile: An Expert’s Warning
Read| Who is Janet Petro? Meet the First Woman to Lead NASA as Acting Administrator
Read| List of Administrators of NASA
Read| GJ 1214 b: A Mysterious ‘Super-Venus’ Exoplanet Unveiled by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope
Read| NASA-ISRO Mission: How Earth Satellite NISAR will see the Earth?
Read| What are the Top Inventions done by NASA?
Read| SpaceX Falcon 9 Launches Starlink 12-7: Key Details and Impact on Global Internet Connectivity
Read| Trump Announces to Build ‘Iron Dome’ Shield: Vision, Strength & Challenges For US Iron Dome
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation