The sun's brilliance and high temperature arise from a remarkable phenomenon termed nuclear fusion. This intricate process transpires within the sun's core, where minuscule atomic particles conjoin, culminating in the formation of more substantial particles. This intricate process results in the emission of copious amounts of thermal energy and radiant light.
Analogously, consider the construction of a sandwich. As two slices of bread envelop a delectable filling, a sandwich is formed. Similarly, the sun orchestrates the fusion of minute particles, resulting in the generation of more significant entities. Analogous to the satisfaction derived from a well-crafted sandwich, the sun basks in an abundance of heat and illumination through this intricate fusion process.
The sustenance of the sun's fiery brightness and searing heat hinges upon the mechanism of nuclear fusion. Were it not for this phenomenon, the sun would adopt a much cooler and dimmer disposition, which would inevitably render Earth uninhabitable. In this context, the sun's incandescence proves pivotal to the sustenance of life on our planet.
ALSO CHECK| Aphelion Day 2023: What Causes the Summer Heat Despite Earth Being Farthest from the Sun?
Nuclear Fusion: A Deeper Insight
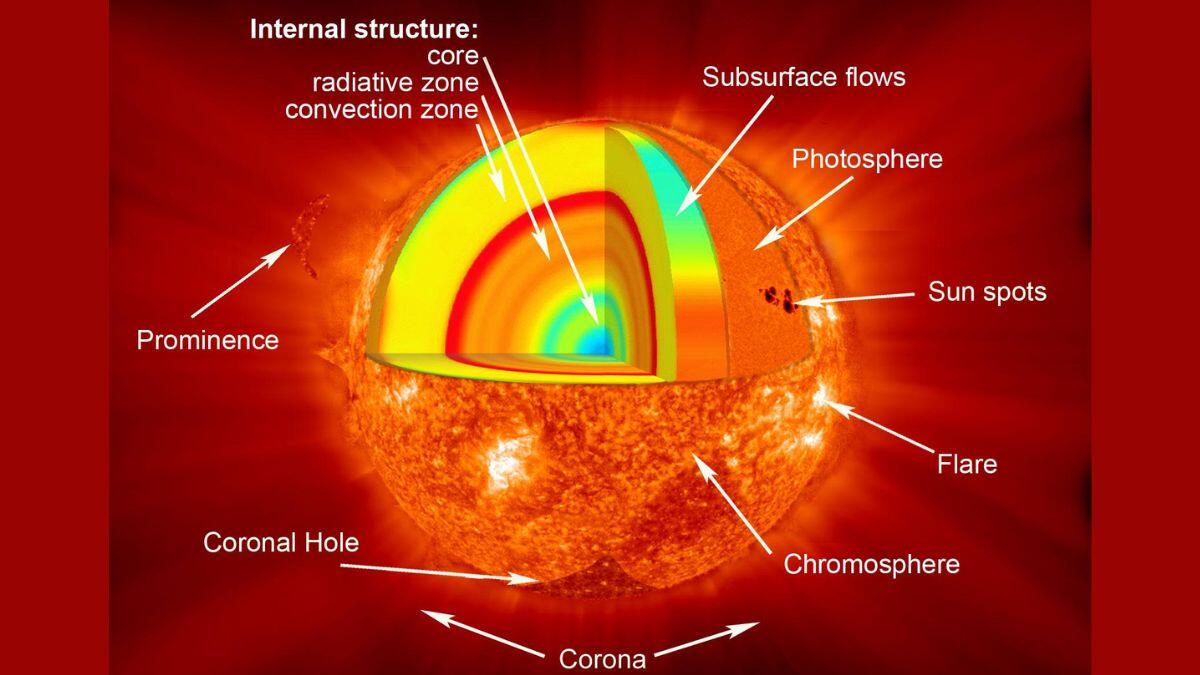
A more comprehensive exploration of nuclear fusion is warranted to appreciate its role in endowing the sun with its radiant warmth and brilliance. The sun assumes the form of an expansive gaseous sphere, predominantly composed of hydrogen and helium. Within its core, the interplay of intense pressure and temperature coerces hydrogen atoms into a tightly compressed state. Under these conditions, atoms fuse, giving rise to the birth of a new element, namely helium. This intricate mechanism is aptly coined nuclear fusion.
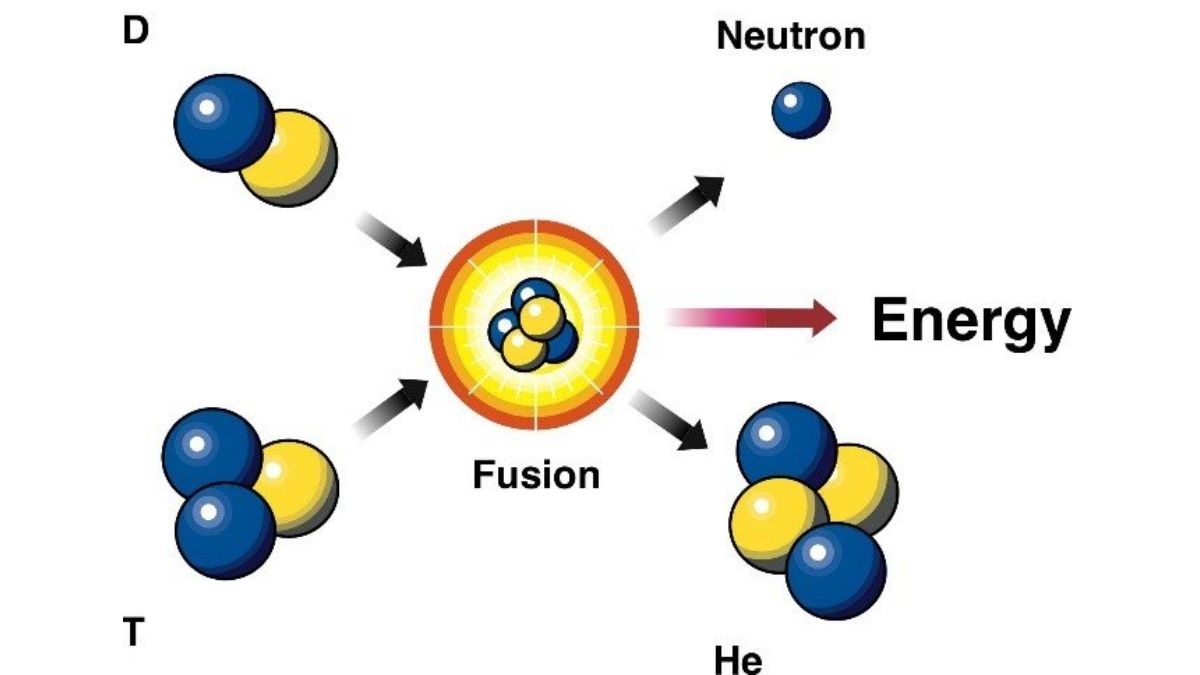
Nuclear fusion yields a prodigious outpouring of energy, manifesting in the form of heat and light. This abundance of energy constitutes the foundation of the sun's luminosity and elevated temperature. The sun's core registers a staggering temperature of approximately 27 million degrees Fahrenheit (15 million degrees Celsius).
The energy derived from nuclear fusion commences a journey from the sun's core, a voyage facilitated through the process of radiation. This energy embarks on a lengthy trajectory, encompassing approximately 100,000 years before reaching the sun's surface. Once this arduous journey concludes, a mere 8 minutes transpire for the energy to traverse the expanse and grace Earth.
ALSO CHECK| August Super Blue Moon 2023: Date, Time and Importance of Celestial Spectacle
Acknowledging the Sun's Significance
The sun's prominence as a celestial entity of paramount importance stems from its role as the wellspring of life-sustaining energy for Earth. Facilitated by the sun's radiance, photosynthetic organisms flourish, engendering sustenance for the entirety of Earth's biota.
Moreover, the sun's thermal energy safeguards Earth's temperature, preserving a climate conducive to habitability. Despite its fervent luminosity and intense luminance, the sun remains an indispensable benefactor. The imperative role it assumes in perpetuating life renders it an object of paramount significance.
Sun Facts
- The sun's enormity is so profound that circumnavigating the sun at a velocity of 60 miles per hour would take over 175 years to complete.
- The sun's proximity to Earth belies the temporal constraints of light. Despite its vicinity, sunlight necessitates 8 minutes to traverse the chasm to Earth, underscoring the finite velocity of light.
- The sun's heat is resounding, capable of engendering instantaneous vaporization upon contact with its surface. This formidable heat underscores the sun's role as an indispensable source of thermal energy.
- The sun, as the quintessential energy fountain, underpins terrestrial life. Its energy cascade fuels the proliferation of plants, which in turn nourish all life forms. Thus, the sun emerges as the ultimate life-bestowing entity.
- The sun's ceaseless activity is striking. Its axial rotation transpires every 27 days, rivalling the rapidity of a phonograph's rotation. Furthermore, the sun's voyage around the Milky Way takes a staggering 225 million years, dwarfing the era since the extinction of dinosaurs.
- The sun's vibrant dynamism extends to its emanation of hot gasses and particles, accountable for awe-inspiring phenomena like the Northern Lights. However, this vigour can also precipitate complications for Earth's technological infrastructure, impacting satellites and power grids.
- The sun's apparent hue may oscillate between yellow and orange in the sky, yet its intrinsic colour is white. The sun's radiant spectrum encompasses all hues of the rainbow; however, Earth's atmosphere disperses certain hues, contributing to the chromatic variations discernible during different times of day. This phenomenon endows sunsets with their resplendent red and orange hues, a manifestation of light's arduous voyage through Earth's atmospheric layers.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation