Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants, CBSE Notes: Revision is the key to success. Students who revise properly before their exams tend to score higher marks. CBSE has revised its syllabus for Class 12 Biology. This has impacted the NCERT Class 12 Biology textbooks as well. For students of CBSE Class 12 Biology, we have designed short revision notes for effective preparation for exams. These CBSE notes will be helpful for quick revision, even for NEET preparation. Thus, these notes will work as CBSE as well as NEET preparation notes.
Below are CBSE Class 12 Biology short notes or revision notes that students can refer to for quick exam preparation. The CBSE Class 12 biology revision notes PDF is attached at the end of this article. Check and download for a better understanding.
CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Revision Notes
Chapter: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Introduction:
- Sexual reproduction is the process that involves the fusion of male and female gametes.
- In flowering plants, sexual reproduction involves the formation of flowers and seed production.
Flower Structure:
- Flowers are reproductive structures of flowering plants.
- Generally a flower consists of four whorls: 1st whorl of the calyx (sepals), 2nd of corolla (petals), 3rd of androecium (stamens), and 4th of the gynoecium (pistil).
- Stamens are the male reproductive organs of a flower which produce pollen grains, while the pistil is the female reproductive organ which contains the ovary.
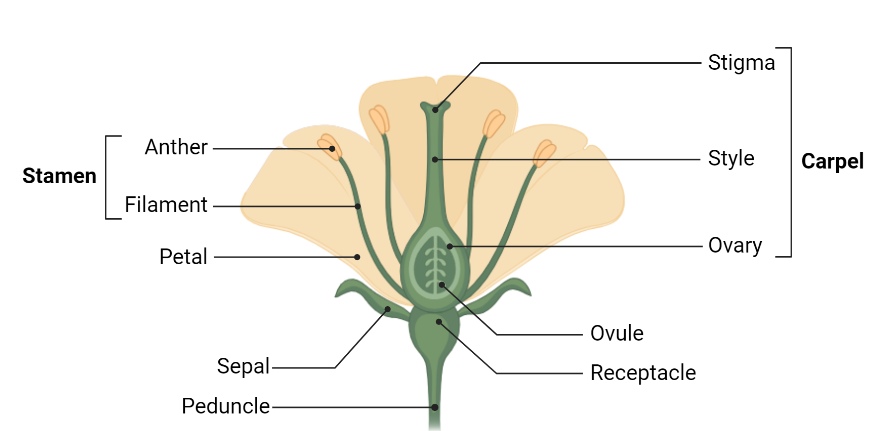
Pre-fertilisation events:
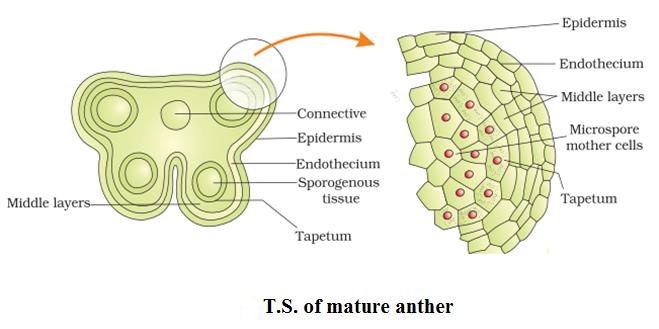
- In androecium
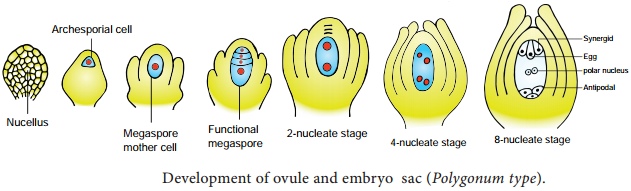
- In gynoecium
Pollen Grains:
- Pollen grains are male gametophytes produced by the anther of a flower.
- Each pollen grain consists of a protective outer layer called the exine and a reproductive cell called the generative cell.
- The generative cell divides to form two male gametes.
Embryo Sac:
- The embryo sac is the female gametophyte produced by the ovule within the ovary.
- It consists of seven cells, including an egg cell, two synergids, three antipodal cells, and a central cell with two polar nuclei.
CBSE Class 12 Biology Mind Map: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Pollination:
- Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower.
- It can occur through various agents like wind, water, or animals (insect pollination).
- When the pollens are transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant is called self-pollination.
- When the pollen is transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different plant is called cross-pollination.
- Seed dispersal helps the species to colonize in other areas and many fruits have mechanisms for the dispersal of seeds.
- Winter Pollinated: Grasses
- Water Pollinated: Vallisneria and Hydrilla
- Insect Pollinated: Yucca
(Types of self-pollination)
Autogamy: In this type, pollination is achieved within the same flower. Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower.
Cleistogamy: In this type, pollination is achieved within the same flower which is permanently closed.
(Types of cross-pollination)
Geitonogamy: Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of another flower of the same plant.
Xenogamy: Transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of a different plant
Double Fertilisation:
- Syngamy+Triple fusion =Double fertilization.
- Double fertilisation is a unique feature seen in flowering plants.
- It involves the fusion of one male gamete with the egg cell to form a zygote, and the fusion of the other male gamete with the two polar nuclei to form a triploid endosperm nucleus.
- This process leads to the development of both an embryo and endosperm within the seed.
Seed and Fruit Formation (Post-fertilisation events):
- After fertilisation, the ovule develops into a seed that have an embryo, endosperm, and seed coat.
- The ovary develops into a fruit, which protects and aids in the dispersal of the seeds.
- Fruits can be classified as dry or fleshy and can have various modes of dispersal such as wind, water, animals, or self-dispersal.
- False Fruit: When parts other than the ovary contribute to the fruit formation. Eg: Apple
- True Fruit: When fruit develops from the ovary Eg: Mango
CBSE Class 12 Biology Important MCQs: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Pollen-pistil interaction
- It is a dynamic process involving pollen recognition followed by pollen tube growth.
- Artificial Hybridisation It is one of the major approaches of crop improvement by using desired pollen grains for pollination. Achieved by emasculation and bagging.
Devices for promoting cross-pollination
- Self-incompatibility
- Arrangement of anther and stigma at different positions.
- Production of unisexual flowers (Dicliny)
- Pollen release and stigma receptivity not synchronised.
Germination:
- Germination is the process by which a seed develops into a new plant.
- It requires favourable conditions of moisture, temperature, and oxygen for the seed to break dormancy and resume growth.
- During germination, the embryo inside the seed grows, develops roots and shoots, and emerges as a seedling.
| Download CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Revision Notes PDF |
CBSE Class 12 NCERT Biology Revised Textbook PDF
CBSE Class 12 NCERT Biology Solutions
Also read:
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation