Judiciary: This article discusses the 'guardian of the Constitution', that is the judiciary. To avoid incidents where the rich and powerful people try to influence the judicial process, the Indian Constitution provides protection in the form of a strong and independent judiciary. Let's find out about the importance of judiciary in the society and the structure of the Indian judiciary.
What is the judiciary?
The judiciary is an essential organ of the government and of the political structure of the nation. It is the guardian of the Constitution. It interprets the law, takes care of disputes and delivers justice to all. Apart from the judiciary, the other important parts of the Indian administration are legislature and executive. Let’s take a look at the role of the judiciary.
What is the role/function of the judiciary?
The judiciary can take decisions on various issues such as in disputes between individuals or parties. The role of the courts can be classified as-
Dispute resolution- The judiciary acts as a mediator to resolve disputes between individuals, between individuals and government, between two state governments or between the centre and state government.
Judicial review- The courts act as an interpreter of the Constitution. The judiciary has the power to repeal any law passed by the Parliament if it violates the basic structure of the Constitution.
Upholding law and enforcement of Fundamental Rights- Every citizen of the country has the right to approach the Supreme Court if they believe that their Fundamental Rights have been violated.
What is the importance of the judiciary?
NCERT explains the importance of judiciary as ‘safeguards rights of individuals, settles disputes in accordance with the law and ensures that democracy does not give way to individual or group dictatorship’. The judiciary helps to establish the rule of law, which means that all citizens are subjected to the same law and no one is above the law. It plays a prominent role in the protection of the Fundamental Rights of individuals. It acts both as the guardian of the Constitution and the protector of Fundamental Rights.
What is an independent judiciary?
The independence of the judiciary means that the other organs of the government cannot interfere with its work. Emphasizing the importance of an independent judiciary, NCERT explains, ‘’It is the independence of the judiciary that allows the courts to play a central role in ensuring that there is no misuse of power by the legislature and the executive. It also plays a crucial role in protecting the Fundamental Rights of citizens because anyone can approach the courts if they believe that their rights have been violated.’’
Also Read: NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Civics Chapter 5 - Judiciary
What is the structure of the judiciary in India?
There is an integrated judicial system in India, which means that decisions of higher courts are binding on lower courts. The structure of the judiciary is as follows- subordinate courts are at the lowest level, district courts are above them, High Courts are above district courts and at the top level is the Supreme Court.
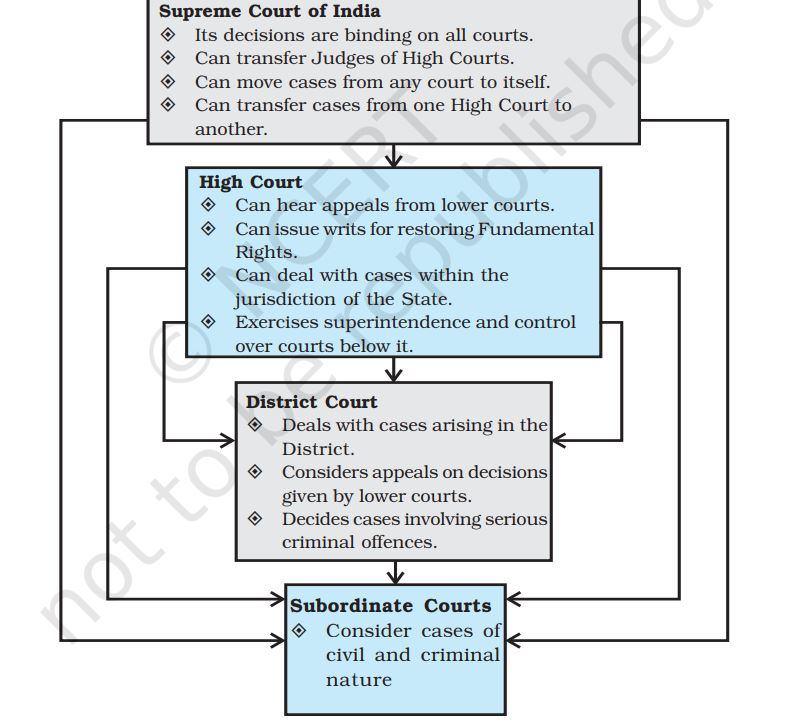
Apart from the above structure, there are also two branches of the legal system- civil law and criminal law.
Civil law- It deals with the harm to the Fundamental Rights of a citizen. The affected party has to file a petition before the court.
Criminal law- It deals with acts that are defined as offences under the law. An First Information Report (FIR) is filed with the police.
CBSE Video Courses for All Subjects for Class 10 Students
Class 10 students can study effectively with the help of video courses prepared by the subject matter experts. These video courses will explain the concepts in a simple and interactive manner which will help learners to understand clearly. The videos are available for all major subjects which includes social science. Refer to the below link:
Note: All images have been taken from NCERT Class 11 Political Science textbook (Indian Constitution at Work).

Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation