The Kerala SSLC Maths Exam 2025 is an important milestone for students appearing in the board exams. The exam assesses their problem-solving skills and understanding of key mathematical concepts. A well-structured question paper ensures a balanced mix of theoretical and application-based questions, testing students’ grasp of the subject. Many students eagerly await the release of the question paper and answer key to analyze their performance.
Students can now check and download the Kerala SSLC Maths 2025 question papers and answer keys to evaluate their responses and estimate their scores. These resources serve as valuable tools for self-assessment and exam preparation. The question papers will be uploaded here as soon as they are available, so stay tuned for the latest updates.
Kerala SSLC Maths Exam 2025: Check Question Paper

Kerala SSLC Maths Exam 2025: Check Question Paper and Answer Key Links
The Kerala SSLC Maths Exam 2025 question papers and answer keys are available here. These resources allow students to evaluate their performance and check how they have attempted the exam.
1. In the figure, O is the center of the circle. If ∠ACB = 70°,
(a) Find ∠AOB
(b) Find ∠ADB
Solution:
Given ∠ACB = 70°
(a) Finding ∠AOB:
The angle subtended by an arc at the center is twice the angle subtended at any point on the circumference.
Hence, ∠AOB = 2 × ∠ACB
= 2 × 70°
= 140°
Answer: ∠AOB = 140°
(b) Finding ∠ADB:
The angles subtended by the same chord on the same side of the circle are equal.
Therefore, ∠ADB = ∠ACB
= 70°
Answer: ∠ADB = 70°
2. Given the arithmetic sequence: 3, 8, 13, ...
(a) Find the common difference (d)
(b) Find the 11th term of the sequence
Solution:
(a) Finding the Common Difference (d):
The common difference d is given by:
d = second term - first term
= 8 - 3 = 5
Answer: Common difference (d) = 5
(b) Finding the 11th Term:
The formula for the nth term of an arithmetic sequence is:
an=a+(n−1)d
where:
- a = 3 (first term)
- d = 5 (common difference)
- n = 11
a11=3+(11−1)×5 =3+10×5= 3+50= 53
Answer: 11th term = 53
3. Numbers from 1 to 20 are written on paper slips and put in a box. A slip is drawn at random.
(a) What is the probability that it is a prime number?
(b) What is the probability that it is a perfect square?
Solution:
(a) Probability of Prime Number:
- Prime numbers between 1 and 20: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19
- Total prime numbers = 8
- Total numbers = 20
P(prime number) = number of favourable outcomes/total outcomes
= 8/20 = 2/5
Answer: 2/5
(b) Probability of a Perfect Square:
- Perfect squares between 1 and 20: 1, 4, 9, 16
- Total perfect squares = 4
- Total numbers = 20
P(perfect square)=number of favorable outcomes/total outcomes
=4/20=1/5
Answer: 1/5

In the figure, O is the center of the circle. Given BC = 4 cm and ∠A = 50°, find the diameter of the circle.
(Trigonometric values given: sin 50° = 0.77, cos 50° = 0.64)
Solution:
In the given figure, BC is the chord of the circle.
Since O is the center, OB = OC (radii of the circle),
and ∠A = 50° (given)
The perpendicular from O to BC bisects BC, so the half-length of BC is 2 cm.
Or BD = 2 cm
We use the formula:
- OB=BD/cos50∘ = 2/0.64 = 3.125 cm
- The diameter is 2 × OB
- Diameter= 2×3.125=6.25 cm
Answer: Diameter = 6.25 cm
5. 6 times of a natural number subtracted from the square of that number gives 187.
(a) Form a quadratic equation.
(b) Find the number.
Solution:
Let the natural number be x.
(a) Given:
x2−6x=187
Rearranging:
x2−6x−187=0
Answer: Quadratic equation: x2−6x−187=0
(b) Solving for x using the quadratic formula:

Answer: Natural number = 17
6. Given two points (2,5) and (3,7)
(a) Find the slope of the line.
(b) Write the equation of the line.
Solution:
(a) Slopeof the line is given as:
m=(y2−y1)/(x2−x1)
=(7−5)/(3−2)=2/1=2
Answer: Slope = 2
(b) Equation of the line using y−y1=m(x−x1)
y−5=2(x−2)=
y−5=2x−4
y=2x+1
Answer: Equation: y=2x+1
7. Consider the arithmetic sequence 2, 8, 14, ...
(a) What is the remainder when terms of this sequence are divided by 6?
(b) Is 176 a term of this sequence? Why?
Solution:
(a) Finding Remainders:
- First term 2 mod 6 = 2
- Second term 8 mod 6 = 2
- Third term 14 mod 6 = 2
Since all terms leave a remainder 2, the remainder is always 2.
Answer: Remainder = 2
(b) Checking if 176 is a term:
Formula for nth term:
an=a+(n−1)d
a = 2, d = 6, a_n = 176
176=2+(n−1)×6
176−2=(n−1)×6
174=(n−1)×6
(n-1)= 174/6=29
n=30
Since n = 30 is a whole number, 176 is a term of the sequence.
Answer: Yes, 176 is a term
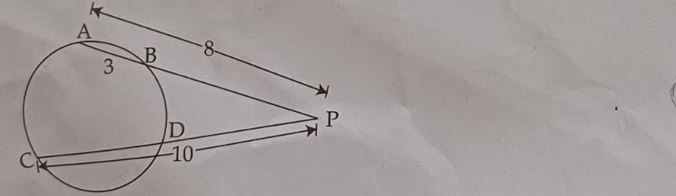
8. In the figure, PA = 8 cm, AB = 3 cm, PC = 10 cm.
(a) Find the length of PB.
(b) Find the length of PD.
Solution:
(a) Using the intercept theorem:
PB=PA−AB
PB=8−3=5
Answer: PB = 5 cm
For PD, using the property of intersecting secants:
PA×PB=PC×PD
8×5=10×PD
40 =10×PD
PD=4
Answer: PD = 4 cms
Kerala SSLC Maths Exam Question Paper 2025 Download PDF | ||
| Kerala SSLC Maths Exam Answer Key 2025 Download PDF (Updating soon...) |


Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation