Magnetism and Matter Formula Sheet Class 12: Physics is a subject filled with plethora of concepts and formulas. Even the exercises are filled with formula-centric questions. Since, it becomes difficult for students to memorise all the formulas in one go, we have brought to you Magnetism And Matter Formula Sheet where you can get the complete list of all formulas of magnetism and matter class 12 along with a PDF download link of the same. The formula sheet can be saved and used as and when required by students. Check the formula sheet of magnetism and matter below and use the same for memorizing the formulas, solving exercises without turning the pages of your book for every question, and keeping it handy for revision and preparation of exams. Students can also take out a print of the same and carry it everywhere since it is quite handy, portable, and convenient to use.
Magnetism and Matter Class 12 Formula Sheet
Formula sheet of magnetism and matter class 12 Physics has been provided below. The formula sheet consists of all the important formulas from the chapter that will be used in solving the exercises. While doing their exercises and revising the chapter, students can also memorize the formulas easily.
- Magnitude of field at a point P due to Solenoid
- Dipole in Uniform Magnetic Field
- Equatorial Field of a Bar Magnet at Distance r
- Axial Field of a Bar Magnet
- Gauss Law
- Magnetisation
- Magnetic Intensity
- Magnetic Permeability
Dipole Analogy
Here is the comparison of a dipole in electrostatic and magnetic field. This difference will help you analyse the situations where the right formulas can be used. Different formulas are used for the same condition in two different types of fields, details of which can be checked in the table below.
| Condition | Electrostatics | Magnetism |
| Dipole moment | 1 εo/p | μo/m |
| Equatorial Field for a short dipole | -p/4πεor3 | - μo m/4πr3 |
| Axial Field for a short dipole | 2p/4πεor3 | μo2m/4πr3 |
| External Field: torque | p x E | m x B |
| External Field: Energy | -p.E | -m.B |
Magnetic Properties of Materials
There are three magnetic properties of materials known as Diamagnetism, Paramagnetism, and Ferromagnetism. Check further details below.
- Diamagnetism- Diamagnetic substances are those which have tendency to move from stronger to the weaker part of the external magnetic field. The most exotic diamagnetic materials are superconductors.
- Paramagnetism- Paramagnetic substances are those which get weakly magnetised when placed in an external magnetic field. Some paramagnetic materials are aluminium, sodium, calcium, oxygen (at STP) and copper chloride.
- Ferromagnetism- Ferromagnetic substances are those which gets strongly magnetised when placed in an external magnetic field. There are a number of elements, which are ferromagnetic: iron, cobalt, nickel, gadolinium, etc.
| Diamagentic | Paramagnetic | Ferromagnetic |
| -1 < χ < 0 | 0 <χ < ε | χ >> 1 |
| 0 < μr < 1 | 1 < μr < 1+ε | μ r >> 1 |
| μ<μo | μ > μo | μ >> μo |
Magnetism and Matter Physical Quantities
Check the physical quantities used in the Magnetism and Matter chapter. Also, have a look at their symbols, dimensions, values, and more.
| Physical Quantity | Symbol | Nature | Dimensions | Units | Remarks |
| Permeability of free space | μo | Scalar | [MLT–2 A–2] | T m A–1 | μo/4π = 10-7 |
| Magnetic field, Magnetic induction, Magnetic flux density | B | Vector | [MT–2 A–1] | T (tesla) | 104 G (Gauss)= 1 T |
| Magnetic moment | m | Vector | [L–2 A] | A m2 |
|
| Magnetic flux | ɸB | Scalar | [ML2T–2 A–1] | W (weber) | W = T m2 |
| Magnetisation | M | Vector | [L–1 A] | A m-1 | Magnetic moment Volume |
| Magnetic intensity | H | Vector | [L–1 A] | A m-1 | B = μ0 (H + M) |
| Magnetic field strength | |||||
| Magnetic susceptibility | χ | Scalar | M = χ H | ||
| Relative magnetic permeability | μr | Scalar | B = μo μr H | ||
| Magnetic permeability | μ | Scalar | [MLT–2 A–2] | T A m-1 N A-2 | μ = μo μr B = μ H |
Also Find:
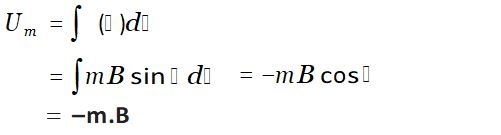

Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation