CBSE Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids Formulas: In this article, students can find the formula sheet for CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 10, Mechanical Properties of Fluids. Along with the list of important formulas, we have also integrated some important definitions and graphs for you all. Students can refer to these when in need. They can also be used as a last-minute revision guide. Students can find a free PDF download link at the bottom of the article to save and download formulas and definitions for future reference.
Mechanical Properties of Fluids is an important chapter since it consists of important concepts, formulae, and definitions. In higher secondary classes, direct definitions are rarely asked in exams, but students have to understand these definitions to be able to solve numerical and derivations. In order to solve all the questions from the chapter students have to practise all the numericals from NCERT exercises as well in-text questions and answers. Additionally, students have to be careful with the relation between different topics, as graphs related to those can be asked in the question paper.
This formula page/formula sheet can be used to revise during exams, practise numericals and derivations, solve questions and answers, memorize definitions, and more. Since they are handy and easy to use, students prefer using formula sheets for their preparation.
Related:
Formula Page for Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids
Formula Sheet for CBSE Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Formulas:
Average Pressure
Density-
Pascals Law-
Atmospheric Pressure-
Calculation of Hydraulic Brake Atmospheric Pressure-
Equation of continuity-
Bernoulli’s Principle-
Change in kinetic energy-
Bernoulli’s equation when fluid is at rest-
Torricelli’s Law-
Coefficient of Viscosity-
Stokes Law-
Terminal Velocity-
Magnitude of surface tension-
Surface Tension of liquid-air interface-
Angle of Contact-
Extra Surface energy if the radius in increased-
Work done-
Soap Bubble-
Concave Capillary-
When pressure inside the tube is less than the atmospheric pressure-
Definitions:
Gauge Pressure- The excess of pressure, P - P, at depth h is called a gauge pressure at that point
Magnus Effect- The difference in the velocities of air results in the pressure difference between the lower and upper faces and there is a net upward force on the ball. This dynamic lift due to spinning is called the Magnus effect.
Viscosity- Most of the fluids are not ideal ones and offer some resistance to motion. This resistance to fluid motion is like an internal friction analogous to friction when a solid moves on a surface. It is called viscosity.
Surface Tension- Liquids have no definite shape but have a definite volume, they acquire a free surface when poured into a container. These surfaces possess some additional energy. This phenomenon is known as surface tension.
Concave Capillary- The contact angle between water and glass is acute. Thus the surface of water in the capillary is concave. This means that there is a pressure difference between the two sides of the top surface.
Common Units of Pressure
1 atm = 1.01×105 Pa
1 bar = 105 Pa
1 torr = 133 Pa = 0.133 kPa
1 mm of Hg = 1 torr = 133 Pa
To download the formula sheet, click on the link below
| Download Formula Sheet for Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluid |
Download Formula Sheet for Class 11 Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluid
We will keep updating formula sheets for more chapters of Class 11 Physics. Students can keep tuning in to JagranJosh to stay updated with all the new content. You can also follow us on our social media handles.
Also read:
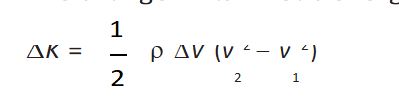
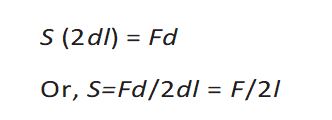
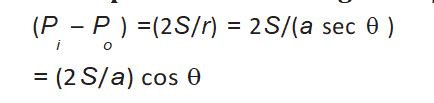
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation