Baikal Gigaton Volume Detector: Why in News?
On March 13, 2021, the Russian scientists launched a deep underwater telescope in Lake Baikal. It is called the Baikal-Gigaton Volume Detector. Purpose of the telescope is to observe neutrinos.
🔭The #Baikal🌊 deep underwater neutrino telescope 'Baikal-GVD' was submerged to a depth of 700-1300 m at Lake Baikal.
— Russia 🇷🇺 (@Russia) March 14, 2021
The telescope is one of the 3️⃣ largest neutrino detectors. #BaikalGVD will allow for breakthrough discoveries in #astrophysics, #cosmology & #physics. pic.twitter.com/V7tC6Z51QB
Baikal: About the lake
- The surface area of the lake is 31,722 kilometre square. The water volume is 23, 615 kilometre cube. Residence time is 330 years and it is also a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- The lake starts freezing at the end of January and temperatures in Siberia drop to -30 degree Centigrade.
- It remains frozen till the month of March. Earlier, it used to remain frozen till May but now due to climate change.

About Neutrinos:
- These are the fundamental parts of the universe that are indivisible. Neutrinos are subatomic particles very similar to electrons but lack an electrical charge.
- It has a very small mass that may be zero. These are the most abundant particles in the universe but are least easy to detect.
- These belong to the lepton category.
Other Types of Fundamental Particles:
Fermions: These include matter and antimatter particles namely
Quarks
Leptons
Antiquarks
Antileptons
Bosons: These are force particles that mediate interactions between fermions. They include
Gauge Boson
Higgs Boson
Facts about Neutrinos
|
All about Baikal Underwater Telescope:
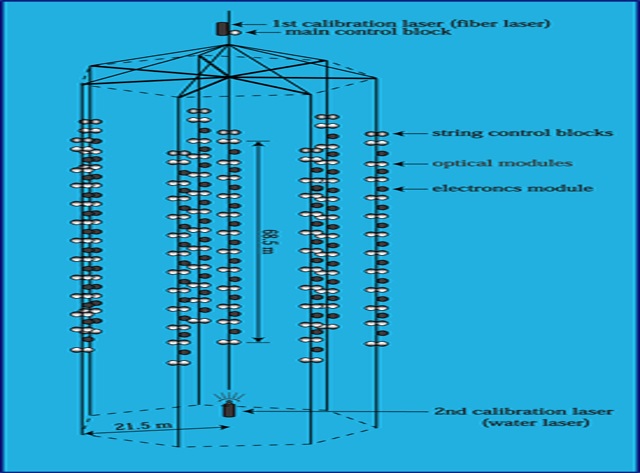
- It is known as the Baikal-GVD (Gigaton Volume Detector)
- It's construction began in the year 2015
- Its objective is to study the neutrinos in detail to find their source or origin
- The Baikal- GVD Collaboration includes 9 institutions and organizations from 4 countries namely Czech Republic, Germany, Poland, Slovakia.
- It is submerged at the depths of 2,500-4,300 feet below Lake Baikal
- The instrument has been placed at the southern part of the lake.
- It has a flat bottom and transparent waters (these conditions are best suited for the floating observatory).
- Baikal-GVD consists of a set of clusters, where each cluster can be used to independently detect high-energy neutrinos.
- Glass spheres containing photomultiplier tubes that detect light are placed in the lake. These are made of string, glass spheres and stainless steel.
- The kind of light produced is called Chrenkov light.
- The Baikal Underwater Telescope (GVD) would detect high energy neutrinos that may have come from Earth's Core or those that could have been produced by the sun.
Why was Lake Baikal chosen?
Whenever there is an explosion, the supernova releases a massive amount (almost 99%) of its energy in the form of neutrinos. Studying them is one of the most challenging tasks for astrophysicists.
Water acts as the best medium for examining them, as it interacts with neutrinos to produce a flash of light.
Moreover, Lake Baikal is the largest and deepest freshwater lake in the world thus it is the most apt location for the placement of this telescope.
The two other neutrino detectors apart from Baikal- GVD are known as IceCube and ANTARES which are located at the South Pole and the Mediterranean Sea, respectively.
Also Read| Solve everyday GK Quiz on static and current events here
Large Hadron Collider at the brink of bringing out New Physics Theory
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation