One day Darian and Albert decided to go scuba diving since they both loved exploring the underwater world. They rented equipment and headed to a nearby beach known for its crystal-clear waters and diverse marine life.
The ocean was calm and inviting as they descended beneath the surface, marvelling at the colourful coral reefs and schools of tropical fish.
Darian spotted a majestic sea turtle gliding gracefully by, leaving them in awe of the beauty of the underwater world. "Wow, a tortoise!" Albert exclaimed, his eyes widening in amazement. "No, it's a sea turtle, not a tortoise," Darian said through his snorkel.
The appearance of these aquatic creatures frequently confuses us. Sea turtles are often mistaken for tortoises due to their similar appearance.
Both sea turtles and tortoises are reptiles, but sea turtles are adapted for life in the water, while tortoises are land-dwelling creatures.
In this article, we'll discuss the core differences between a turtle and a tortoise and how to differentiate them so that the next time you encounter one, you'll be able to identify whether it's a sea turtle or a tortoise. Let's dive in!
For You:
Difference Between Tortoise and Turtle
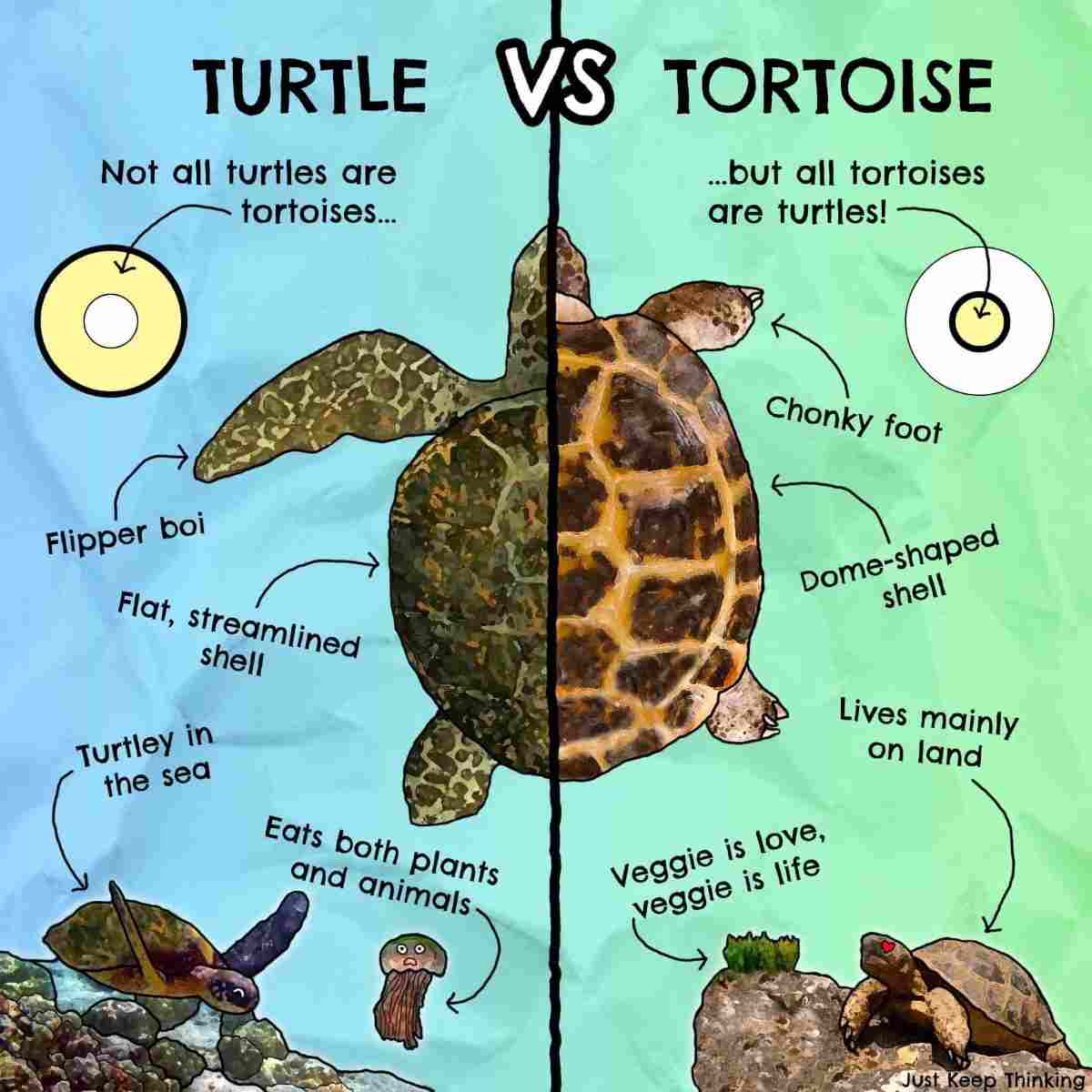
Tortoises and turtles are both reptiles that belong to the same order, called Testudines, but they have distinct differences that set them apart. Here’s a simple breakdown of their main characteristics:
1. Habitat
- Turtles: Most turtles live in water, such as oceans or freshwater lakes. They spend a lot of time swimming and only come ashore to lay eggs.
- Tortoises: Tortoises are land dwellers. They primarily live on dry land and only go near water to drink or bathe.
2. Physical Features
- Shell Shape: Turtles typically have a flatter and more streamlined shell, which helps them swim efficiently. In contrast, tortoises have a domed and heavier shell that protects land.
- Leg Structure: Turtles have legs that are adapted for swimming, often resembling flippers. Tortoises have sturdy, column-like legs that resemble those of elephants, which help them walk on land.
3. Diet
- Turtles: Most turtles are omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and animals. Their diet can include fish, jellyfish, and aquatic plants.
- Tortoises: Tortoises are mainly herbivores, feeding on grass, leafy greens, and other vegetation.
4. Lifespan
- Turtles: The lifespan of turtles varies widely but generally ranges from 20 to 40 years.
- Tortoises: Tortoises tend to live much longer, with lifespans often reaching between 80 to 150 years.

Key Takeaways
- All tortoises are technically turtles, but not all turtles are tortoises. This means that while they share some similarities, their adaptations to different environments make them unique.
- When identifying whether you are looking at a turtle or a tortoise, consider where it lives (water vs. land), its shell shape, leg structure, and diet.
Check Out| Beyond Gold: The Most Expensive Metals on Earth
How do the Diets of Turtles and Tortoises Differ?
Turtles and tortoises have significantly different diets that reflect their distinct lifestyles and habitats. Here’s a clear comparison of what each typically eats:
1. Turtle Diet
- Omnivorous: Turtles are omnivores, meaning they eat both animal and plant matter.
Common Foods:
- Animal Sources: Insects, fish, worms, crustaceans.
- Plant Sources: Fruits, vegetables, algae, and grasses.
- Feeding Behaviour: Turtles often hunt for live food in their aquatic environments, and they require a varied diet to stay healthy.
- For example, box turtles may consume a mix of meat and plants, with a diet consisting of about 50% protein sources like worms and snails.
2. Tortoise Diet
- Herbivorous: Tortoises are primarily herbivores, meaning they eat only plant material.
Common Foods:
- Leafy Greens: Collard greens, dandelion greens, kale, and other dark leafy vegetables.
- Fruits: Limited amounts of fruits such as apples and strawberries can be offered as treats.
- Feeding Behaviour: Tortoises typically graze on grasses and leafy plants. Their diet should consist mainly of fibrous plant material to support their digestive health.
- Unlike turtles, tortoises do not require animal protein in their diets.
Key Takeaways
- Turtles enjoy a mixed diet that includes both plants and animals, while tortoises thrive on a strictly plant-based diet.
- Understanding these dietary needs is crucial for the proper care of each species. Providing the right food helps ensure their health and longevity.
In Case You Missed| The Land of the Morning Calm: 10 Fascinating Facts About South Korea
Why do Turtles have Lighter Shells Compared to Tortoises?
Turtles and tortoises have different shell structures that reflect their adaptations to their environments, which explains why turtles generally have lighter shells than tortoises.
1. Shell Structure and Function
- Turtles: Turtles possess flatter, streamlined shells that are thinner and lighter. This design helps them swim more efficiently in water, reducing drag as they move through their aquatic habitats.
The lighter shell allows for greater mobility and agility in the water, which is essential for escaping predators and hunting for food.
- Tortoises: In contrast, tortoises have thicker, dome-shaped shells that provide robust protection from predators.
Their heavier shells are designed for life on land, facing different threats. A tortoise's shell's added weight and sturdiness help shield them from attacks and environmental hazards.
2. Adaptations to Habitat
The differences in shell weight and structure are adaptations to their respective environments. Turtles need to be agile swimmers, so a lighter shell is advantageous. Tortoises, being land dwellers, benefit from the durability and protective features of a heavier shell.
Conclusion
In summary, turtles have lighter shells because they are adapted for swimming in water, while tortoises have heavier, more protective shells suited for life on land. This difference is crucial for their survival in their specific habitats.
Also Read:
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation