Acids and Bases: We have heard these terms in our day-to-day lives but hardly thought of the science behind them. Well, now you can understand these terms easily through this explainer. This detailed article on acids and bases will discuss their definitions, properties, uses, theories, and examples. Read to know more.
Acids and Bases Definition
Acids and bases are two fundamental categories of chemical substances that have distinct properties and reactions. An acid is a substance that donates hydrogen ions (H⁺) in a solution, while a base is a substance that accepts hydrogen ions or donates hydroxide ions (OH⁻) in a solution.
pH of Acids and Bases
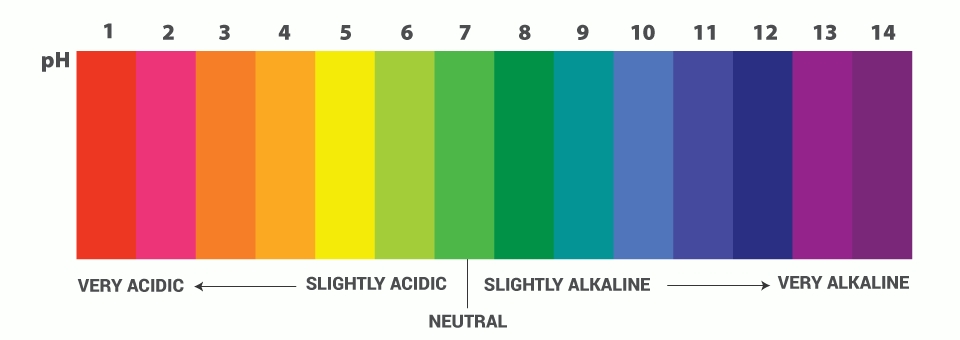
The pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. A pH less than 7 indicates an acidic solution, while a pH greater than 7 indicates a basic (alkaline) solution.
Properties of Acids and Bases
Properties of Acids:
- Taste sour
- Turn blue litmus paper red
- React with metals to produce hydrogen gas
- Conduct electricity in solution
- Corrosive to metals and skin
Properties of Bases:
- Taste bitter
- Feel slippery
- Turn red litmus paper blue
- Do not react with metals in the same way acids do
- Conduct electricity in solution
Also Read:
- Lewis Structure of Carbon Dioxide
- Valence Electrons: Definition and Characteristics
- Intensive and Extensive Properties
Theories of Acids and Bases
Several theories have been developed to explain the behaviour of acids and bases. The most notable theories include the Arrhenius concept, the Brønsted-Lowry theory, and the Lewis concept.
Arrhenius Concept of Acids and Bases
According to the Arrhenius concept:
- Acid: A substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺) when dissolved in water. For example, HCl → H⁺ + Cl⁻.
- Base: A substance that increases the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻) when dissolved in water. For example, NaOH → Na⁺ + OH⁻.
Brønsted-Lowry Theory of Acids and Bases
According to the Brønsted-Lowry theory:
- Acid: A substance that donates a proton (H⁺). For example, HCl + H₂O → H₃O⁺ + Cl⁻
- Base: A substance that accepts a proton (H⁺). For example, NH₃ + H₂O → NH₄⁺ + OH⁻
Conjugate Acids and Bases
In the Brønsted-Lowry theory, each acid has a conjugate base formed when the acid donates a proton, and each base has a conjugate acid formed when the base accepts a proton.
- Conjugate Acid: The species formed after a base gains a proton.
- Conjugate Base: The species formed after an acid loses a proton.
Lewis Concept of Acids and Bases
According to the Lewis concept:
- Acid: A substance that accepts an electron pair.
- Base: A substance that donates an electron pair.
For example, in the reaction between ammonia (NH₃) and boron trifluoride (BF₃):
- NH₃ (Lewis base) donates an electron pair to BF₃ (Lewis acid), forming a coordinate covalent bond.
Uses of Acids and Bases
Uses of Acids:
- Hydrochloric Acid (HCl): Used in stomach digestion, cleaning metal surfaces, and manufacturing.
- Sulphuric Acid (H₂SO₄): Used in car batteries, fertilisers, and chemical manufacturing.
- Acetic Acid (CH₃COOH): Used in food preservation (vinegar) and as a chemical reagent.
Uses of Bases:
- Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH): Used in soap making, paper production, and drain cleaning.
- Calcium Hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂): Used in construction (plaster), sewage treatment, and agriculture.
- Ammonium Hydroxide (NH₄OH): Used in household cleaners and fertilisers.
Examples of Acids and Bases
Get here 10 examples of acid and base that are generally asked in question papers. This table provides a clear overview of various common acids and bases, their chemical formulas, and their typical uses or occurrences.
| Acid | Formula | Common Use/Occurrence | Base | Formula | Common Use/Occurrence |
| Hydrochloric Acid | HCl | Used in stomach digestion, cleaning metals | Sodium Hydroxide | NaOH | Used in soap making, drain cleaner |
| Sulphuric Acid | H₂SO₄ | Used in car batteries, fertilisers | Calcium Hydroxide | Ca(OH)₂ | Used in construction (plaster), agriculture |
| Acetic Acid | CH₃COOH | Found in vinegar, food preservation | Ammonium Hydroxide | NH₄OH | Used in household cleaners, fertilisers |
| Nitric Acid | HNO₃ | Used in fertilisers, explosives | Potassium Hydroxide | KOH | Used in soap making, electrolyte in batteries |
| Phosphoric Acid | H₃PO₄ | Used in soft drinks, rust removal | Magnesium Hydroxide | Mg(OH)₂ | Used in antacids, laxatives |
| H₂CO₃ | Found in carbonated beverages | Aluminium Hydroxide | Al(OH)₃ | Used in water purification, antacids | |
| Citric Acid | C₆H₈O₇ | Found in citrus fruits, used as a preservative | Lithium Hydroxide | LiOH | Used in battery electrolytes, air purification |
| Lactic Acid | C₃H₆O₃ | Found in sour milk, used in food industry | Barium Hydroxide | Ba(OH)₂ | Used in analytical chemistry |
| Formic Acid | HCOOH | Found in ant venom, used in leather production | Zinc Hydroxide | Zn(OH)₂ | Used in medicine, manufacturing processes |
| Tartaric Acid | C₄H₆O₆ | Used in baking powder, wine production | Strontium Hydroxide | Sr(OH)₂ | Used in sugar refining, water treatment |
References and Further Reading
You can refer to the reference material in the links below for better preparation and understanding of scientific concepts.
- Books
NCERT Class 10 Science Textbook PDF
NCERT Class 12 Physics Textbook PDF
- Online Resources
CBSE Class 10 Science Video Tutorials
CBSE Class 12 Physics Video Tutorials
- Also Check
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation