Bernoulli's Principle Definition, Formula, Equation And FAQs: Bernoulli's Principle was formulated by Daniel Bernoulli. It states that as the speed of the moving fluid increases, the pressure within the fluid decreases.
It was Leonhard Euler who derived Bernoulli’s equation in its usual form.
What Is Bernoulli's Principle?
The total mechanical energy of the moving fluid comprising the gravitational potential energy of elevation, the energy associated with the fluid pressure, and the kinetic energy of the fluid motion, remains constant.
Bernoulli’s Principle Formula
Bernoulli’s Equation formula is a relation between pressure, kinetic energy, and gravitational potential energy of a fluid in a container.
The formula for Bernoulli's principle is as follows:
Here, p is the pressure exerted by the fluid, v is the velocity of the fluid and h is the height of the container.
Bernoulli’s Equation Formula
Consider a pipe with varying diameter and height through which an incompressible fluid flows. Let us take the relationship between the areas of course sections as A, the flow speed v, height from the ground y, and the pressure p at two different points 1 and 2.
The total work done on the fluid is as follows:
dW = F1dx1 – F2dx2
dW = p1A1dx1 – p2A2dx2
dW = p1dv – p2dv = (p1 – p2)dv
It is the conservation of change and gravitational potential energy due to which the work is being done. Therefore, the change in kinetic energy can be given as:
As said above, the change in potential energy is
dU = m2gy2 – m1gy1 = ρdvg(y2 – y1)
Therefore, the energy equation is given as:
dW = dK + dU
Now, if we rearrange the equation, the equation can be seen as:
Applications Of Bernoulli’s Principle
Sailboats: The application of Bernoulli’s principle is used in the design of sails to generate forward propulsion.
Blood Flow: This principle is involved in blood circulation, where the constriction of blood vessels increases blood flow velocity and reduces pressure.
Here’s a skeletal information on the Bernoulli’s principle:-
- Incompressible Fluid: Bernoulli’s principle applies to incompressible fluids, which means their density remains constant.
- Steady Flow: The principle of steady flow means that the fluid properties at a specific point and doesn’t change over time.
- Speed and pressure: There is an inverse relationship between the speed of the fluid and vice-versa according to the principle.
- Total Mechanical Energy: The total mechanical energy remains constant along a streamline.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
1. How is Bernoulli's principle used today?
It allows the engineers to make sense of the fluid dynamics phenomenon to safely design the fluid flow in and around the aeroplane wings.
2. What are 2 examples of Bernoulli's principle?
- When a truck moves very fast, it creates a low-pressure area, so the dust is being pulled along in the low-pressure area.
- If we stand very close to a railway track, we get pulled towards the track because of the low-pressure area generated by the speed of the train.
Related Links
Electrostatics: Definition, Examples, Formulas And FAQs
Maxwell’s Equation: Definition, Laws, Explanation And Formulas!
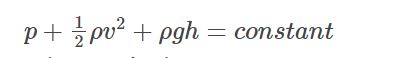
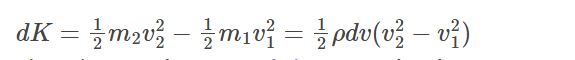
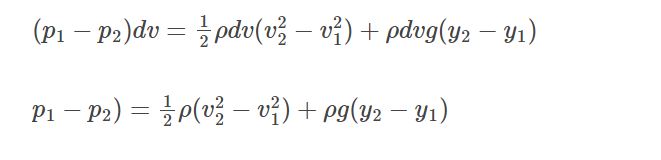
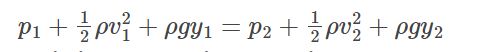
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation