HBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus: A well-designed syllabus plays a key role in guiding students through the learning process. The HBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus, in the same way, serves as a structured framework that outlines the objectives, content, expectations, and assessment scheme, providing a roadmap for students to master the subject effectively.
In this article, we have provided the detailed syllabus of Haryana Board Class 10 Science which is officially released for the current academic session, 2024-2025. Students must go through the complete syllabus and analyse it to create a comprehensive study plan that will help them achieve success in their annual board examination. Check and download the complete syllabus in PDF here.
HBSE Class 10 Science (Code - 013) Course Structure 2024-25
Chapter-wise marking scheme for HBSE Class 10 Science is mentioned below based on which the annual examination will be conducted.
| Sr. No. | Unit | Chapter | Marks |
| 1 | Chemical Substances - | Chemical Reactions and Equations | 20 |
| 2 | World of Living | Life Processes | 18 |
| 3 | Natural Phenomena | Light-Reflection and Refraction | 10 |
| 4 | Effects of Current | Electricity | 10 |
| Total | 60 | ||
| Practical Examination | 20 | ||
| Internal Assessment | 20 | ||
| Grand Total | 100 | ||
HBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus 2024-2025
Unit 1: Chemical Substances - Nature and Behaviour
Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chemical equations: Writing a chemical equation, Balanced chemical equations; Types of chemical reactions: Combination reaction, Decomposition reaction, Displacement reaction, Double
displacement reaction, Oxidation and reduction; Have you observed the effects of oxidation reactions in everyday life: Corrosion, Rancidity
Chapter 2: Acids, Bases and Salts
Understanding the chemical properties of acids and bases: Acids and bases in the laboratory, How do acids and bases react with metals, How do metal carbonates and metal hydrogencarbonates react with acids, How do acids and bases react with each other, Reaction of metallic oxides with acids, Reaction of non-metallic oxide with base; What do all acids and all bases have in common: What happens to an acid or a base in a water solution; How strong are acid or base solutions: Importance of pH in everyday life: Are plants and animals pH sensitive, what is the pH of soil in your backyard, pH in our digestive system, pH change as the cause of tooth decay, self defence by animals and plants through chemical warfare; More about salts: Family of salts, pH of salts, Chemicals from common salt: common salt – a raw material for chemicals, sodium hydroxide, bleaching powder, baking soda, washing soda, Are the crystals of salts really dry: Plaster of Paris
Chapter 3: Metals and Non-metals
Physical properties: Metals, Non-metals; Chemical properties of metals: What happens when metals are burnt in air, What happens when metals react with water, What happens when metals react with
acids, How do metals react with solutions of other metal salts, The reactivity series; How do metals and non-metals react: Properties of ionic compounds; Occurrence of metals: Extraction of metals,
Enrichment of ores, Extracting metals low in the activity series, Extracting metals in the middle of activity series, Extracting metals towards the top of the activity series, Refining of metals: electrolytic
refining; Corrosion: Prevention of corrosion
Chapter 4: Carbon and its Compounds
Bonding in carbon-the covalent bond; Versatile nature of carbon: Saturated and unsaturated carbon compounds, Chains, branches and ring, Will you be my friend, Homologous series, Nomenclature of carbon compounds; Chemical properties of carbon compounds: Combustion, Oxidation, Addition reaction, Substitution reaction; Some important carbon compoundsEthanol and Ethanoic acid: Properties of ethanol: reaction with sodium, reaction to give unsaturated hydrocarbon, Properties of
ethanoic acid: esterification reaction, reaction with a base, reaction with carbonates and hydrogencarbonates; Soaps and detergents
Unit 2: World of Living
Chapter 5: Life Processes
What are life processes; Nutrition: Autotrophic nutrition, Heterotrophic nutrition, How do organism obtain their nutrition, Nutrition in human beings; Respiration: Break-down of glucose by various pathways, Human respiratory system; Transportation: Transportation in human beings: Our pump-heart, double circulation, blood vessels, maintenance by platelets, lymph, Transportation in plants: transport of water, transport of food and other substances; Excretion: Excretion in human beings, Excretion in plants
Chapter 6: Control and Coordination
Animals- nervous system: What happens in reflex actions, Human brain, How are these tissues protected, How does the nervous tissue cause action; Coordination in plants: Immediate response to
stimulus, Movement due to growth; Hormones in animals
Chapter 7: How do Organisms Reproduce?
Do organisms create exact copies of themselves: The importance of variation; Modes of reproduction used by single organisms:Fission, Fragmentation, Regeneration, Budding, Vegetative propagation, Spore formation; Sexual reproduction: Why the sexual mode of reproduction, Sexual reproduction in flowering plants, Reproduction in human beings: male reproductive system, female reproductive system, what happens when egg is not fertilised, reproductive health
Chapter 8: Heredity
Accumulation of variation during reproduction; Heredity: Inherited traits, Rules for inheritance of traits- Mendel’s contributions, How do these traits get expressed, Sex determination
Unit 3: Natural Phenomena
Chapter 9: Light-Reflection and Refraction
Reflection of light; Spherical mirrors: Image formation by spherical mirrors, Representation of images formed by spherical mirror using ray diagrams: image formation by concave mirror, image formation by convex mirror, Sign convention for reflection by spherical mirrors, Mirror formula and magnification; Refraction of light: Refraction through a rectangular glass slab, The refractive
index, Refraction by spherical lenses, Image formation by lenses, Image formation in lenses using ray diagrams, Sign convention for spherical lenses, Lens formula and magnification, Power of a lens
Chapter 10 : Human Eye and Colourful World
The human eye: Power of accommodation; Defects of vision and their correction: Myopia, Hypermetropia, Presbyopia; Refraction of light through a prism; Dispersion of white light by a glass
prism; Atmospheric refraction: Twinkling of stars, Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset; Scattering of light: Tyndall effect, Why is the colour of the clear sky blue
Unit 4: Effects of Current
Chapter 11: Electricity
Electric current and circuit; Electric potential and potential difference; Circuit diagram; Ohm’s Law; Factors on which the resistance of a conductor depends; Resistance of a system of resistors: Resistors in series, Resistors in parallel; Heating effect of electric current: Practical applications of heating effect of electric current; Electric power
Chapter 12: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Magnetic field and field lines; Magnetic field due to a currentcarrying conductor: Magnetic field due to a current through a straight conductor, Right-hand thumb rule, Magnetic field due to a current through a circular loop, Magnetic field due to a current in a solenoid; Force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field; Domestic electric circuits
Unit 5: Natural Resources
Chapter 13: Our Environment
Eco-system-what are its components: Food chains and webs; How do our activities affect the environment: Ozone layer and how it is getting depleted, Managing the garbage we produce.
Practicals:
1. Study the chemical reaction of an iron nail with aqueous copper sulphate.
2. Find the pH of the given samples of solutions of solids or fruit juices using pH paper.
3. Show that crystals of copper sulphate contain water of crystallisation.
4. Study the reaction of metals with water under different temperature conditions.
5. Study esterification reaction between alcohol and carboxylic acid.
6. Study the action of salivary amylase on starch solution.
7. Study the phenomenon of phototropism and geotropism in plants.
8. Study the parts of a flower and their role in sexual reproduction.
9. Determine the focal length of a thin convex lens by obtaining image of a distant object.
10. Trace the path of a ray of light through a glass prism and to measure the angle of deviation.
11. Study the dependence of the potential difference across a resistor on the current through it and to determine its resistance and to verify the Ohm’s law.
12. Draw magnetic field lines of a bar magnet.
Practical and Internal Assessment
Practical examination will include the following components:
- Two experiments of 6 marks each.
- One activity of 3 marks.
- Practical record of 2 marks.
- Viva-voce of 3 marks.
For internal assessment there will be periodic assessment that would include:
i) For 4 marks- Two SAT exams will be conducted and will have a weightage of 04 marks towards the final Internal Assessment.
ii) For 2 marks- One half yearly exam will be conducted and will have a weightage of 02 marks towards the final Internal Assessment.
iii) For 2 marks- One Pre-Board exam will be conducted and will have a weightage of 02 marks towards the final Internal Assessment.
iv) For 2 marks- Subject teacher will assess and give maximum 02 marks for CRP (Classroom participation).
v) For 5 marks- A project work to be done by students and will have a weightage of 05 marks towards the final Internal Assessment.
vi) For 5 marks- Attendance of student will be awarded 05 marks as:
- 75% to 80% - 01 marks
- Above 80% to 85% - 02 marks
- Above 85% to 90% - 03 marks
- Above 90% to 95% - 04 marks
- Above 95% to 100% - 05 marks
HBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper Design 2024-25
There will be an annual examination based on the entire syllabus. The annual examination will be of 60 marks, practical examination will be of 20 marks and 20 marks weightage shall be for internal assessment. The type and format of questions for the annual exam will be as per the following pattern:
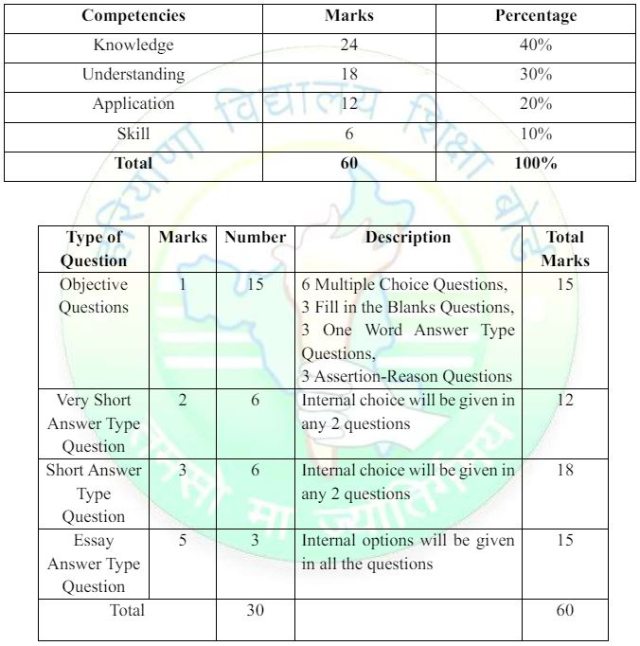
Prescribed Books:
- Science- Text book for Class X, BSEH Publication (© NCERT)
- Laboratory Manual-Science-Class X, NCERT Publication
- Exemplar Problems- Science-Class X, NCERT Publication
Download the complete syllabus in PDF below:
HBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus 2024-25 (PDF) |
Also Check: HBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2024-25 (All Subjects)
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation