Manufacturing Industries: In today's times the manufacturing process has become so seamless that it can produce anything and everything. Did you know that this wasn’t the case earlier? Before Industrial Revolution began, the process of manufacturing majorly relied on manual labor which resulted in limited quantity of goods produced. One of the earliest factories was John Lombe's water-powered silk mill at Derby, operational by 1721. Let's find out more about manufacturing industries.
What is Manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process of turning raw materials into finished goods with the help of human labour and machinery. It involves the production of goods in large quantities in large industries. Workers in factories turn the materials into usable products.
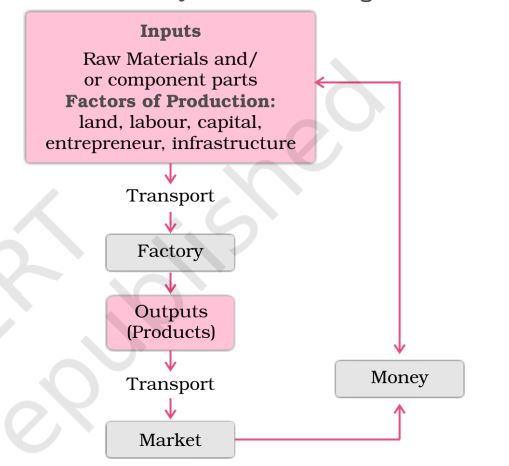
Industry Market Linkage
What is the importance of manufacturing industries?
Manufacturing industries provide support in the modernisation of agriculture by increasing production. They enable people to find jobs in sectors other than agriculture thus reducing the overall dependence on it. Trade depends on the export of goods.
What are the factors which influence the location of manufacturing industries?
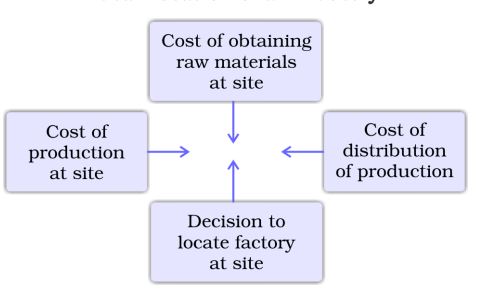
There are various factors which influence the location of an industry. They include the availability of labour, land, capital, raw materials, market among others. Since all these factors are hard to find in a single place, industries tend to choose locations where these can be arranged easily at an economical cost.
Ideal Location of an Industry
How are manufacturing industries classified?
The classification of industries is as follows-
On the basis of raw materials used- Manufacturing industries are classified as mineral based and agro based on the basis of raw materials used.
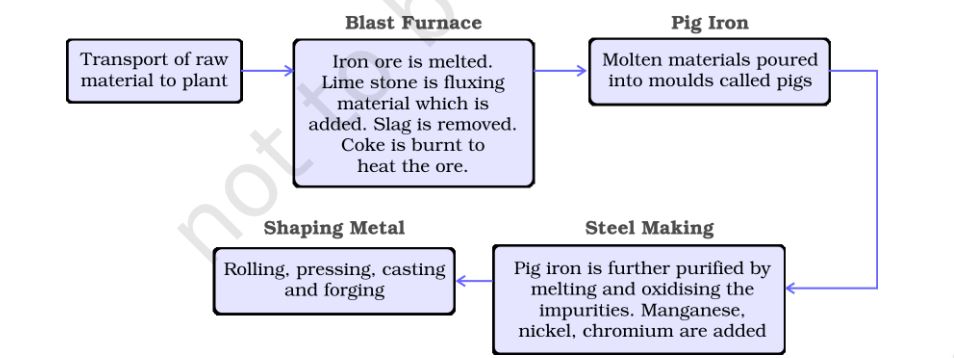
Mineral based- Includes industries which are based on minerals as their raw materials such as iron and steel, cement and aluminium.
Processes of Manufacture of Steel
Agro based-Includes industries which are based on agricultural raw materials such as cotton, jute, silk and coffee.
On the basis of main role- Manufacturing industries can be classified as basic and consumer industries on the basis of the roles they perform.
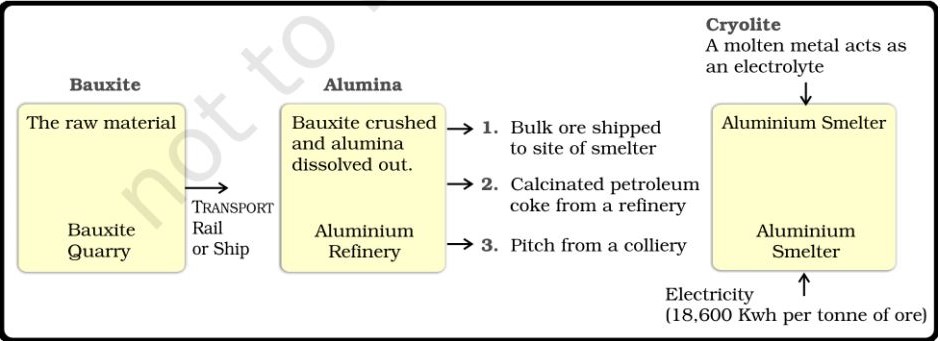
Basic- Includes industries which act as the supplier of raw materials for the manufacture of finished goods. For example aluminium smelting.
Process of Manufacturing in Aluminium Industry
Consumer- Includes industries which manufacture finished goods such as sugar.
On the basis of capital investment- Industries can be classified as small scale, medium scale and large scale.
On the basis of ownership- Manufacturing industries are grouped as public sector industries, private sector industries, joint sector industries and cooperative sector industries. They can be defined as:
Public- Ownership and operation is in the hands of government agencies such as Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL).
Private- Ownership and operation is in the hands of a group of individuals such as Bajaj Auto Ltd.
Joint- Ownership and operation is in the hands of both state and group of individuals. For example Oil India Ltd.
Cooperative- Ownership and operation is in the hands of producers of raw materials. Example- Sugar industry of Maharashtra.
On the basis of bulk, weight of raw materials and finished goods- Manufacturing industries are classified as heavy and light industries.
Heavy- Examples are iron and steel.
Light- Examples are electrical products.
What are the effects of manufacturing industries on the environment?
While on one hand, manufacturing industries act as the backbone of economic development, on the other hand, they lead to the degradation of the environment. Industries cause air, water, noise and thermal pollution.
CBSE Video Courses for All Subjects for Class 10 Students
Class 10 students can study effectively with the help of video courses prepared by the subject matter experts. These video courses will explain the concepts in a simple and interactive manner which will help learners to understand clearly. The videos are available for all major subjects which includes social science. Click on the below image:
Note: All images have been taken from NCERT Class 10 Geography textbook (Contemporary India II).
Also Check:

Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation